Disease of Newcastle Disease (ND) is one of the important avian viral diseases. This disease has a pattern of rapid spread and transmission, as well as resulting in considerable economic losses. We are certainly no stranger to one of the endemic poultry diseases in Indonesia. Various efforts have been made to reduce the incidence of ND disease in livestock.
The combination of biosecurity and vaccination as well as good maintenance management is certainly still the main way for prevention. But ND cases still appear every year. Based on data collected by the team Technical Education and Consultation PT. Medion, nd disease still occupies the top 5 viral Diseases nationally, both in chickens layer or broiler although the vaccination program has been implemented routinely. Some of the factors that cause high nd disease will try to review.
1. External environmental factors
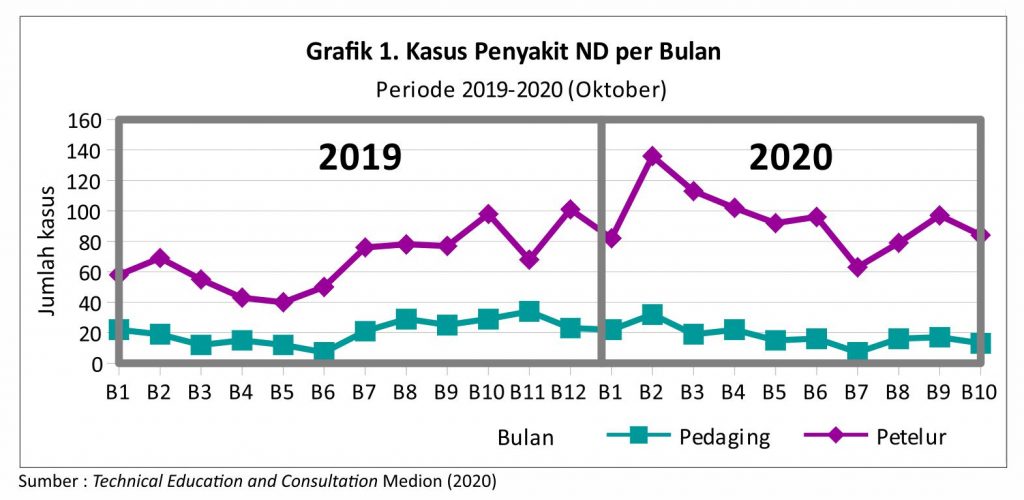
From 2019 to 2020 this nd disease tends to increase in the months of change of season and rainy season. As we know, the transition causes chickens to be susceptible to stress and results in a decrease in chicken immunity. In such conditions, chickens will be susceptible to disease one of them ND.
2. Faktor internal virus penyebab ND
Newcastle Disease It was first discovered in Newcastle, England in 1926. The disease is caused by viruses Avian paramyxovirus-1 (APMV-1) which belongs to the genus Avulavirus in the family Paramyxoviridae.
Nd viruses have genomes single stranded (ss) RNA with amplified structure. Division by its serotype, nd virus that attacks birds included in Avian paramyxo virus I (APMV-1). The malignancy (pathotype) of the ND virus is also subdivided into 4 groups :
- Velogenic : high level of violence
- Mesogenic : moderate level of violence
- Lentogenic : mild degree of violence
- Apathogenic enterotropic : non-malignant nd virus.
The next classification of ND is based on its genotype. Along with the latest technological developments. Classification of ND viruses is distinguished by the core material of the virus through DNA sequencing. In this classification, nd viruses are divided into 10 genotypes. The genotypes that are predominant in circulation in the world and are virulent are : V, VI, VII and VIII. The genotype in ASIA is VI (1960 s / d 1985).
