Mas Nurhadi – By Email
Please explain for chicken production given concentrate with crude protein 30% decreased production to 60%. How much % addition of soybean meal to increase crude protein of feed mixture? Thank you
Answer:
Thank you Mas Nurhadi for the question submitted. Concentrate is a semi-finished feed that needs to add energy source raw materials to meet the nutritional needs of livestock. In the preparation of a balanced ration, often added energy source raw materials include corn, bran or Bran. The balance of the formulation in the mixing of feed ingredients can be done with the arrangement of 50% corn, 35% concentrate and 15% bran or Bran. The preparation of the ration needs to take into account the specific nutritional needs of livestock. These needs are adjusted based on the physiological phase of livestock include starter phase (age 0-5 weeks), grower (age 6-16 weeks), pre-layer (age 17-18 weeks) and layer/production (age 19 to reject). The nutritional needs of production phase laying hens are listed in Table 1.
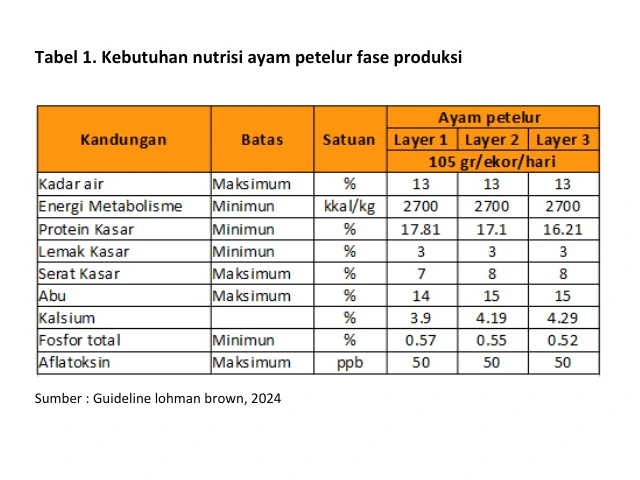
The nutritional needs of livestock can be optimized through careful consideration of the feed composition Matrix. The concentrate has a crude protein content of at least 30% (SNI, 2025). Addition of soybean meal (BKK) or also called soybean meal (SBM) in the concentrate can increase the crude protein content of the total ration. BKK is a feed source of vegetable protein derived from the byproducts of soybean oil processing that has undergone a drying process. Crude protein content of 43 – 48% BKK, able to meet the needs of poultry protein up to 50% (Sitompul, 2004). In addition, lysine digestibility in BKK showed the highest value (91%) compared to other protein source feed ingredients (Willis, 2003). Feed with good protein and amino acid content supports livestock growth for optimal body weight and production.
Soybean meal quality
The quality of BKK is largely influenced by processing, handling and storage procedures. The following BKK quality parameters need to be considered :
- Protein. The geographical location of soybean production and the types of soybeans are factors that can affect the diversity of crude protein content and amino acid composition of BKK (Baker et al., 2011).
- Fat. The crude fat content in BKK should not be more than 3.5% (SNI, 2024). Fat content is influenced by the process of oil separation by solvents. If the separation process is not perfect, then the remaining oil will be high, adding energy value. However, if stored for a long period of time, it will be easily rancid because it undergoes an oxidation process.
- Fiber. The fiber content in BKK should not be more than 7% (SNI, 2024). The fiber content can be affected by the amount of skin that is processed. Foreign contaminants in BKK can also increase the high coarse fiber content. The high fiber content will lower the energy content of the metabolism.
- Antinutrients. BKK contains antinutrients, namely non starch polisaccaride (NSP) 17,86-31,5% (Bach Knudsen, 1997), asam fitat 0,6% (Van Eys, et al., 2004) and trypsin inhibitor 4,5-6% (Hartini and Choc, 2010) . NSP can increase the viscosity/viscosity of intestinal fluids so that the nutrients absorbed by the body decreases and causes wet dropping or diarrhea. Phytic acid can reduce the availability of Ca, P, micro minerals and protein so that bone growth and egg shell formation is not optimal. Trypsin inhibitor can reduce the activity of protease enzymes so that the protein is not used optimally and livestock performance decreases. Enzymes need to be added to break down antinutrients so that the digested feed nutrients will be more. One of the characteristics of enzymes that work in 4. specific, meaning that the enzyme can only work to adjust the type of substrate. The phytase enzyme will release more phosphorus and amino acids bound by phytic acid. The enzyme xylanase can decompose arabynoxylan of the NSP antinutritional type into simple carbohydrates. Protease enzymes can reduce the negative influence of antinutrients trypsin inhibitor so that the digestibility of proteins becomes better. The trend of using enzymes in rations continues to increase to cope with the varying quality of ration raw materials.
