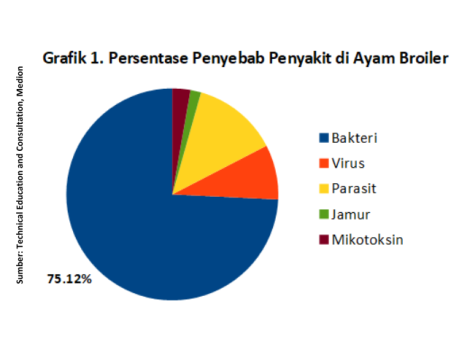
The poultry industry is one of the alternative solutions to bridge the nutritional gap for most Indonesians. Chicken meat breeds such as chicken broiler it is a source of nutrition rich in animal protein and economical. However, the challenge of diseases caused by infectious and non-infectious agents still continues to threaten the world of poultry farming. According to data compiled by Tim Technical Education and Consultation Medion in Graph 1, the disease-causing pathogen most commonly found in chickens broiler are bacteria. The incidence of diseases caused by bacteria was found to be 75.12% during 2022 to June 2024. These pathogens can attack the respiratory system, digestion or other organs.
Yehia et al (2023) mention that the respiratory system is the most crucial organ. The respiratory tract is never free from the threat of disease-causing pathogens. Of the wide variety of disease challenges, respiratory diseases pose the most real threat to global health due to their high prevalence, mortality and morbidity, the need for expensive treatment, and their impact on declining chicken performance broiler.
The respiratory tract of chickens consists of the nose, sinus infraorbitalis, larynx, trachea, bifurcatio trachealis, bronchi, bronchioles, lungs up to air sac. The respiratory system of chickens is also equipped with physical immune organs such as cilia which serves to repel all foreign objects that enter. Naturally, the respiratory organs will be constantly exposed to unpredictable environmental conditions. So the risk of damage to the defense system that is in the respiratory tract. These conditions allow the respiratory organs as the main gateway for the entry of seeds of diseases such as viruses, bacteria, and fungi. Nevertheless, respiratory diseases are a major challenge that is difficult in determining the right diagnosis. Because most of the causes of respiratory diseases are very complex and sometimes it is the combination with more than one pathogen that increases the severity of the disease.
Until now respiratory diseases are still the main source of financial losses in the poultry business. Respiratory infections are a serious problem facing the poultry sector and cause great economic losses. Based on data from Medion Disease Incidence, frequent respiratory diseases in chickens broiler caused by bacteria such as Mycoplasma gallisepticum, Eschericia coli, and Avibacterium paragallinarum. While respiratory diseases caused by viruses include Newcastle Disease (ND), Avian Influenza (AI) and Infectious Bronchitis (IB). In addition, respiratory diseases caused by fungi such as Aspergillosis are still found in broiler chicken farms. This is certainly a vigilance for farmers to improve the application biosecurity the disease control program in farm so that the incidence of respiratory disease cases can be minimized.