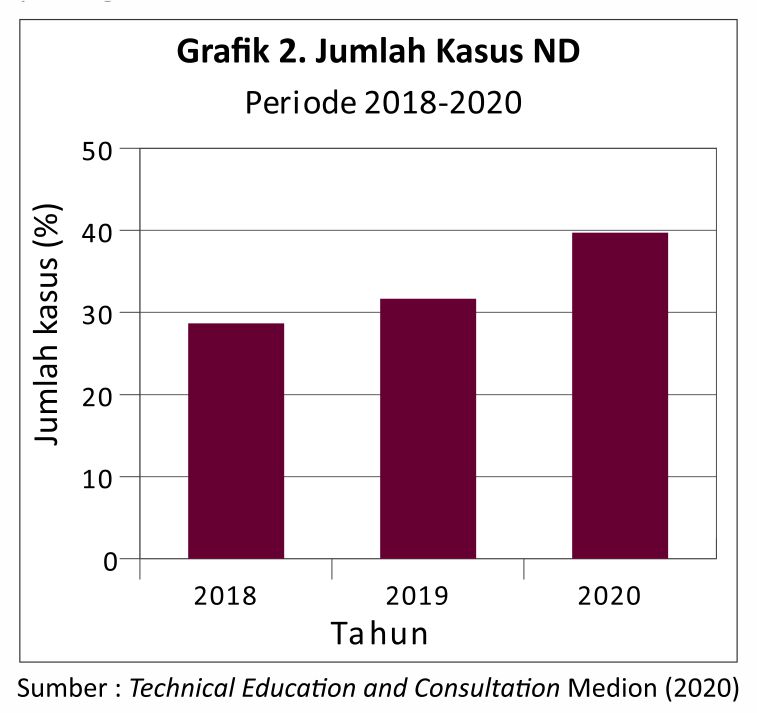
Medion is always actively following the development of ND cases in the field. Based on data collected by the team Technical Education and Consultation from a sample of a sick chicken organ suspected of being infected with ND for the last 3 years, a positive confirmed case of ND from PCR data (Polymerase Chain Reaction) showed an increase in cases of 20.04%
The results of the PCR test are then followed by a DNA test sequencing. DNA process sequencing performed to see the genetic makeup of the ND virus. The results of the analysis found that the dominant nd virus circulating in Indonesia today is genotype 7 nd Virus (velogenic) where the virus is far separated from the old nd virus genotype 2 (La Sota).
Nd velogenic group is a nd virus that has a high level of malignancy so that when infecting into the body of chickens will cause a high death rate as well. Velogenic ND itself is divided into 2 groups, the first is Viscerotropic velogenic. Attacks of ND of this group are acute with high mortality. Typical changes that are often found in chickens infected with this virus are wounds and hemorrhages in the intestine.
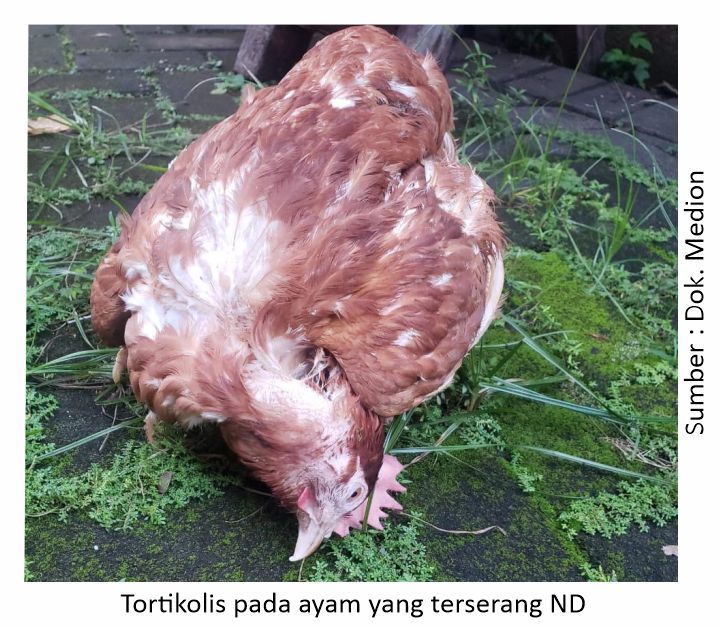
Chickens will show symptoms of lethargy, decreased appetite, egg production drastically, diarrhea and death rate > 90%. The second form is Neurotropic velogenic which is characterized by the appearance of respiratory disorders and abnormalities in the nerves commonly called torticollis or three. Affected chickens become weak due to difficulty eating and drinking.