- Physical. A good BKK has the characteristics of smooth, shiny, light brown, smelling fresh (not musty), does not smell burnt, homogeneous texture, free to move, does not clot, and is free from fine particles and dusty.

The decline in production can be influenced by feed conditions, chickens and maintenance management applied. Here are some solutions to decreased production in laying hens:
1. Quality feed
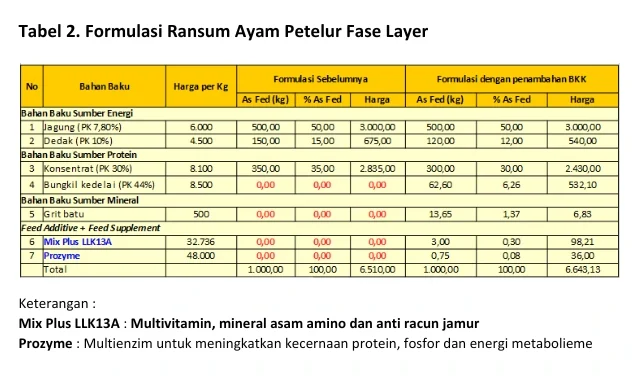
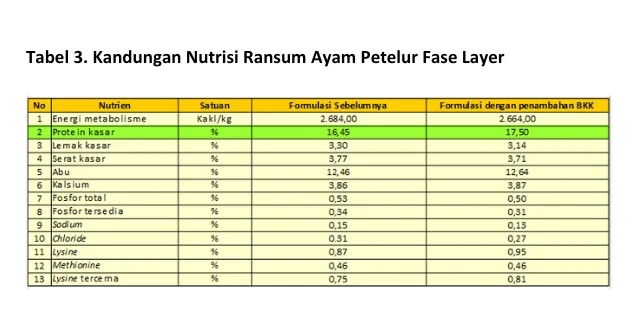
Quality feed is feed that is formulated to meet the nutritional needs of chickens to produce optimal performance. Quality feed comes from quality raw materials. BKK as an energy source raw material can be added to increase the total ration crude protein. However, replacing part of the concentrate with BKK also needs to pay attention to other nutrients such as calcium and phosphorus. The need for raw materials such as mineral resources dicalcium phosphat (DCP),monocalcium phosphat (MCP) and grit stone. Premix supplementation also acts as back up to meet the needs of micronutrients, especially when obtaining substandard raw materials due to variations in raw materials. The composition of the premix consists of feed supplements in the form of various minerals, vitamins and amino acids. Premixes for concentrates can use Mix Plus LLK13A with additional toxin namely hydrated sodium calcium aluminium silicate (HSCAS) to bind fungal toxins in the digestive tract. The digestibility of BKK can be increased by the addition of feed additive one of them is enzymes. Prozyme it contains several enzymes (phytase, protease, amilase dan xylanase) and biocatalysts that can bind and accelerate the work of enzymes. The formulation and nutritional content of the concentrate with the addition of BKK are indicated in Tables 2 and 3.


2. Chicken
High-quality pullets support the achievement of optimal egg production. Characteristics of good-quality pullets include uniformity above 85% in terms of body weight, skeletal structure (frame size), and sexual maturity (sexual maturity). In addition, continuous monitoring is necessary to maintain the hens’ condition up to peak production. Monitoring includes ensuring feed intake meets the standard, body weight is on target, and uniformity is well maintained.
3. Maintenance management
Maintenance management is an art in the maintenance of laying hens to be able to produce optimal production. When the condition of the feed is good quality and the quality of the chicken is good, but not balanced with proper feeding management, finally the feed consumption is not achieved optimally. This is one of the causes of egg production problems. Therefore, it is important to pay attention to maintenance management factors ranging from feeding management, cage density, lighting, etc. From the above discussion can be concluded that to prevent and overcome the problems of egg production, can be done with the addition of raw materials such as protein sources BKK, supplementation through feed in the form of premixes as back up nutrients and feed additive to improve the digestibility of feed. In addition, it should also always be balanced with the quality of chicken and good maintenance management. May be useful.










