Bapak Mahmud
Kediri-East Java
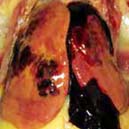
I am a chicken farmer layer. It so happened that my chicken was in the production phase. However, there was a decrease in production and mortality, although mortality was less than 5%. When dissected, there is a large accumulation of fat in the abdominal cavity and it extends to the surface of the liver. The liver is larger than normal in size, yellowish in color and brittle. In addition, there is slight bleeding in the liver. What I want to ask, from the symptoms are estimated to lead to what disease? What factors lead to the appearance of the disease? For the answer I thank you.
Answer:
Based on the symptoms you mentioned, the diagnosis leads Fatty Liver Hemorrhagic Syndrome (FLHS) which is a metabolic disorder in chickens layer and it can lead to death and a sudden drop in production. This disease is mostly found in chickens layer in the battery enclosure.
The syndrome is caused by obesity and fatty liver accompanied by bleeding. Many factors influence the incidence of FLHS in chickens layer, among them :
- Genetics
Differences in sensitivity to FLHS vary between strains chicken. Chicken broiler more susceptible to attack than layer. High egg production rates in chickens layer modern is one of the factors causing the occurrence of FLHS. High egg-laying ability stimulates the occurrence of fatty liver caused by intensive estrogen metabolism.
- Nutrition
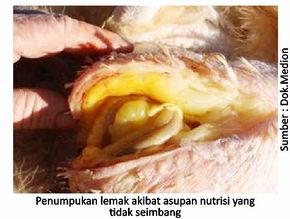
Excess energy consumption in chickens layer will be deposited in the form of fat in the liver as a result of increased gluconeogenesis process. In addition, an unbalanced ratio between protein and energy can also be a predisposing factor for FLHS. Calcium deficiency causes high energy and protein input and stimulates the occurrence of FLHS. Calcium deficiency also causes haemorrhages in liver tissue. This is related to the function of calcium which plays an important role in the blood clotting process. Low consumption of calcium will suppress the hypothalamus, thereby decreasing the secretion of gonadotrophin hormones that cause egg production to decrease. Excessive consumption of feed will be converted into fat that will be deposited on the liver tissue.
- Temperature and enclosure
The high incidence of FLHS in hot climates may be closely related to increased fatty acid synthesis in the liver so that accumulation in the organ also increases.
Poultry layer chickens that are kept in battery cages will have a higher fat content in the liver compared to chickens that are kept with a postal system that uses litter. This is due to the limited movement space of the chicken so that the energy needed to move is low. Likewise layer those kept in dense cages tend to be susceptible to FLHS.
- Stress
Acute stress will increase the secretion of corticosterone and glucocorticoids but will decrease the vitamin C content of the adrenal glands. Corticosteroids will stimulate gluconeogenesis and increase fat formation (lipogenesis). In stressful conditions, body weight will decrease and be accompanied by excessive fat deposition in the liver so that the incidence of FLHS increases clearly.
- Toxin
The presence of aflatoxins, which are toxins produced by Aspergillus flavus will affect the production and performance chicken layer. Occurrence of FLHS in chickens layer may occur by the presence of aflatoxin in the ration at a level of 20 ppb. Toxicity seen in the form of decreased egg production and weight, yellowish liver color, and enlarged liver size.
- Hormones
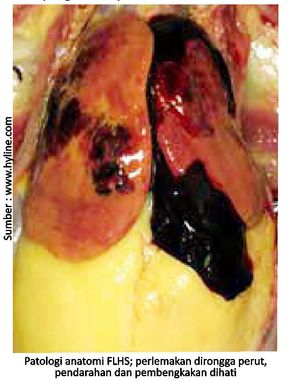
On chicken layer patients suffering from FLHS can be found in the presence of high levels of estradiol in the plasma. This suggests an interaction between hormones and energy, which may support FLHS. Excessive estrogen production can lead to lipogenesis that does not react with the feedback process. Thyroid Status also affects fat deposition in the liver.
The best way to prevent FLHS is to limit the intake of energy that enters the chicken's body or decrease metabolic energy from feed. The type of grain used as feed raw materials can affect the fat content in the liver, although this condition is also influenced by the metabolic energy of the feed. In some cases, the substitution of corn, millet and wheat can overcome FLHS. Addition of fishmeal, flour alfafa, dehydrated dried grains in chicken feed layer it can suppress the deposition of fat in the liver.
Evaluation of cage management also needs to be considered. Avoid battery enclosure density and high temperatures. Providing sufficient space for movement in chickens can suppress the occurrence of FLHS. Chickens affected by the syndrome should be avoided from things that can trigger various stressful conditions. In addition, it can be added to the use of herbal remedies that can prevent liver damage such as Heprofit. Heprofit is an oral solution preparation containing nimba protects liver cells from damage and optimizes chicken performance.