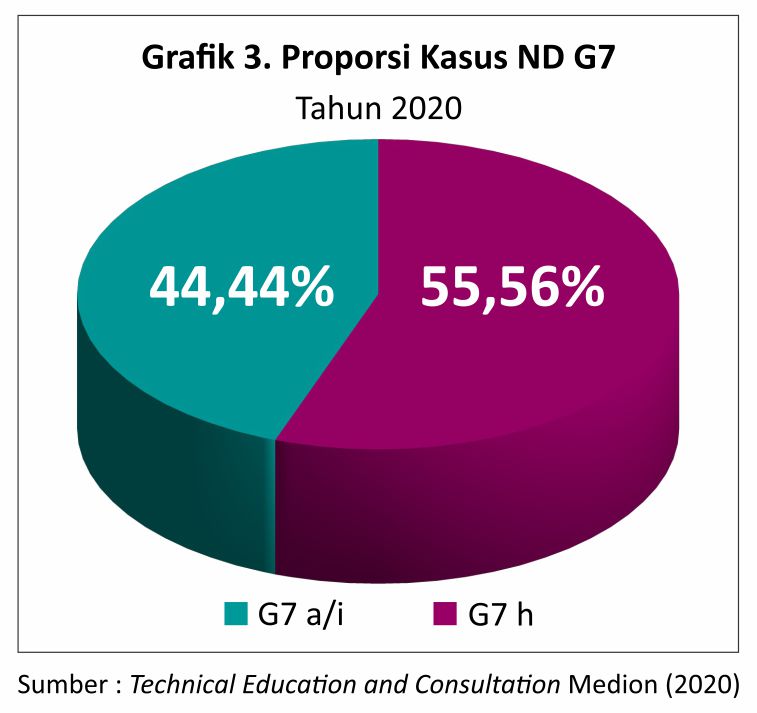
Here's the graph 3. proportion of ND genotype 7 cases successfully analyzed by Medion. From the following graph the case of ND genotype 7 dominant circulating in Indonesia there are two subgenotypes namely ND G7 a/i and ND genotype h (Shohaimi et al, 2015 & Dimitrov et al, 2016).
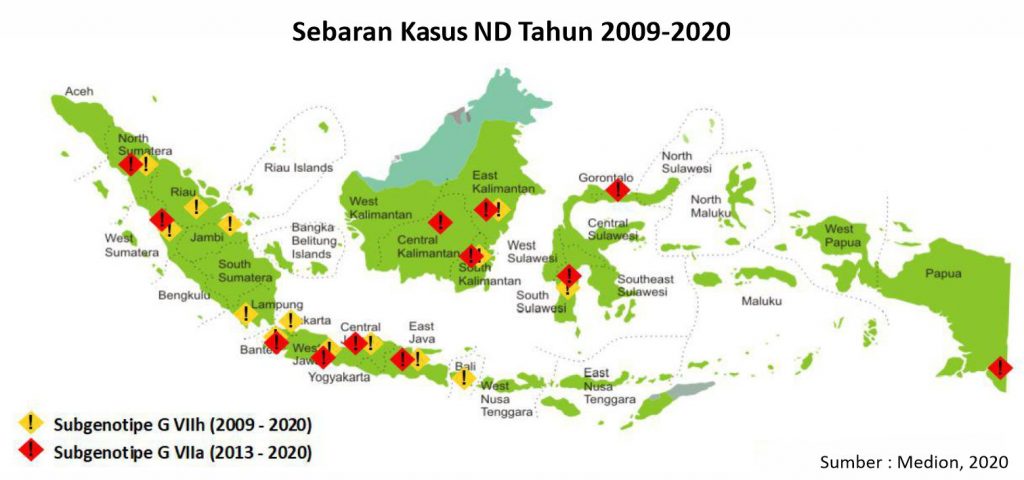
More deeply we see from these ND cases have spread throughout parts of Indonesia as seen on the map below.
Nd diagnostics in the field
Accuracy in diagnosing a disease determines success in its treatment in the field. But unfortunately, the current constraints in diagnosing nd diseases that attack due to the characteristics of clinical symptoms and changes in anatomical pathology that appear quite difficult to distinguish from other diseases.
