Mouth and hoof disease (FMD) that attacks livestock such as cows, buffaloes, goats, sheep is a scourge for farmers. The disease is highly contagious and affects all cloven-hoofed animals. The transmission rate of FMD is very high, reaching 90-100%. As well as it can cause 1-5% mortality in old animals and more than 20% in young animals. This will certainly lead to losses for breeders.
Symptoms seen in livestock affected by FMD include fever, decreased appetite, excessive salivation (hypersalivation), blisters on the mouth area (tongue, gums, palate) and nails. Cattle can also show symptoms of lameness, collapse, nipple injuries, decreased milk production, and even death.
Handling of livestock affected by FMD is always sought as soon as possible so that it does not spread and the livestock soon recover. When getting a report of suspected FMD, animal health workers and the local animal husbandry office will immediately conduct isolation and handling or treatment of livestock. To accelerate healing, it is necessary to pay special attention to the farmer in caring for his livestock.
Treatment of livestock affected by PMK
PMK is caused by a virus so the treatment is done on livestock by overcoming the symptoms that appear. Livestock affected by FMD need to be treated as early as possible since the first clinical symptoms appear in order to avoid secondary infection and recover quickly. With early detection of the disease and immediate treatment, the healing rate or treatment success will be faster. It is important for the farmer to really pay attention to the condition of his livestock.
Here are some treatment efforts that can be done on livestock infected with PMK :
Separate sick cattle
If symptoms of fever appear or there are wounds around the mouth or nails, then the thing that needs to be done immediately is to separate the livestock from healthy livestock. This is done so that sick cattle do not act as a source of infection for other livestock that are in the same stable. Then immediately report to the nearest animal health officer for further treatment.

- Provide supportive therapy
Multivitamins Vita B Plex Bolus Extra Flavor it can be given through the mouth to increase endurance and accelerate healing.
- Handling of injuries
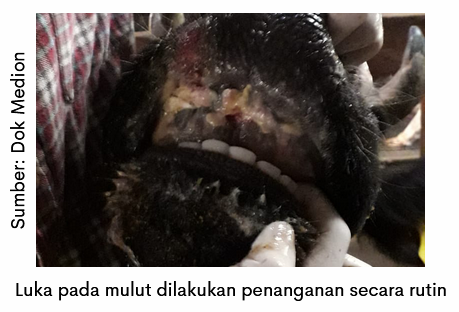
Wounds on the mouth and feet can be given antiseptics (Antisep) so that the wound dries quickly. Antisep safe to use for the mouth and tongue. The method of administration can be done by spraying into all parts of the wound. For the tongue can also rub it into the nostrils and let the cow lick it so that the tongue can also be cured. This treatment is done every day until the wound heals.
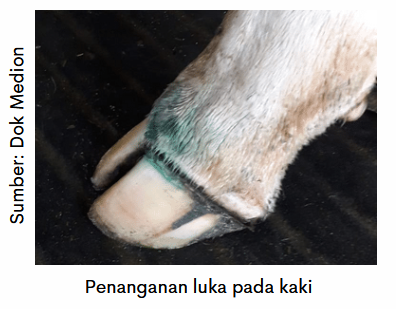
Wounds on the feet also need to get regular treatment. The feet of cows infected with PMK and there are wounds are cleaned first. Then brush or spray (,) using Antisep. Need to ensure spray Antisep maximally reach the inner wound of the nail.
The presence of an open wound or the smell of fresh blood will attract flies Chrysomya bezziana for perch and laying eggs. Fly eggs will hatch and grow into larvae, then move into the tissue. So that the presence of open and wet wounds will be at risk myasis or maggots. To prevent this, farmers can spray Dicodine as a spray to accelerate wound healing and prevent its occurrence myasis. To overcome wounds need patience and routine every day so that the wound dries quickly. This treatment is carried out until the livestock is completely cured and its condition improves.
- Handling of animal health workers handling is done according to the condition of the livestock. For example, by providing therapy to overcome the symptoms of fever, pain and inflammation. Can also be given energy supplements such as Bioselvita. As well as to cope with a secondary infection can be given antibiotics.
Disinfection Of Cattle Pens
It is no less important in the handling and care in the case of FMD is the disinfection of the cage. This aims to reduce the number of viruses in the cage and prevent transmission or minimize the spread of the virus. Disinfection of the cage is also carried out independently by the breeder. When PMK cases occur, disinfection needs to be carried out regularly every day in the morning and evening. In cages containing livestock, disinfection is necessary using Desinsep at a dose of 180 ml/liter of water. While in vehicles, equipment and empty cages, it is necessary to carry out decontamination and disinfection with Sporades or Formades. Sporades used at a dose of 100-200 ml dissolved into
20 liters of water. While Formades used at a dose of 500-1000 ml dissolved in 25 liters of water. The FMD Virus can persist for a long time in the environment. So the cleaning and disinfection of the cage needs to be done regularly and continuously.

To optimize the handling and accelerate the healing of livestock, it is necessary to carry out regular maintenance measures and disinfect the cages in a disciplined manner. As well as providing vitamins so that livestock quickly recover.