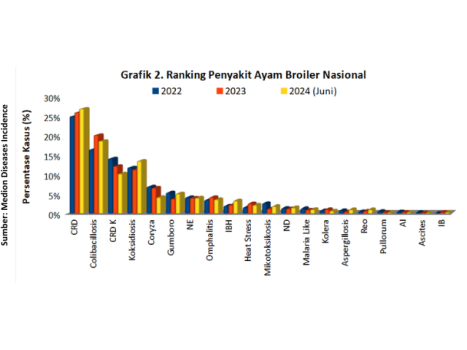
Chronic Respiratory Desease (CRD) and Colibacillosis are still challenging diseases most commonly found in broiler chicken farms. Seen in graph 2 which shows that CRD disease is ranked number 1 disease in Indonesia. Then followed by other respiratory diseases such as Colibacillosis, complex CRD, Coryza and others. CRD disease also experienced an increase in the percentage of incidence of disease cases from 2022 to June 2024. In addition, cases of other respiratory diseases both caused by bacteria, viruses and fungi need to be watched out too. Because these diseases can have an impact on economic losses for poultry farmers in Indonesia. Here are some examples of factors that can predispose to respiratory diseases, among others:
- Poor ventilation system
Most of the triggers for the appearance of respiratory diseases are ventilation problems. Ventilation systems or poor air governance can affect the temperature and humidity in the cage. If the temperature, humidity and air requirements in the cage are inadequate, it can trigger stress and reduce the comfort level of chickens. As a result, chickens will be susceptible to disease and maintenance performance is not achieved optimally. - High density
High population density correlates with the amount of feces produced by chickens. This can certainly risk increasing ammonia and carbon dioxide levels in the cage. Ammonia Gas is formed as a result of the evaporation of feces along with ureolytic bacteria present in the environment, and is supported by humid and wet environmental conditions. High ammonia levels (>5 ppm) can trigger damage from respiratory cilia. It is also important to note that carbon dioxide is a highly toxic product of respiration in high concentrations. - Poor cage hygiene
Dirty and dusty cage conditions and high ammonia levels can also have a direct impact on the health of chickens. All these factors coupled with the presence of environmental pathogens as well as the presence of immunosupressants are the main predispositions to the appearance of irritation, inflammation or damage and lesions to the respiratory tract mucosa. In addition, due to stress and poor ventilation systems can have an impact on damage to physical immune organs such as cilia found in the upper respiratory tract. This will certainly facilitate the entry of various pathogens that cause disease.
Some examples of Respiratory Diseases in Broiler Management
Many disease-causing pathogens in poultry utilize the respiratory tract as the main route of entry for Disease agents. It can also facilitate the transmission or spread of disease within a population. Yehia et al (2023), the types of pathogens that most often cause respiratory disease problems are viruses and bacteria. Respiratory diseases caused by viruses include Infectious Bronchitis (IB), Newcastle Disease (ND), Avian Influenza (AI), and Avian Metapneumovirus. While respiratory diseases caused by bacteria include CRD, Colibacillosis, Coryza, and Ornithobacteriosis. Here is a brief description of some respiratory diseases in chickens broiler recently reported :
1. Infectious Bronchitis (IB) virus of
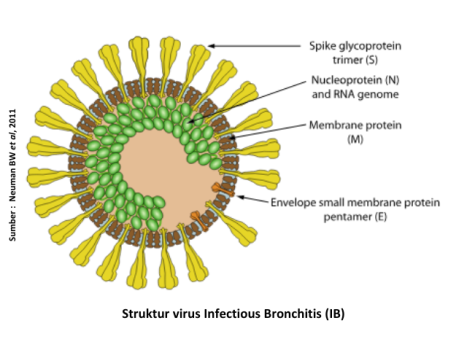
Infectious Bronchitis (B) it is a disease caused by Gammacoronavirus which includes amplified virus types. The Virus that causes IB is relatively unstable in the environment. It can be inactivated at 56°C for 15 minutes and 45°C for 90 minutes. The Virus that causes IB is also sensitive to all types of disinfectants such as Medisep, Neo Antisep or Formades. IB disease can cause economic losses for chicken farmers broiler. On chicken broilerin addition, IB disease can affect the respiratory and urinary systems. The main Target organs attacked by the virus that causes IB are bifurcatio trachealis, bronchi and kidneys. Respiratory symptoms caused by the disease can have an impact on decreasing feed intake, Feed Conversion Ratio (FCR) are high, as well as the achievement of the weight of the harvest is not optimal. IB disease can be transmitted horizontally either directly or indirectly or through personal intermediaries and equipment contaminated with the virus. The incubation period of IB disease can be very fast, which is about 18-36 hours and can spread within a population.