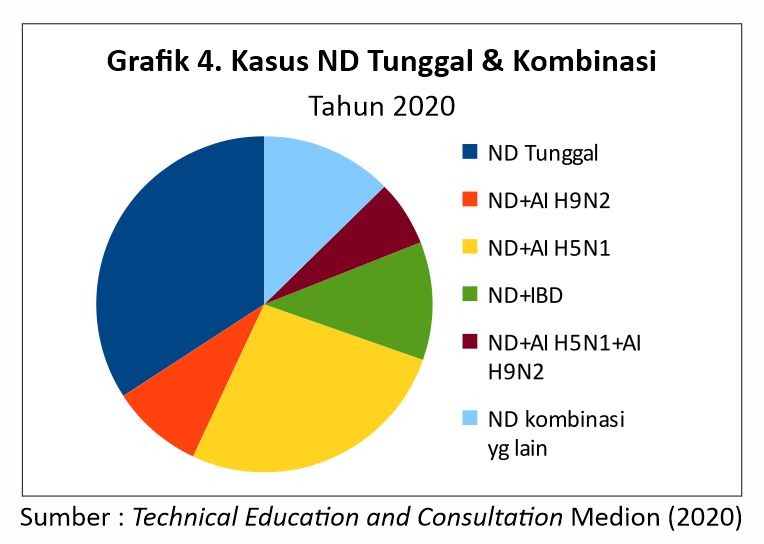
In addition, the ND virus that attacks usually does not stand alone, but in the form of a combination with other viral or bacterial diseases. Here is graph 4. nd attacks both single and in combination with viral diseases throughout 2020. Observation of clinical symptoms and changes in anatomical pathology should be carried out thoroughly because ND disease can affect almost all body systems.
The clinical symptoms that appear due to ND are still the same as in previous years, the characteristics that can be seen from the outside are respiratory tract disorders, such as gasping or the sound of snoring. Other symptoms that appear such as chicken weakness, decreased appetite, dull feathers, green diarrhea mixed with White Moss and still found chickens experiencing torticollis.
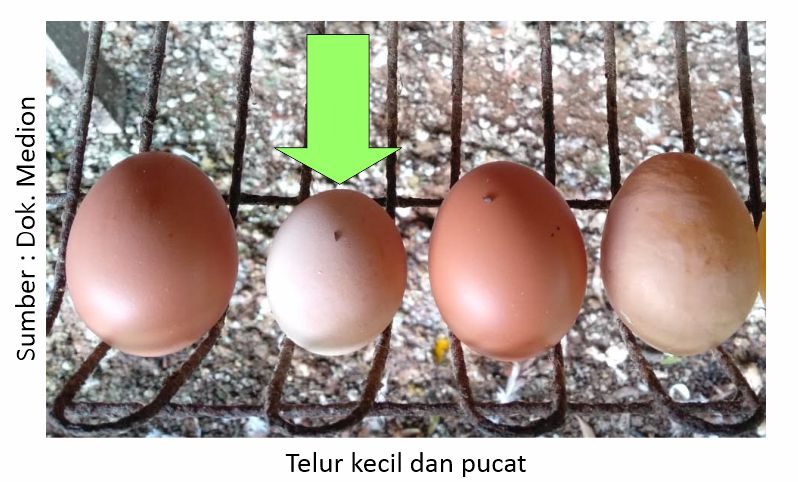
In quantity, egg production decreased varies from 7 to 60%, in terms of the quality of eggs from chickens infected with ND is usually pale in color with a small egg size. As for the death rate from ND infection varies from 5-100% depending on the type of ND that attacks.
In addition to the observation of clinical symptoms, changes in anatomical pathology ND also has some similarities with other diseases. Some changes found in confirmed ND cases from PCR test results as shown in graph 5. here.
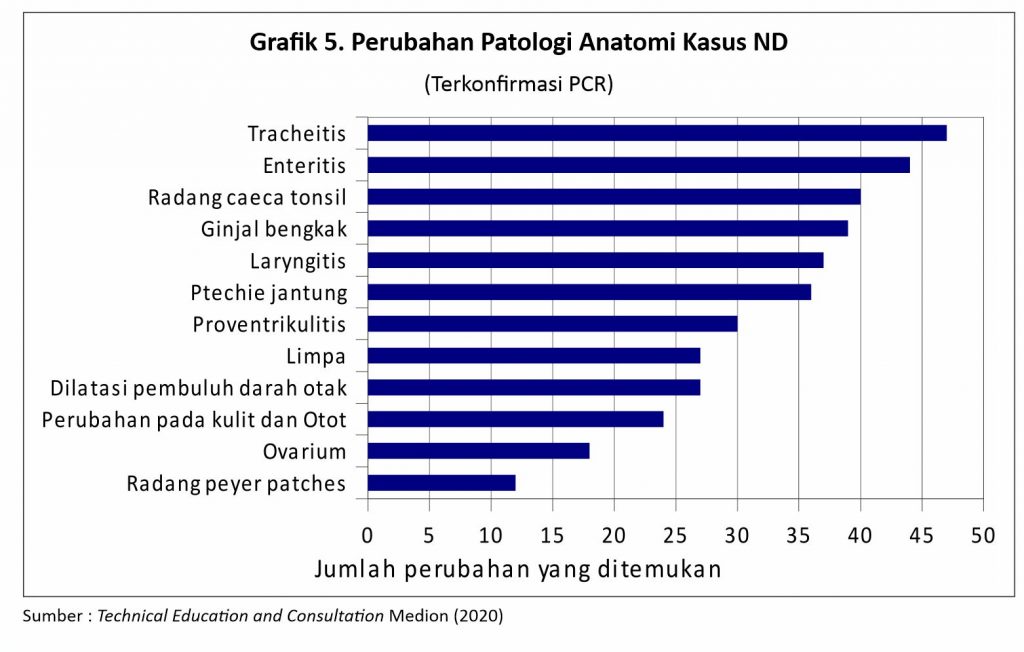
Anatomical pathologies that are seen when surgery is performed on chickens with clinical symptoms leading to ND include the presence of inflammation in the respiratory tract, including laryng and trachea. In the digestive tract, enteritis was found, in addition, one of the typical symptoms (pathognomonis) was also found in the case of ND, namely the inflammation of the proventricular papillae and the limphoid organs in the digestive tract, namely peyer patches dan caeca tonsil. In the reproductive system, an inflamed ovary and a flabby shape resembling a cauliflower are found.
