The current heat stress is a challenge for farmers in livestock rearing. Various efforts were made to minimize the negative impact caused by the heat stress. One of the effects is heat stress. Heat stress this is due to the lack of (negative balance) between the heat generated by the body and received from the environment with the heat removed from the body of the cattle. Increased temperature and humidity of the environment lead to inhibition of the release of heat from the body of livestock.
Poultry do not have sweat glands that are used as a defense during heat stress in removing heat from the body. So that when there is extreme heat stress susceptible poultry heat stress. Heat stress causing a decrease in livestock performance and significant losses for farmers. Handling needs to be done starting from management aspects such as Cage density, air circulation, proper ventilation arrangements, etc. In addition, aspects of the nutritional approach are also important to consider as an effort to reduce the impact heat stress.
Effect of heat stress on feed consumption and chicken performance
The normal temperature of a chicken is 40.6-41.7°C. To be able to maintain a normal chicken body temperature required ambient temperature of 25-28°C with a humidity of 60-70%. When the ambient temperature is higher, the chicken will begin to experience heat stress.
Environmental temperature affects behavior livestock mainly feed consumption and drinking water consumption. Tamzil et al., (2013) in his research showed that the increase in ambient temperature has a significant effect on increasing drinking water consumption and reducing feed consumption.
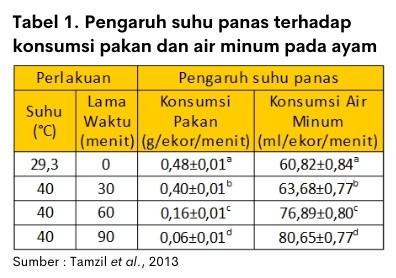
In addition, the impact of heat stress leads to physiological disruption, decreased immunity and performance of livestock. Broilers when heat stress decreased performance such as weight, feed intake and swell it Feed Convertion Ratio (FCR). Table 2 shows the decrease in body weight gain, feed consumption and FCR at the time heat stress.
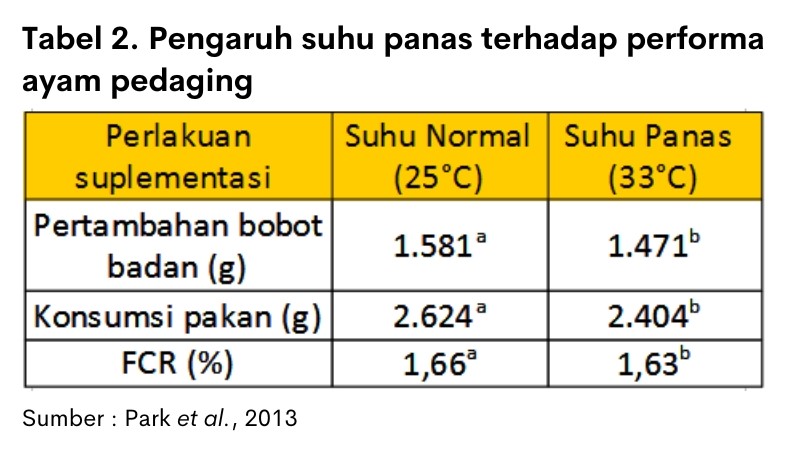
In addition, the impact of heat stress leads to physiological disruption, decreased immunity and performance of livestock. Broilers when heat stress decreased performance such as weight, feed intake and swell it Feed Convertion Ratio (FCR). Table 2 shows the decrease in body weight gain, feed consumption and FCR at the time heat stress.
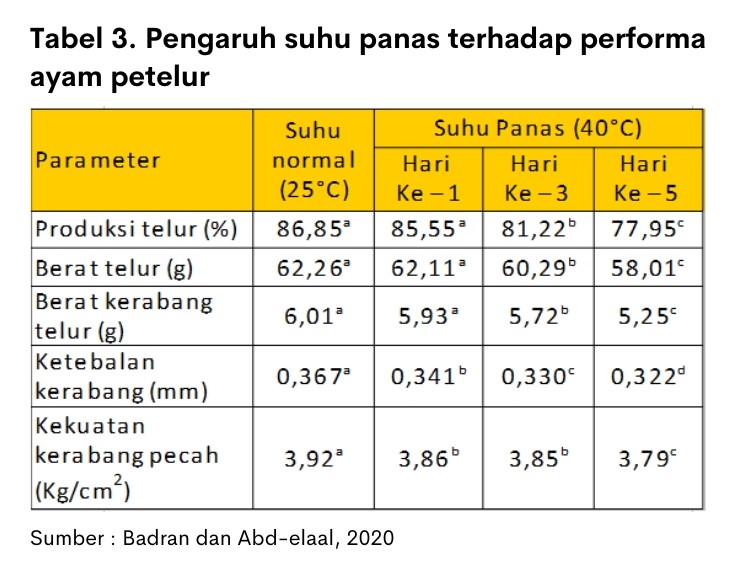
Nutritional strategies during heat stress
Nutritional strategies are needed to reduce the negative impact of heat stress in poultry. Approaches to manipulation of nutrition when heat stress, it also needs to be accompanied by proper feeding management. There have been many studies that review and apply nutritional manipulation approaches during heat stress, among others:
- Electrolyte supplementation
Heat stress causes disruption of electrolyte homeostasis in the blood plasma of cattle. In addition, during heat stress conditions electrolytes in the body are also reduced. Electrolyte supplementation is known as thermotolerance agent can be added through feed and drinking water. Supplementation in drinking water can add supplements containing electrolytes such as Vita Stress.