Infectious Bronchitis (IB) can be classified into 2 types that are often found in boiler chickens, namely IB classic dan IB variant. Based on test data Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) and Sequencing Medion, lately in 2024 there have been frequent cases of IB variant in broiler chickens that have not received IB vaccination variant. IB diseases fall into the top 3 ranking diseases for the category of diseases caused by viruses in chickens broiler attacks on the respiratory system (Figure 2). This disease can attack at any age either young or before harvest. On chicken broiler, the incidence of IB disease is often found between 3-5 weeks of age (Neuman et al, 2011). This is also supported by field data collected by the team Technical Education and Consultation Medion during the year 2022 to June 2024, indicating that the age of IB case attacks in broiler most often it occurs at the age of 15-21 days and 22-28 days (graph 3).
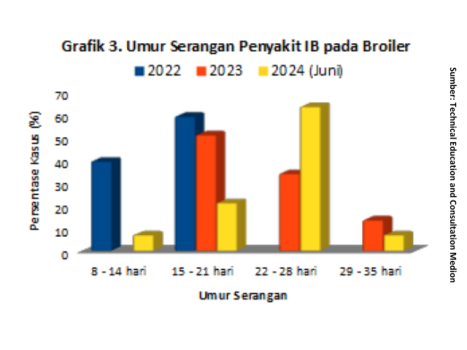
Age of IB disease attack in chickens broiler very varied. Based on the results of the PCR test and Sequencing Medion in July 2024, positive (+) IB Case Reports variant at the broiler 25 days old. The IB vaccine is administered in hatchery using the IB vaccine classic. Possible vaccinations using the IB vaccine classic alone is not enough to protect livestock from IB virus attacks variant. The IB vaccination program variant on chicken broiler need to be a consideration. In this case, reports of total mortality (mortality rate) reach 5-7%. According to information that high mortality in cases of IB is usually accompanied by secondary infection by bacteria for example Colibacillosis (dyspnea, heart and liver covered by fibrin). Reported clinical symptoms of snoring, decreased appetite, slow growth and the weight does not reach the standard. While the observed anatomical pathological changes are sinusitis, laryngitis, tracheitis, airsacculitis, inflammation of the bifurcatio trachealis, pericarditis and swollen kidneys.
2. Avian Influenza
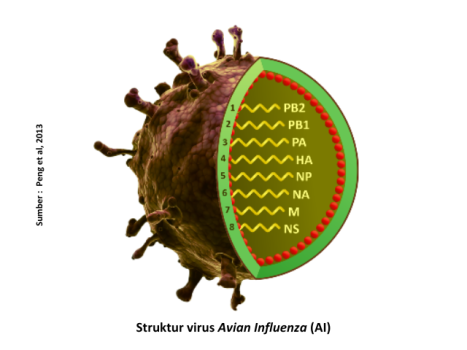
Avian Influenza (A) is a disease caused by Orthomyxovirus from genus Influenzavirus A which includes amplified virus types. The virus has 8 genetic segments / proteins, including 2 most important proteins that can determine the subtype and malignancy of the virus AI HA protein (Hemagglutinin) dan NA (Neuraminidase). As well as in Indonesia, the AI virus subtypes found are H5N1 and H9N2. Based on its malignancy, H5N1 is a subtype of AI virus that has high malignancy or often known as High Pathogenic Avian Infuenza (HPAI). AI H5N1 found in Indonesia is dominant from clade 2.3.2.1 c, although also found clade 2.3.4.4 b. While H9N2 is a subtype of AI virus that has low malignancy or known as Low Pathogenic Avian Influenza (LPAI). H9N2 has only been found clade that is h9.4.2.5 (Y280). The AI Virus is relatively unstable in the environment, but it can survive well in cool and humid conditions. In addition, the AI virus is also easy to experience mutations or genetic/protein changes, especially in the HA and NA proteins.