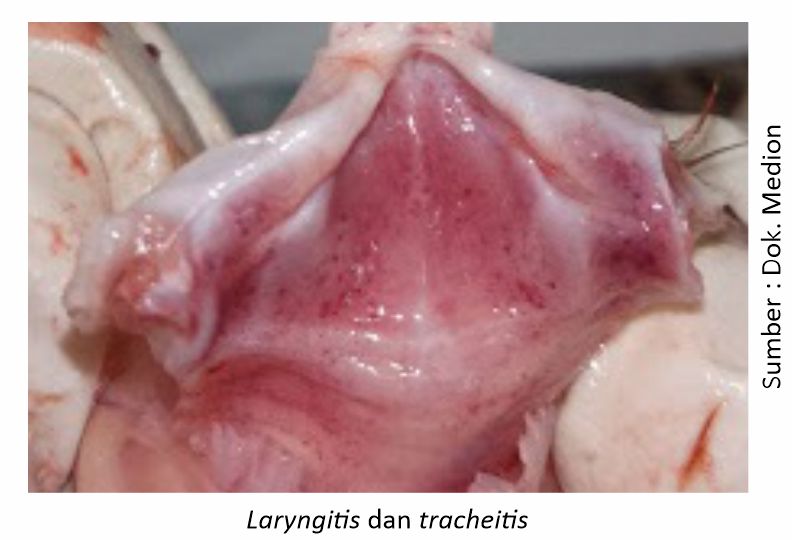
The findings of these anatomical pathological changes in the field are very varied and are often confused with other viral diseases such as AI, IB, and bacterial diseases such as CRD and Coryza. Therefore, in these conditions there is also a need for confirmation by lab tests.
Common tests carried out by farmers include serological tests with HI test to help direct diagnosis, even up to isolation tests and identification of the presence of ND virus infectious agents using PCR tests and sequencing.
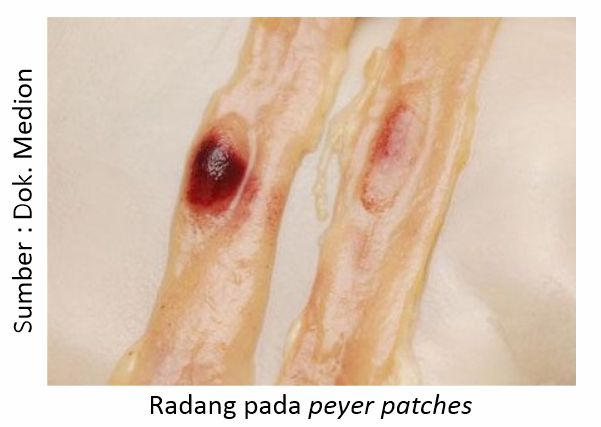
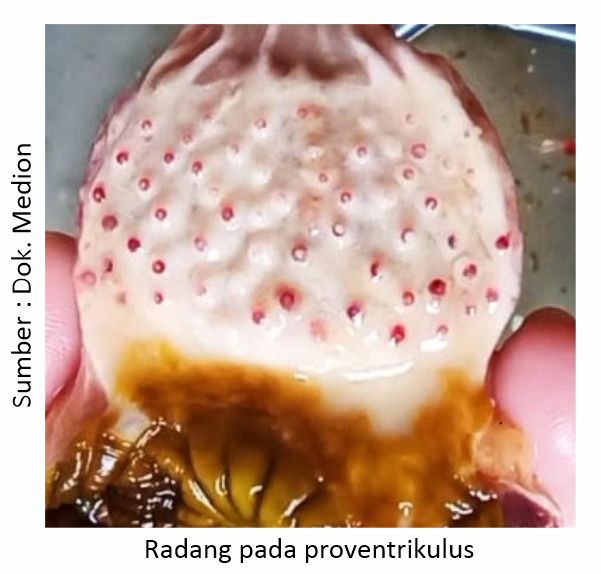
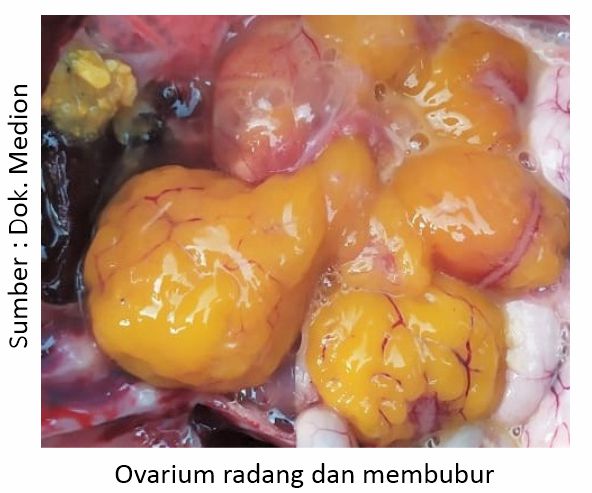
Nd Disease Control
Vaccination can prevent the harm caused by this disease. Related to ND vaccination, in order for the vaccination to successfully form optimal immunity/antibodies and be able to protect chickens from ND attacks, there are several things that must be considered below:
a. The physical quality of the vaccine is still good
Use nd vaccines that are still of good quality and have been registered. Well, here it means that the seal is intact, the shape has not changed, the vaccine has not expired, and the label is still well attached.
b. Should use homologous vaccines
The selection of the right type of vaccine is very influential on the success of vaccination in warding off virus attacks. A good vaccine is a vaccine whose virus content is homologous to a field virus that will provide more optimal protection and is able to suppress the virus shedding (prevention of ND virus spread in the field).
To keep the vaccine updated, the existing vaccine needs to be tested using the latest challenge virus. If passed, then the vaccine can still be used to deal with the virus circulating today. From the kinship Tree of ND virus shows that the dominant nd virus circulating in Indonesia to date is genotype 7.
