Liver or liver is the largest organ in the body. This Organ is a brownish-red color composed of liver cells or hepatocytes. The liver is an important organ that secretes material for the digestive process. The liver plays a role in bile secretion, detoxification, red blood cell formation, metabolism, and vitamin absorption (Ressang, 1984). The liver has a detoxification function performed by liver enzymes. Namely by converting toxic compounds or toxins from metabolism and originating from outside the body into substances that are physiologically inactive.
In poultry, the liver will be damaged if there are mycotoxins (fungal toxins) or other toxins in excess in the body. Liver damage can also be caused by the impact of the emergence of a disease, as well as excessive use of chemicals. Therefore, it is necessary to know the factors that damage the liver and their effects in supporting appropriate prevention efforts so that optimal livestock performance.
Know the role and function of the liver
The liver has a complex function, among others, in the metabolism of carbohydrates, fats, proteins and iron. Liver functions include:
- Detoxification
Removal of residual substances and hormones as well as drugs and other foreign compounds such as toxic substances and heavy metals. Detoxification occurs because the liver contains antioxidants and enzymes that can damage the reactive oxygen group, namely glutathione (GSH), vitamins C and E.
- Nutrient metabolism
Carbohydrates after processing in the gastrointestinal tract will become glucose, and then absorbed through the intestines into the blood circulation and liver. In the liver some glucose is metabolized so that energy is formed that functions to maintain body temperature and energy to move.
The remaining glucose is converted into glycogen and stored in the liver and muscle or converted into fat stored in the subcutaneous tissue (Guyton & Hall, 2008). The function of the liver in protein metabolism is to form amino acids, the formation of the end result of metabolism to remove ammonia from body fluids, and form other compounds from amino acids.
- Formation and excretion of bile
Bile is formed through the interlobular bile ducts found in the liver. The resulting bile is drained and stored in the gallbladder. The liver can secrete about 1 liter of bile in a day. Bile salts are important for the digestion and absorption of fats in the small intestine. This salt is partially reabsorbed by the small intestine and drained back into the liver.
- Other
Other liver functions include the liver is a storage of vitamins and iron, forming substances used for blood coagulation in large quantities and removing substances that are not needed.
Causes Of Liver Damage
Liver damage is usually caused by environmental influences and maintenance management system errors, such as poor feed management so that it is contaminated with mycotoxins, excessive administration of chemical drugs, unbalanced absorbed nutrients, and the influence of infectious viruses that cause serious diseases. Specifically, some of the factors that cause liver damage in chickens can be explained as follows:
- Mycotoxins
Poultry is the most sensitive livestock to mycotoxins. The presence of mycotoxins in animal feed has an impact on the health of livestock in the form of decreased production, causing immunosuppression (weakening of the immune system), and causing damage to organs such as the liver. Mycotoxins are organic compounds of a toxic nature (toxins), which are produced by certain molds (fungi). If the mold dies, then the production of mycotoxins stops, but the mycotoxins that have been formed do not disappear (Tabbu, 2002).
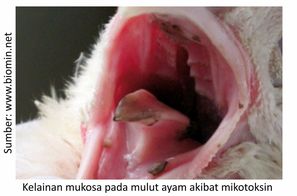
Environmental conditions such as high temperature and humidity, production processes, harvesting and storage are not good cause high concentrations of mycotoxins in feed raw materials, causing the disease mycotoxitosis. Clinical symptoms of mycotoxicosis in chickens are usually not very specific, generally in the form of impaired performance or decreased productivity of chickens.

Symptoms vary depending on health status, age, sex, environmental conditions, type and duration of exposure to mycotoxins. At high concentrations, when the chicken is dissected can be diagnosed that mycotoxins attack directly specific organs such as liver damage, kidney, gastrointestinal tract, nervous system and reproductive tract. In acute mycotoxin poisoning, there is an overhaul of blood clotting, a failure in carbohydrate and fat metabolism and a decrease in protein synthesis in the liver, resulting in a decrease in liver function.
- Excessive chemical drugs (paracetamol)
Liver damage can also occur as a result of continuous use of paracetamol over a long period of time and improper dosage. Paracetamol or acetaminophen is a drug that lowers body temperature (antipyretic) and pain reliever (analgesic) which is often used as therapy in chickens, both broilers and layers. One of them in the case of Gumboro that it is common if farmers use paracetamol to help reduce body heat in chickens. When the disease attacks several organs that will experience inflammation and bleeding and the response shown by the chicken is Fever.
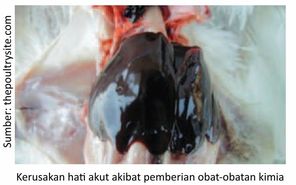
The action of paracetamol is explained in the liver by metabolites in the form of inactive compounds but still toxic (poison). If paracetamol is consumed in excess and not according to the applicable dose, the body's glutathione or antioxidant compounds will not be able to bind to paracetamol. These metabolites will then freely react with important enzymes from the liver, so that this will spur severe damage and even death due to liver failure.