The HA Protein is essential for the attachment of the virus into the host cell during the infection process. While the NA protein plays a role in the release of virion (the result of viral multiplication) of already infected host cells. The incubation period of AI disease lasts very quickly, which is several hours to 3 days. LPAI disease can be transmitted vertically and horizontally. While HPAI disease is only transmitted horizontally directly from infectious sick chickens to healthy chickens or through air, feed, drinking water, personal and equipment contaminated with the virus. Nevertheless, the AI virus can be eradicated with all kinds of disinfectants such as Medisep, Neo Antisep, Sporades or Formades.
Since 2003, Avian Influenza (AI) is still a problem and epidemic in Indonesia. AI disease is a challenge in animal husbandry broiler because it occupies the top 3 ranking diseases caused by viruses that invade into the respiratory system (Chart 2). The age of AI disease attacks varies from the first week of maintenance to before the harvest period. Recent case reports compiled by the team Technical Education and Consultation Medion in early August 2024 reported on broiler chickens aged 30 days. PCR test results showed positive ( + ) AI H5N1. In this case no AI vaccination has been carried out since hatchery, so there is no protection against AI virus attacks ahead of the harvest period. The harm caused by AI diseases cannot be underestimated for chicken farmers broiler. Sitohy et al (2022) noted that the mortality rate caused by AI diseases, especially H5N1, can reach 100% after 3-5 days post-infection. Based on field data collected by the team Technical Education and Consultation Medion during the year 2022 to June 2024, indicating that the age of the AI Case attack in broiler most often it occurs at the age of 22-28 days (graph 4).
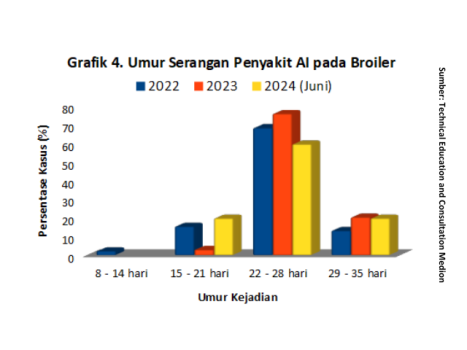
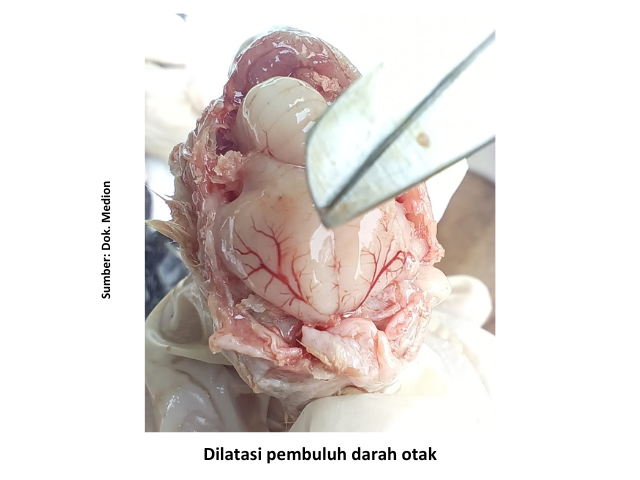
Up to now Avian Influenza (AI) is still a global challenge due to its wide spread and high mortality rate. Surveillance of AI disease in poultry is very important to monitor the development of AI virus in Indonesia. It also helps analyze and ensure the vaccine virus used is really in accordance with the virus variants circulating in the field. More importantly, it can help track and identify possible viral mutations, given that AI viruses are constantly changing over time. Based on the description of cases of AI H5N1 that occurred in broiler in August 2024, the reported mortality or total mortality rate reached 66%. This event lasts for 2-3 days. Reported clinical symptoms include sudden death, snoring, feverish body, bluish Combs and legs and greenish-white diarrhea. While the anatomical pathological changes found are cerebral vascular dilatation, ptechie heart muscle fat, tracheitis, proventricular inflammation, ptechie in abdominal fat, pale liver, enteritis, swollen spleen and swollen kidneys.