One of the ND vaccines homologous to the field nd virus is Medivac ND T Emulsion is the latest generation of emulsion-form inactivated nd vaccine to prevent ND in poultry. Medivac ND T Emulsion contains viruses Newcastle disease (ND) genotipe II strain La Sota and the latest field isolates included in genotype VII, namely MD54 and MD65 strains that are able to protect against ND genotypes 7h and 7a/i.
Medion also produces various inactivated ND vaccines that are homologous to field nd viruses such as vaccines Medivac ND G7 Emulsion, Medivac ND G7-EDS Emulsion, Medivac ND G7-EDS-IB Emulsion, and Medivac ND G7-IB Emulsion.
Classical vaccines are mainly active vaccines such as vaccines Medivac ND La Sota, Medivac ND Hitchner B1, Medivac Clone 45, or Medivac ND-IB it still needs to be given to bully the rapid and protective formation of ND immunity. In addition, basically nd viruses have cross protection (cross-protection) between virus pathotypes. So, between the classic nd vaccine and ND G7B has cross-protection.
c. Arrange nd vaccination program according to the condition of each farm
Consider in advance about the age of attack of the disease, the age of chickens, data monitor antibody titer, and the type of ND vaccine used.
The active nd vaccine has the ability to bully antibody formation faster than the inactivated nd vaccine. Within 2-3 weeks the antibody titer from vaccination with the active nd vaccine has reached the protective standard, while the inactivated nd vaccine only reaches the protective standard at 3-4 weeks. Despite this, antibody titers produced by inactivated nd vaccines relatively last longer over protective than active ND vaccines.
Based on the pattern of antibody titer formation, as a general guide, nd vaccination in chickens broiler can be given 1 time at the age of 4 days with active vaccine at the same time ND killed. On chicken layer nd vaccination is given 4-5 times before entering the egg-laying period.