- Fatty Liver Hemorrhagic Syndrome
Fatty Liver Hemorrhagic Syndrome (FLHS) or known as fatty liver is a condition of excess fat in the liver in productive chickens. Excessive intake of energy in the ration and not as needed is the main causative factor of fatty liver in chickens. The high ratio of energy to protein causes high fat formation.
Calcium deficiency also causes high energy and protein intake and stimulates fat accumulation. In this case, there is an increase in body weight and liver weight, which is accompanied by a decrease in egg production, depending on the degree of deficiency. Excessive consumption of feed also results in excessive nutrient intake and will be stored into fat. The body weight of laying hens should be considered because often the weight does not correspond to the age and production phase, this is mainly due to the excess accumulation of fat in the abdominal cavity. When viewed during carcass surgery, the liver is swollen, pale yellowish in color and bleeding occurs. In the abdominal cavity there will be a large accumulation of fat.
In addition to excess nutrient intake, FLHS can be caused by variations in poultry strains. Different egg laying abilities due to genetic differences in this strain variation will stimulate the occurrence of fatty liver caused by intensive estrogen metabolism.
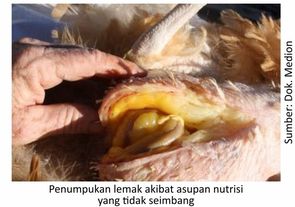
Acute stress will also increase fat formation (lipogenesis). Stress can be caused due to high temperature increases or poor battery enclosure systems. This battery cage system causes the activity of livestock in the release of energy tends to decrease, so that excess energy will be stored into fat. With this system, the chicken cannot be separated from the deficiency of essential nutrients and cannot choose the temperature that suits the needs.

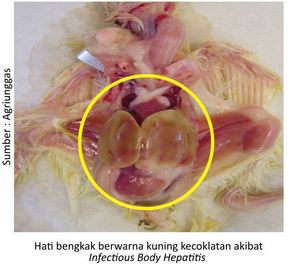
- Other infectious diseases
Other diseases that can cause liver damage are Inclusion Body Hepatitis (IBH) and Lymphoid Leukosis (LL). Inclusion Body Hepatitis (IBH) is an infectious disease in chickens, which is characterized by anemia and hepatitis accompanied by inclusion bodies in the nuclei of liver cells. The disease is caused by adenoviruses. Poultry affected are chickens, especially laying hens and broilers at the age of 2-13 weeks. Attacked chickens are characterized by lethargic symptoms, drooping wings, swollen heads, pale Combs and wattles, sometimes diarrhea and vomiting, watery discharge from the nose. When the chicken is dissected can be seen swollen liver brownish yellow, there are spotting, bleeding and flabby.
While in Indonesia on laying hens Lymphoid Leukosis (LL) more commonly known by the name Big Liver Diseases. The disease is caused by Leukoviruses and includes a form of complex leukosis. LL disease is mostly found in laying hens at the age of 16 weeks or more. The disease is easily transmitted by direct contact between sick chickens (horizontally) and vertically. The Virus is excreted in feces and can contaminate the environment of the cage, where chickens eat and drink. Symptoms that appear in LL disease in the form of decreased appetite, depression, Combs and wattles look pale to bluish, the stomach appears enlarged and when palpated feels hard and has changes in the typical anatomical pathology in the liver. Tumors are found in various organs of the body after 4 months of age chickens on the kidneys, lungs, heart and other organs, but most often found in the liver (Big Liver Diseases). The Tumor can be nodular (lump), diffuse (spread) or a combination of these forms.

The impact of liver damage on chickens
Damaged liver can not detoxify as fast as a healthy liver, therefore, if the detoxification process is slower and the liver has not finished detoxifying it has been given an attack of toxins that must be detoxified, the result will be more toxins circulating throughout the body through the blood (BPOM, 2004).
Damage that occurs to liver cells can be temporary and permanent. Liver cells will try to adapt to maintain life by repairing their own cells and is commonly called regeneration. However, some toxins that cannot be destroyed due to the liver's working capacity are not strong enough so that it will be difficult to be removed from the body because it escapes the liver's working process. As a result, these toxins accumulate as fat in important organs such as the liver, brain and nervous system cells.
This causes normal cell membranes to be damaged so that the balance of body fluid expenditure will be disturbed. Damage to liver cell membranes causes an increase in the amount of water into the cells, causing the cells to become swollen and filled with water droplets.
If the liver is damaged, the overall metabolic process is disrupted so that poultry appetite decreases resulting in stunted chicken growth and egg production, as well as decreased immunity (immunosuppression). Decreased immune response or immunosuppression will increase the risk of disease, increase the severity of the disease, increase the difficulty of treatment or difficult to cure chicken, poor immune response, and activate tumor formation. Toxic substances also cannot be excreted and accumulate in the body, endangering other organs such as the kidneys.