3. Infectious Coryza
Infectious Coryza is a respiratory disease caused by bacteria Avibacterium paragallinarum. Bacteria that cause Coryza include types of gram-negative bacteria ( - ), short rod-shaped encapsulated and do not form spores. Avibacterium paragallinarum also facultative anaerobic, which means that the bacteria can live in media / where there is oxygen or no oxygen. Sinus infraorbitalis it is the main target organ that is attacked by these bacteria. Transmission of Coryza disease occurs horizontally from sick chickens to healthy chickens or through personal intermediaries, equipment, air, feed and drinking water contaminated with mucus containing bacteria. The incubation period of Coryza disease lasts about 1-3 days. On chicken broileraddition, Coryza disease can lead to a decrease feed intake, slow growth, achievement of non-optimal body weight and high culling rates.
Avibacterium paragallinarum it spreads through contact with infected chickens or mucus containing bacteria. The Cured chicken will be carrier (carrier) of these bacteria over a long period of time. Once a chicken population is infected, all chickens are considered carriers. Chickens are more susceptible to developing Coryza if they have previously been exposed to other respiratory viruses or bacteria. Based on data collected by the team Technical Education and Consultation Medion during the year 2022 to June 2024, indicating that the age of the attack Coryza case in broiler most often it occurs at the age of 15-21 days and 22-28 days (graph 5). Nevertheless, Avibacterium paragallinarum sensitive to sunlight, heat and can be eradicated with all kinds of disinfectants such as Medisep, Neo Antisep or Formades.
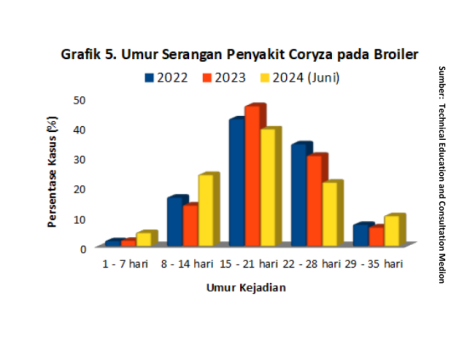
In Indonesia, Coryza case occupies the top 5 ranking diseases in chickens broiler during the years 2022 to June 2024 (graph 2). The bacterial strains that cause Coryza are classified into three serogroups (A, B, and C), which have nine serovar hemagglutinin (HA) yaitu A-1 hingga A-4, B-1, dan C-1 hingga C-4 (El-Naenaeey et al, 2021). Berdasarkan data hasil uji PCR dan Sequencing Medion, secara global Avibacterium paragallinarum yang ditemukan di Indonesia berasal dari serovar A1, B1, C1 dan C4.
El-Naenaeey et al (2021) mentioned that Coryza disease is usually acute and spreads quickly. Generally the pain rate (morbidity) is very high reaching 60-80%. While the mortality rate (mortality) can range from 1 to 15% and tends to increase when accompanied by other pathogens. Clinical signs include swelling around the face, especially sinus infraorbitalisaddition, swelling of the face may occur on one or both sides, thick or pus-like discharge from the nostrils, watery eyes, difficulty breathing, sneezing and decreased breathingeat. Anatomical pathological changes that are observed, namely inflammation of the upper respiratory tract, especially the sinuses infraorbitalis.


4. Ornithobacteriosis
Ornithobacteriosis is a respiratory disease caused by bacteria Ornithobacterium rhinotracheale (ORT). ORT bacteria include Gram-negative ( - ), rod-shaped, non motile, are pleomorphic and sensitive to all kinds of disinfectants. The incubation period of ORT disease varies depending on the severity of the infection, on average around 4 days post-infection. Since the beginning of these bacteria have characteristics as bacteria non hemolytic. But in 2011 it was discovered strain hemolytic which was isolated from the lungs and trachea of chickens with pneumonia. Strain hemolytic this needs to be watched out because it can produce toxins hemolysin-like protein which can have an impact on the health of chickens (Barbosa et al, 2020). Transmission of ORT disease can occur vertically and horizontally. Bacterial infection Ornithobacterium rhinotracheale which together with other pathogens can provoke the severity of the disease.