- Vitamin supplementation
During heat stress there is an increase in free radicals in the body resulting in disruption and decreased synthesis of lipids, DNA, and proteins in various tissues (Barutu, 2016). Supplementation of vitamin C and vitamin E can serve as antioxidants, so it can help minimize the negative impact of heat stress. According To Simar et al. (2012), increased concentrations of vitamins C and E are associated with a reduction in oxidative stress. Vitamin C can play an important role in preventing organ cell damage and maintaining homeostasis during heat stress. Vitamin E plays a role in preventing the oxidation of unsaturated lipid materials in cells, thereby protecting the oxidative damage of cell membranes (Yue et al., 2010). High-dose vitamin supplements such as Top Mix HC which contains high levels of vitamin C and E can help supply vitamin needs during heat stress.

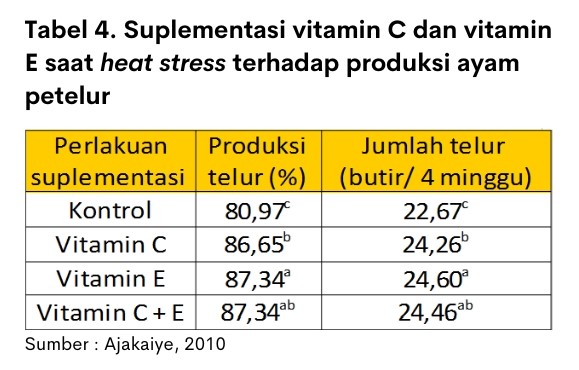
- Suplementasi mikro mineral (Zn, Se, Cr)
Some minerals (trace mineral) acts as an antioxidant that has the ability to capture free radicals during heat stress. Micro minerals such as Zn, Se, and Cr. In addition, mineral microelements play an important role in many metabolic processes in the body, increasing productivity and the immune system in livestock. Mineral micro-supplementation can be added in such feeds Endomix which contains a combination of micro minerals.
In addition, the content of micro-minerals in Endomix also functions in optimizing the quality of eggshells such as the color of pale eggshells. Some micronutrient elements such as Fe, Cu, Mn, and Zn function as chelate carriers in the molecular structure of protoporphyrin IX (Solomon, 1987), so that when the supply of micro-minerals is met the optimal pigmentation process of shellfish.
- Feeding management
It is necessary to take into account the quality of the feed (feed intake) can enter according to the target. Feed consumption will be reduced by 1.2% every 1°C increase at a temperature of 22-32°C and greater 5% every 1°C increase at a temperature of 32-38°C (Ranjan et al., 2019). This is related to the right feeding time to avoid high temperatures, which causes a decrease in feed consumption, due to increased heat production from nutrient digestion metabolism in the body of livestock. When the condition of the chicken is not strong, the components or nutritional content in the feed must be compacted (changed formulation) so that the intake of nutrients to support chicken productivity can be met. If necessary can be applied modification of Administration Management “ " leakage” (addition of water plus vitamins in the feed to spend the morning meal ration), as well as the addition of additional feeding hours (midnight feeding) at night.
- Modified feed formulation
An important aspect in making feed formulations during heat stress conditions is to limit heat increament arising from the feed. Heat increament represents metabolic heat generated from the process of feed metabolism in the body. Use of alternative energy sources of oil or fat (eg crude palm oil (CPO), coconut oil, soybean oil) is highly recommended at the time of heat stress. The use of oil or fat will produce heat increament low compared to other feed ingredients so that it is expected to suppress the effect heat stress from the chicken's body (metabolic products). The addition of sodium bicarbonate can also be added in the formulation of about 0.1-0.5% as a strategy to minimize the time heat stress.
By conducting nutritional approach strategies during heat stress ranging from electrolyte supplementation, vitamin supplementation, micro-mineral supplementation, feed formulation modification and also accompanied by good feeding management to reduce the impact of heat stress at this time. So that livestock performance is maintained optimally. May be useful.