Prevention Of Liver Damage
Liver damage has no specific symptoms so it is difficult to see from the outside without surgical removal of the carcass. If liver damage has occurred, it can interfere with the growth rate and production of livestock, especially in chickens. For this reason, preventive and treatment measures are needed to reduce the decline in production due to liver damage. Prevention of liver damage can be done in several ways, including:
- Good management and strict implementation of biosecurity and discipline is very important in an effort to prevent the spread of infectious agents that cause liver damage in poultry. Humidity litter or the base of the cage must be considered. Before chick in disinfection should be carried out (sprayed with Medisep, Sporades, or Formades). The use of disinfectants is expected to be effective against viruses, bacteria and fungi.
- Durability and shelf life of rations and raw materials are highly dependent on the moisture content contained in them. Indonesian national standard (SNI) set the ideal number of water content in the ration does not exceed 14% so as not to grow fungi that trigger mycotoxins. The shelf life of chicken rations in the warehouse is 21-30 days from the date of production (batch). Good ration form crumble (details), pellet or mash (flour), will experience a decrease in quality when passing through the period. For example, corn with an initial moisture content of 12.5% stored for 40 months will experience an increase in dry weight loss in line with increasing storage time.
- Prevention of ration contamination can be done by preventing the growth of bacteria and the formation of mycotoxins. Prevention can be done by maintaining low humidity or no more than 70%, the ideal temperature of the room between 18-24°C, keeping rations fresh and clean, caring for ration equipment. The storage area should also be bright and clean, have good ventilation for air circulation, free from insects and rodents that can damage the ration.Give it up (pallet(A) in the form of a stack of raw materials and set the storage position in accordance with the time of arrival (first in first out). Deterioration in the quality of rations due to improper storage will result in digestive health and thus interfere with the performance of the chicken.

- Ration restrictions according to needsthe efforts made to prevent fatty that will interfere with the functioning of the liver is to limit the ration. This restriction can be by replacing carbohydrates with additional fats. This modification means that the liver needs to synthesize sedi kit fat. Replacement corn can be with oil.
- Routine ration quality controldo a routine inspection of the quality of raw materials, especially upon the arrival of raw materials or rations. To inhibit the growth of fungi can add mold inhibitor into the ration with propionic acid (0.5-1.5 g/kg ration) or thiabendazole (100 mg/kg ration).
- Reduction of the use of excessive chemical drugsfor the use of drugs to help relieve symptoms of the disease reduce the use of paracetamol and other chemical drugs in excess or give according to the applicable dose. To treat liver function can use alternative ways of giving herbal supplements such as Heprofit in neutralizing free radicals from the use of chemical drugs. This can be seen in Graph 1 which shows that the higher the score, the more severe the degree of liver damage. Heprofit is safe to use every day because it is made from herbal ingredients to help protect against liver damage due to excessive administration of chemical drugs.
Treatment Of Liver Damage
In dealing with the incidence of liver damage in chickens can do several things as follows:
- Selection of raw materials or ration perform ration material selection if found very much fungal contamination, do not use these raw materials. If the ration material is slightly contaminated, it can be mixed with raw materials or rations that have not been contaminated.
- When toxin contamination has been found, it is necessary to add mycotoxin binding agents to the ration and those in the digestive tract and remove them through secretion. Additional toxin (mycotoxin binding) on the ration mix with Freetox. Administration of antioxidants such as Butyrated hidroxy toluene (BTH), vitamin E and selenium can also be added to reduce the effects of mycotoxins.
- Multivitamin administration for endurance vitamin supplementation, especially fat soluble vitamins (A, D, E, K), amino acids (methionine and penilalanin) and increase the levels of protein and fat in the ration is also able to reduce losses due to mycotoxins. High-dose multivitamins such as Fortevit could be a solution.
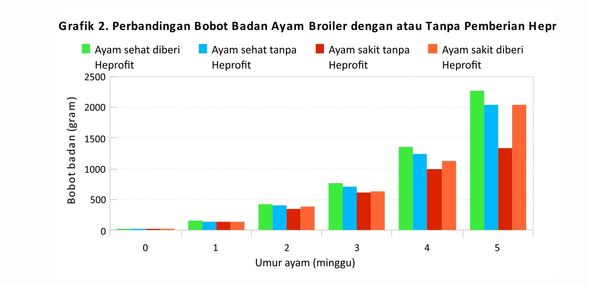
- Administration of hepatoprotectorsHeprofit it can also be given when the poultry has experienced a condition of liver damage, herbal medicine is given as a supportive measure. Heprofit has a function as a hepatoprotector that has proven potential in repairing liver damage. From data trial Research and Development (R&D) Medion (2016) in graph 2, heprofit administration in normal week (Green) looks best body weight (statistics on real with others. While in chickens sick with afiatoksin case, giving Heprofit (orange color) can also increase body weight. So Heprofit able to help increase body weight (performance). May be useful. Salam