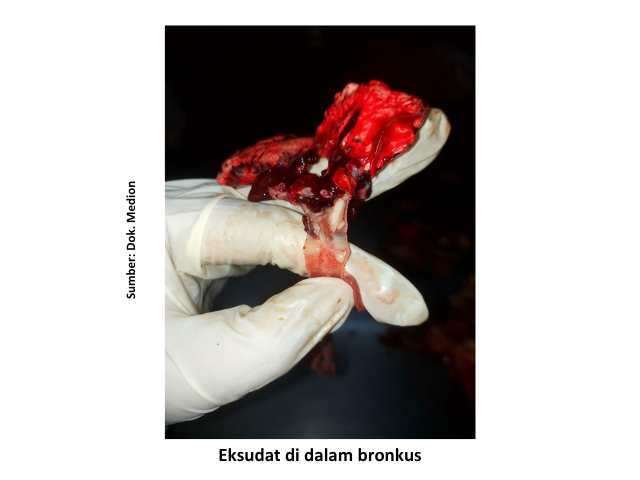
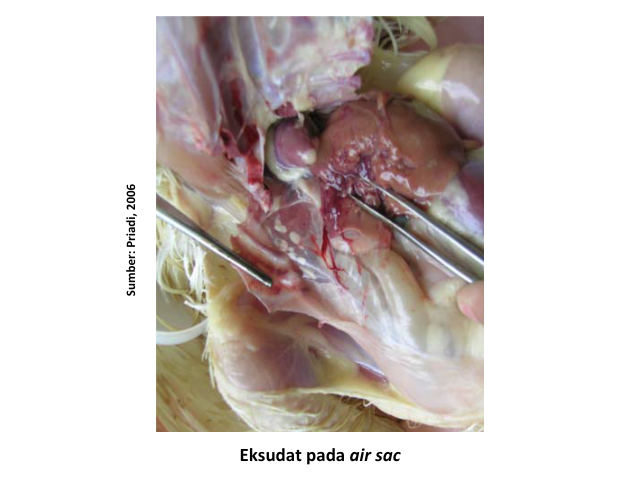
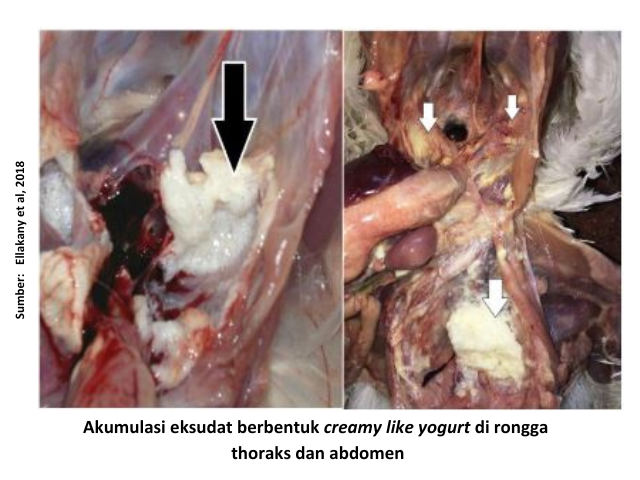
Some other factors that can determine the severity of ORT disease are high ammonia levels in cages, poor ventilation systems, high population density, and temperature and humidity extremes. According To Kursa et al (2022), respiratory distress due to ORT leads to a decrease feed intake thus the impact on growth disorders, low uniformity, increased FCR and mortality. On chicken broiler, clinical symptoms are generally seen at the age of 3-5 weeks. Ranging from mild respiratory symptoms such as sneezing, mucous discharge from the nose to death slightly increased. While anatomical pathological changes include tracheitis, airsacculitis, pneumonia, found exudate in the bronchi and air sac, even found accumulations of exudate in the form of creamy like yogurt in the thoracic and abdominal cavities.
