Treatment is an effort to minimize losses due to diseases that are infecting, both in terms of chicken performance and costs incurred. Improper treatment practices will have an impact on diseases that do not heal, higher treatment costs, and the risk of increasing antimicrobial resistance.
Antimicrobial resistance is becoming a frightening scourge. According to the WHO, antibiotic resistance has resulted in the death (as of 2014) of about 700,000 people each year. By 2050, antimicrobial resistance deaths are expected to be higher than cancer deaths. Therefore, efforts are needed to prevent the development and spread of infection due to resistant microorganisms. Efforts that can be done in the livestock industry is to do a wise and targeted treatment, one of them by obeying the rules of use of each drug used.
Determination of the correct diagnosis and treatment
Consult livestock health to authorized medical personnel (veterinarians) to diagnose and treat. The stage of diagnosis starts from Anamnesis and then continued observation of clinical symptoms and changes in anatomical pathology. In some cases, laboratory tests are needed. After the determination of the diagnosis, farmers will get treatment advice and other supportive advice for handling the case.
In general, the principles of treatment include :
- Drugs administered according to the infecting disease
Drugs are very diverse. Therefore, it is necessary to diagnose in advance to determine the direction of the disease. If the disease leads to bacterial can be treated with antibiotics. When the disease leads to parasites such as coccidiosis can be assigned antiprotozoa. Proper diagnosis will determine the suitability of the drug to be administered.
- The drug can reach the site of work or target pain
Selection of treatment routes is important to determine the type of drug chosen because it determines the range of action of the drug. For example, if the target organ is in the skin, the administration of topical drugs will be more effective than the administration of drugs through drinking water. In addition, it is also necessary to consider the degree of severity. When the disease is severe and the consumption of drinking water also decreases, treatment should be done by injection route so that the drug reaches the target organ faster.
- The drug is available in sufficient levels
The drug will give the effect of treatment when it has exceeded levels Minimum Effective Concentration (MEC), but should not exceed the rate Minimum Toxic Concentration (MTC). Therefore, it is very important to pay attention to the dosage in accordance with the rules of use so that the drug can work optimally without causing toxicity. The injection drug will provide a faster treatment effect than peroral drugs because it is able to achieve a faster MEC.
- The drug is available in sufficient time
The drug takes time to work providing a therapeutic effect. Therefore, it is necessary to pay attention to the duration of the time of administration of the drug. Examples for antibiotics acting effect like Lincomed LAdrug, with a single administration by injection can work for three days. So that if needed repetition can be done once every three days. In contrast to antibiotics short acting like Tinolin Injection which requires daily repetition for 3 days. For drugs administered through drinking water such as Tinolin it needs daily administration also for 3-5 days. Preferably for drugs that are given through drinking water given in divided doses to maintain the stability of drug levels in the blood remains the same. Here's an example of giving Tinolin with divided doses of 2x/day (maximum duration of 6 hours once administration) for 1000 chickens with an average body weight of 1.85 kg :
The need for dosage in one day
= Population x body weight x drug dose
=1000 ekor x 1,85 kg x 0.4 ml/kg
= 740 ml
Administration for divided doses 2x/day
= Dose requirement in one day : 2
= 740 ml : 2
= 370 ml (for one administration)
Therefore Tinolin can be given in one day as much as 2x, namely 370 ml at 07.00-13.00 and 370 ml at 13.00-19.00.
Wise application of Medicine in the field
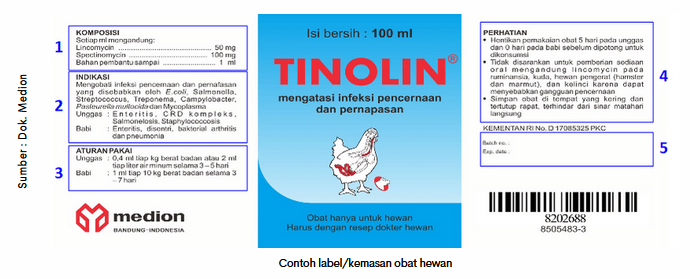
Before using the drug, pay attention to the information listed on the label/packaging of the drug. Things that need to be considered from the label/packaging of the drug, namely :
- Pay attention to the composition of the drug. In the case of antibiotics (rolling antibiotics), should use drugs with a composition and class of antibiotics that are different from the products used previously to avoid the occurrence of antibiotic resistance of certain groups. Therefore, it is best to consult with authorized medical personnel before carrying out rolling antibiotics.
- See the indication of the drug, whether it corresponds to the targeted animal/purpose.
- Obey the rules of use. Use the dosage and duration of the Drug Administration in accordance with the rules indicated on the package. Do not reduce or increase the dose without the approval of authorized medical personnel, as it may reduce the effectiveness of the drug or cause toxicity.
- Pay attention to the warnings of Use and storage of the drug to avoid unwanted things. Appropriate storage will affect the physical quality of the drug.
- Note the expiration date of the drug (expired date) to ensure that the drug is still fit for use. Do not use drugs that are not feasible such as damaged seals or physical changes such as color, odor, and shape of the drug.
When using the drug through the application of drinking water also need to pay attention to the following points :
- The water used to dissolve the medicine does not mix with disinfectants, as this can decrease the effectiveness or even damage the medicine. For example, the ionosphere (Antisep, Neo Antisep) which is a strong oxidizer, so it will damage the drug / vitamin when mixed. When drinking water from the tap water tap (tap water tap water tap water tap water tap water tap water tap water tap water tap water tap water tap water tapDesinsep), must first be precipitated for at least 6-8 hours before use to dissolve the drug. (Except for the fact that it can be used as an antiperspirant, it can also be used as an antiperspirant, and it can also be used as an antiperspirant, and it can also be used as an antiperspirant (Medisep, Zaldes).
- Check the quality of drinking water used to dissolve the drug because it can affect the solubility and stability of the drug. For example, the pH of water that is too acidic will precipitate sulfonamide antibiotics and β- lactam. Whereas if the pH is too alkaline it can precipitate tetracycline and Trimetropin antibiotics.

- The Volume of water used to dissolve the drug, the distribution of chicken drinking places when using manual drinking places such as chicken drinking places (TMA), and Dosatron scale settings when using nipple drinker. This will affect the amount of the drug and the uniformity of the dose received by the chickens.
- Do not increase the dose of the drug without the consent of authorized medical personnel. The use of drug doses that are not in accordance with the rules of use has the potential to increase the incidence of antibiotic resistance
If the treatment has been done but the condition of the chicken does not improve, the evaluation of treatment methods through:
- Ensuring the use of drugs is appropriate both in terms of selection of drug compatibility with the disease as well as dosage and feed rules have been run properly.
- Make sure the diagnosis is correct. If it does not go away, you should immediately consult a medical professional so that you can re-diagnose the cause of the disease. If the main cause is a viral disease, then antibiotics cannot be treated.
- Make sure the antibiotics that have been used have experienced resistance with antibiotic sensitivity tests. If resistance is detected, use antibiotics from other groups that are still sensitive according to the recommendations of medical personnel.
Things that cause antibiotic resistance are :
- Poor treatment practices, such as the use of doses that are not in accordance with the rules of use, the incompatibility of antibiotics used with the disease being treated, and incomplete treatment.
- Internal factors of bacteria, such as mutations, changes in enzymes, and receptors.
By obeying the rules of drug use and conducting wise and appropriate treatment will accelerate the healing of a disease and suppress the increase in cases of antimicrobial resistance. May be useful.










