Father Sonny
Email : centriosoft@yahoo.com
My chickens aged 12-14 days many died of colibacillosis. How's it going?
Answer:
Thanks Sony for the question. Colibacillosis (dyspnea, heart and liver covered by fibrin) is a disease caused by bacteria E. Col. Bacteria E. Coli infection is a gram-negative enteric bacterium and is a normal flora in the digestive tract of animals, but can cause disease if the population increases. Colibacillosis (dyspnea, heart and liver covered by fibrin) can be transmitted through contamination of drinking water chickens, litterair, and feces. In addition, Colibacillosis (dyspnea, heart and liver covered by fibrin) it can also be transmitted vertically from mother to Chick.
Aftermath Colibacillosis (dyspnea, heart and liver covered by fibrin) usually chickens die acutely after a short period of symptoms, namely anorexia (unwillingness to eat) and lethargy. The death of chicks can occur up to 3 weeks of age with symptoms of omphalitis, edema (swelling), the tissue around the navel becomes mushy memorable like porridge.
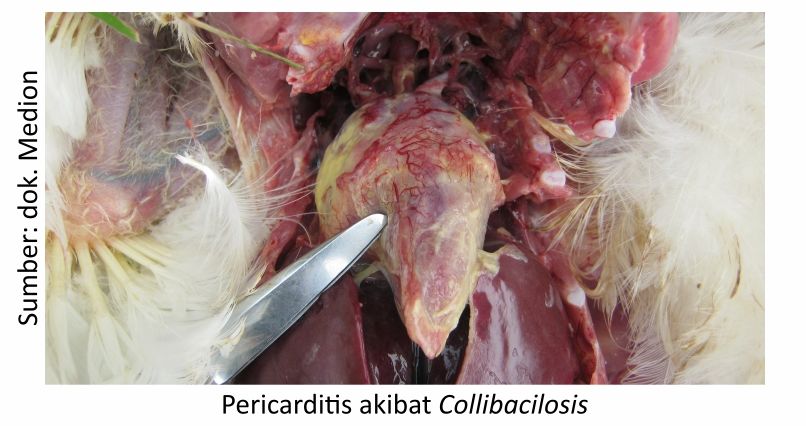
Abnormalities that can be found after surgery the carcass of the affected chicken organs Colibacillosis (dyspnea, heart and liver covered by fibrin) have fibrinous pericarditis (inflammation of the lining of the heart), peritonitis (inflammation of the thin layer of the inner wall of the abdomen), air pockets that thicken and are covered with fibrinous fluid, salphingitis (inflammation of the oviduct), opthalmia (inflammation of the eye), and in chicks found omphalitis enteritis (inflammation of the navel), enteritis (inflammation of the intestine), as well as synovitis (joint inflammation).
Handling that can be done is:
- Culling (selection) chickens with severe conditions such as dull feathers, decreased appetite, impaired growth, green diarrhea and characteristic odor, and dirty and sticky feathers around the rectum. Culling this is done because sick chickens can transmit to other chickens and in severe conditions the cure rate for the disease is relatively small.
- Administration of antibiotics with a spectrum of action for Gram-negative bacteria (proper selection of drugs). This is because bacteria E.bra is a Gram-negative bacterium or to match the type of bacteria. Antiobiotics are used such as Neo Meditril, Proxan-S, Koleridin, Ampicol, Coliquin (choose one) with a dose based on body weight. The amount of medicine given per day to chickens will affect the success of treatment. Less dosage will cause chickens to easily occur resistance (immunity) bacteria. Therefore, it is necessary to carefully calculate the drug (exact dosage). Give antibiotics at least 2 times every 6 hours so that the drug is in the body for at least 12 hours. For example, calculating the drug needs for 1 day as much as 200 grams, then it can be given in the morning (07.00 – 13.00) as much as 100 g and afternoon (13.00 – 19.00) as much as 100 grams. The amount of drinking water used to dissolve the drug is adjusted to the consumption of chicken drinking water. The purpose of this method of administration is so that the dose/amount of the drug can enter the chicken's body appropriately.
- Supportive therapy with the administration of vitamins is also recommended to accelerate the healing process and increase appetite, among other things by administering Fortevit, Kumavit, or Solvit.
- Improve cage management, such as setting chicken density according to body weight and ensuring smooth air circulation.
- Spraying disinfectants using Antisep, Medisep or Neo Antisep every day to reduce the population of bacteria E. Coli infection in a stable environment.
So that similar cases do not occur in the next period, prevention efforts that can be done are :
- Seed selection or culling DOC with not good quality, such as the area around the rectum is wet, the navel has not closed. This is because it can cause bacterial transmission E.Col.
- Management litter so that it does not get wet and damp. Ammotrol can be given in drinking water to control ammonia levels and odor.
- Administration of antibiotics/cleaning program, that is, antibiotics are given before the symptoms of the disease appear. Cleaning programs aims to kill the seeds of the disease, where in fact in the body has been infected with the seeds of the disease but has not shown real clinical symptoms. So to be more secure, you should cleaning program administered 3-4 days before the occurrence of the appearance of clinical symptoms based on previous maintenance cases. In this case, it is given at the age of 9-11 days.
- Treatment on drinking water given to chickens. Treatment what can be done is sterilization using antiseptics. Sterilization/disinfection of drinking water using antiseptics such as Desinsep. Usage dosage Desinsep namely : Desinsep 30 ml per 1000 liters of drinking water. In normal conditions (the farm is no case of colibacillosis), the disinfection program can be done once a week or depending on the needs. Preferably after mixing Desinsep, drinking water is precipitated in advance for 6-8 hours before use to dissolve the drug. But if there is a case of disease on the farm Colibacillosis (dyspnea, heart and liver covered by fibrin) the disinfection program can be carried out in the evening after the treatment has been completed and stop the disinfection program using antiseptics, if it is close to the vaccination schedule.
- Another prevention is sanitationcage with the Antisep, Forms, or Sporades. Litter kept from drying out and dusty, by installing litter not too thick (7-12 cm only).