Respiratory Disease Control Strategies in Broiler Management
Disease control strategies can be classified into two things, namely prevention and treatment when cases of disease occur. Disease prevention efforts through strategic and continuous action from several aspects, namely the implementation of management and biosecurity a good, proper vaccination program and supportive feeding to increase the resistance of the chicken's body. While the treatment of the disease can be given medication or treatment according to the type of disease that attacks. In addition, it is also necessary to consider adequate facilities and infrastructure to support the success of chicken maintenance and health management. Here are some things that need to be done in anticipation of respiratory disease in broiler :
Application of management good ventilation
Good ventilation management should be applied since chick in or at the time brooding period,. Aspects of temperature, humidity and air velocity in the cage must always be considered and ensured in accordance with the standard. It is also important to observe the activity or behavior of chickens in the cage as a measure of chicken comfort. As age and body weight increase, population density must be considered. Perform selection and thinning, especially in the third week on chickens that already have a body weight >1 kg and are ready to be sold. It aims to reduce population density so as to minimize the incidence heat stress. In addition, pay attention to management litter and make sure the conditions are not wet and damp which can risk increasing ammonia levels in the cage. Perform alternations, additions and back and forth litter on a regular basis to condition litter keep it dry. Give Ammotrol via drinking water to keep chicken feces dry and control ammonia levels in the cage.
Implementation biosecurity the tight
Biosecurity an important aspect that must be considered by farmers broiler right now. Biosecurity is the main foundation in preventing the entry of disease seeds into the cage, as well as preventing the spread of disease from and to the outside farm. Application biosecurity includes 3 important things, namely isolation or separating chickens (based on age, or other types of poultry), traffic control (any personal, goods, vehicles or other animals can carry disease seeds, so it is important to limit traffic to minimize disease agents that are likely to be brought into farm), then sanitation and disinfection of cages, equipment and vehicles using Medisep/Neo Antisep/Formades. Before disinfecting, first do the washing or cleaning using a detergent solution to clean the remaining organic material (feces, mucus, blood) attached to the cage and equipment. In addition, sanitize the personal who will enter the environment farm , conducted via Medisep/Neo Antisep. It is also important to routinely sanitize drinking water using Desinsep to minimize disease transmission via drinking water and do flushing , conducted via Bioflush to eliminate biofilm on drinking water pipes. After that, do a cage rest of at least 14 days counted after the disinfection process is completed to break the chain of transmission of the disease.
The right vaccination Program
Vaccination needs to be done to prevent disease by forming antibodies and protecting livestock from disease according to the vaccine given. Considerations in creating a vaccination program in chickens broiler must pay attention to some important things such as Case history, age of disease, type of disease that often attacks and updates disease conditions around farm. Based on the description of several types of diseases above, to prevent IBD variant can be considered vaccination using Medivac IB Variant/Medivac ND G7 IB Variant Emulsion. Prevention against AI diseases can be considered vaccination using Medivac ND AI. Then prevention against Coryza disease on broiler can be considered vaccination using Medivac ND Coryza. Such vaccination schedule can be carried out in the hatchery through Program Vaksinasi DOC (PVD) Medion.
Regular supportive care
Multivitamins (Vita Stress/Neobro/Fortevit) and immunostimulants (Imustim) to keep the immune system remains optimal livestock. In addition, other supportive services such as Respitoran to help relieve breathing disorders caused by respiratory diseases.
Treatment of respiratory diseases
Respiratory diseases caused by viruses have not found a cure so that the handling is more emphasis on aspects of improved management and biosecurityand support (Respitoran) to alleviate the symptoms. The treatment of respiratory diseases caused by bacteria can be given antibiotics (Rofotyl/Erydoxcy) and in combination with supportive (Respitoran) to accelerate healing.

The economic impact caused by respiratory diseases in the poultry sector, especially broiler can not be underestimated. So that the control strategy is very important to note to reduce losses and encourage investment progress in the chicken farming sector broiler in Indonesia.