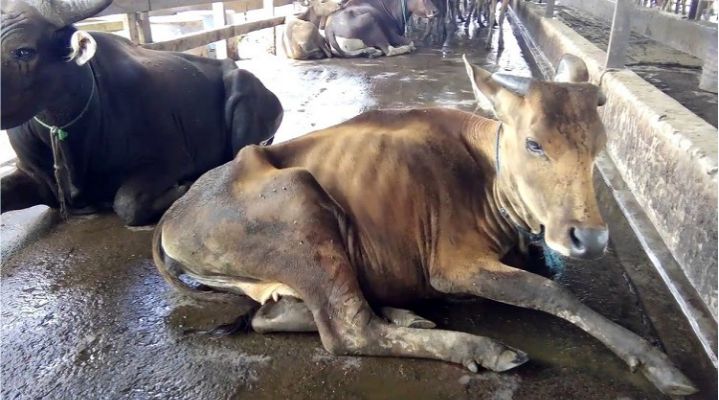
A few months before the Eid al-Adha farmers have prepared stocks of sacrificial animals and the number is getting closer to the holiday. During the maintenance period, of course, the breeder will provide the best care. The condition of the COVID-19 pandemic does not make it a reason to reduce the quality of livestock care. The care includes providing quality feed, maintaining the health of the livestock as well as the cleanliness of the cages and the environment so that buyers are satisfied when giving the best animals for worship.
The condition of livestock as sacrificial animals must be healthy. But from the results of post-slaughter examination, worms are often found in internal organs, especially liver worms. Worms are often ignored or considered trivial because the risk of death is relatively small. But the fact is that worms, including liver worms, can cause economic losses such as weight loss, low daily weight gain, liver damage, medical expenses and death in severe conditions.

Heartworm disease or also called fasciolosis is a disease caused by worms Fasciola sp. which lives in the liver and bile ducts. In Indonesia it is generally caused by Fasciola gigantica which is shaped like a leaf. This worm can infect ruminants such as cows, goats, sheep and buffaloes. In cattle and Buffalo it is usually chronic or the disease process lasts a long time while sheep and goats are acute or rapid. In young cattle it is more susceptible than in adult cattle.
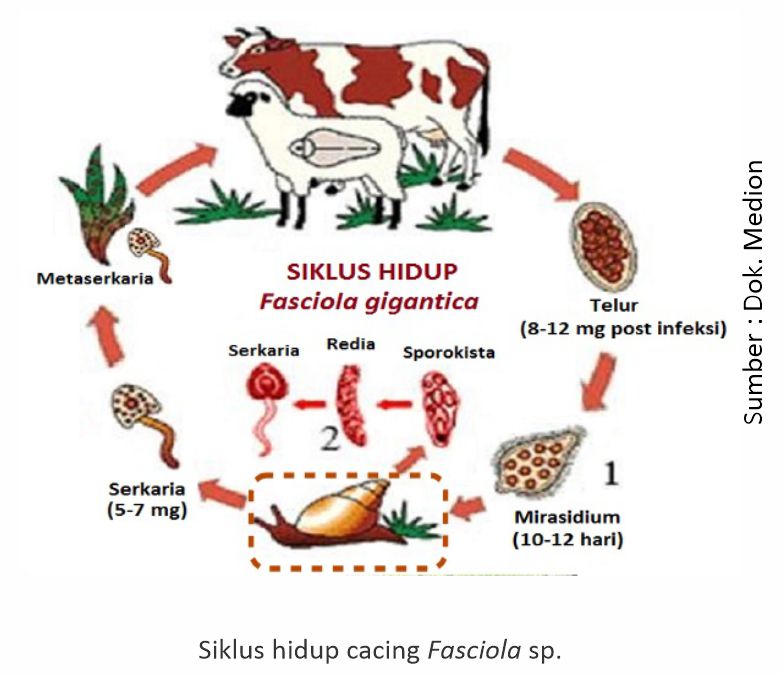
A wet environment is a suitable place for the development and transmission of worms Fasciola sp. Because in its life cycle requires freshwater snails Lymnaea rubiginosa as an intermediate host. Worm eggs that come out with feces will develop into miracidium. In the body of the snail, the miracidium develops into sporocysts, redia and cercariae. Next, the cercariae will come out of the snail's body to find a suitable place, the cercariae will turn into cyst-shaped metacercariae. Cysts can be in water or attached to plants. Furthermore, water and plants containing these cysts will be a medium of transmission for other cattle that accidentally swallow metacercariae that pat on the grass.
Symptoms can be mild or severe depending on the number of metacercariae ingested or infected and their infectivity. If metacercariae are ingested in large quantities, it will cause more severe symptoms and depend on the stage of infestation, namely the migration/ displacement of young worms and the development of adult worms in the bile ducts.