The first nd vaccination is given as in chickens broiler. Repetition of ND vaccination in the production period if using an active vaccine can be done once every 1-2 months, while if using an inactivated vaccine can be done once every 2-3 months. The exact revaccination schedule can also be based on the results monitor titer of antibodies to ND.
Especially during the first nd vaccination, namely at the age of 4 days, it is generally recommended that farmers give active and inactive nd vaccinations. It is not for nothing that such recommendations are made. The first reason is of course that the stress of the vaccination is relatively lighter than if the vaccination were carried out separately.
In addition, associated with the mechanism of antibody formation of both vaccines, active vaccine antibodies begin to form on 3-4 days post vaccination and reach protective standards at 2-3 weeks post vaccination. While the inactivated vaccine begins to form on 6-7 days post vaccination and reach protective standards at 3-4 weeks post vaccination.
Therefore, when vaccination using both active and inactivated vaccines, the antibodies that first work come from the active vaccine, then only the antibodies from the inactivated vaccine continue. Thus, when the antibody titer of the active vaccine begins to fall (the immunity of the active vaccination result is quickly formed but quickly falls), the antibody titer of the inactivated vaccine result (the immunity of the inactivated vaccine is slowly formed but lasts longer) is still above protective (protective).
d. Watch how handling/ handling of ND vaccine since purchased until given to chickens.
- When distribution and temporary storage, the temperature of ND vaccine should always be conditioned at 2-8oC.
- Before giving it to chickens, do not forget about the process thawing. Thawing aimed at raising the temperature of the vaccine previously 2-8oC is close to the body temperature of a chicken (⑧41oC) or until the vaccine does not feel cold again, that is, with a temperature of about 25-27oC. Once in-thawing, nd vaccine should not be put in the refrigerator again/marina cooler because it can lower the potency of the vaccine.
- The active nd vaccine must be discharged for a maximum of 2 hours, while the inactivated nd vaccine must be discharged within 24 hours.
- If the ND vaccine does not run out, then the rest cannot be stored for later use again. The rest of the vaccine and the package must first be soaked in disinfectant, and only then removed/buried.
e. Make sure the dose of ND vaccine given is correct.
f. Before being vaccinated, chickens are in healthy condition and not in immunosuppressed conditions (eg stress or crd disease, Gumboro, mycotoxins, etc.) which can reduce the optimization of antibody titer formation.
g. The skills of the vaccinator must be good for the vaccination application to be done correctly.
Other important efforts are being made to support vaccination and the successful prevention of ND, including:
- Good management treatment needs to be considered to reduce the possibility of stress and immunosuppression in chickens. Strive for conditions litter keep dry and ammonia concentration low. High ammonia levels cause upper respiratory tract irritation that can trigger respiratory disease infections. Also adjust the density in the cage to minimize stress. Make sure the air circulation in the cage is sufficient, wherever possible do the system “all in all out” and the application of cage rest for at least 2 weeks.
- Multivitamins such as Vita Stress or Fortevit plays a role to increase the stamina and endurance of the chicken. Give Imustim, herbal immunostimulants that can help improve the functioning of the immune system. Awarding Imustim before and after vaccination has been shown to work by accelerating the increase in antibody titers from vaccination. Imustim given 0.5-1 ml per 2 liters of drinking water 3 consecutive days before and after the vaccination period so that the vaccination results are more optimal.
- In addition to vitamins, premixes can also be added to the ration so that the metabolic processes of the chicken's body's defenses go to the maximum.
- Limit the traffic of people / vehicles coming in and out of the cage. If entering the enclosure, disinfect both vehicles and personnel, especially if coming from an infected farm enclosure. It is possible that feces contaminated with the ND virus are carried through vehicle wheels / footwear.

- Perform cage and equipment sanitation (cage cleaned, washed and sprayed) with Neo Antisep or Medisep, preventing guests, stray animals and other pets from entering the enclosure environment. If there is an outbreak, spraying is carried out every day because the transmission of the ND virus can occur through the air. Sanitize drinking water by providing antiseptics such as Desinsep or Neo Antisep to suppress disease transmission through drinking water.
By implementing the steps above, it is hoped that farmers will be enlightened on how to avoid the threat of ND, so that ND cases in Indonesian farms can decrease or even not reoccur. Greetings.