In mild infections can not appear clinical symptoms. However, in severe infections cattle will experience lethargy, weakness, decreased appetite, anemia characterized by conjunctiva or clusters of pale inner eyes, diarrhea, edema or swelling filled with fluid in the lower jaw. Sometimes in acute cases there are also symptoms of rapid breathing, an enlarged stomach and feeling of pain.
The process of tissue damage begins when young worms penetrate the intestinal wall but tissue damage is more severe when the worms move into the tissues of the liver and when in the bile ducts. The development of such worms will lead to injury and tissue death.
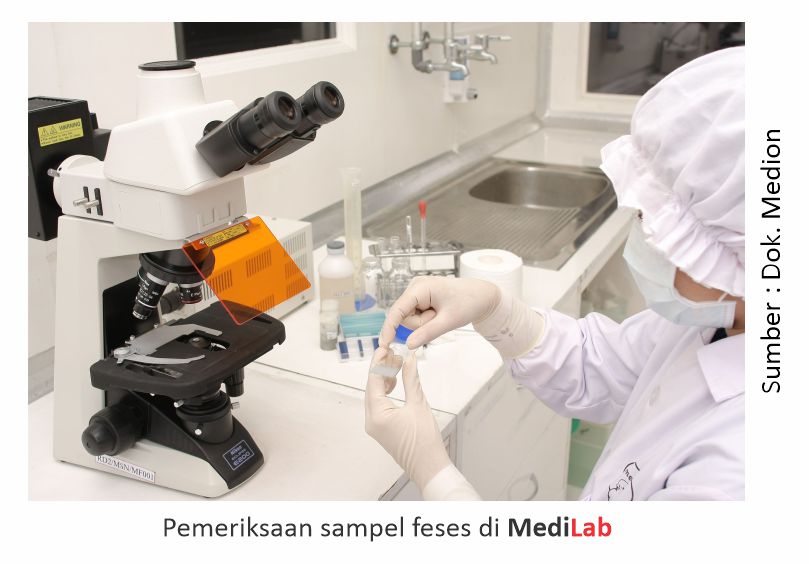
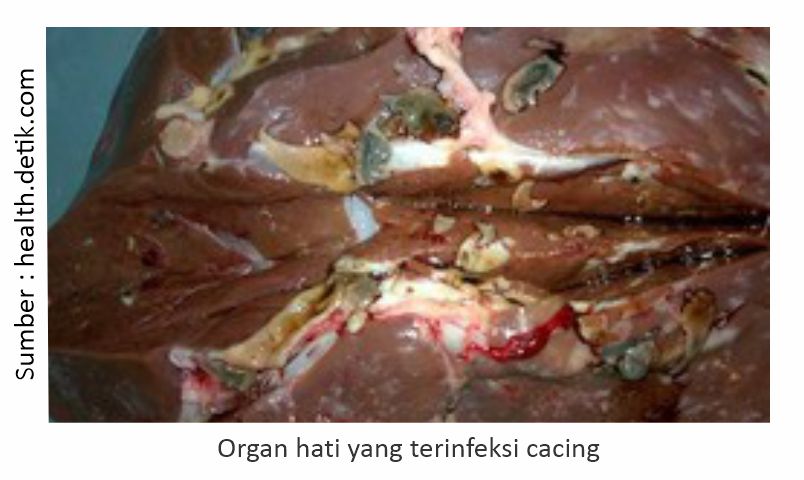
The Diagnosis of liver fluke disease is based on clinical symptoms and is confirmed by laboratory examination of a sample of feces (feces) to identify the presence of worm eggs or by post-slaughter examination to identify adult worms in the affected organ.If worms are found in the liver, then the liver is not suitable for consumption and needs to be diafkir. But the meat is still safe for consumption.
Control and prevention measures that can be done are cattle are not grazed too early because at that time the dominant worm larvae are on the surface of the grass is still wet, cutting grass on the surface of the water and lay it first. Perform grazing in turns. cage sanitation and environmental cleanliness by not allowing cow dung to accumulate, eradicating intermediate host populations need to be done by maintaining humidity and around the cage is not wet, health checks and regular deworming programs. Examples of anthelmintic drugs used to eradicate liver worms are with Wormectin Plus, Wormectin Plus-B or can also with Wormzol-B. Deworming also needs to be repeated periodically every 2-3 months. Wormectin Plus and Wormectin Plus-B it is a broad-spectrum anti-parasite that effectively eliminates internal parasites (worms) and external (fleas, ticks, mites).

In addition, it is also important to provide multivitamins regularly every 2-3 months that function to increase endurance and inspection eggs and larvae of worms regularly 2-3 months through a stool test. Medion has a laboratory that can serve the test is MediLab which has spread in several regions in Indonesia.