Gumboro is a disease that often affects young birds. This disease causes high economic losses among farmers. Therefore, Gumboro disease control strategies are needed to minimize both the incidence of disease and losses due to this disease.
A Brief Review Of Gumboro
Gumboro disease that has other names Infectious Bursal Disease (IBD) is a disease that attacks the immune system of chicken organs bursa Fabrisius. This disease is caused by avibirnavirus, an RNA virus with a non-amplified structure. Clinical symptoms of Gumboro disease are trembling, fever, dehydration, dull and standing feathers, and white diarrhea. The following is a list of some of the changes that have been made to the system (striae) in the muscles of the thigh and chest, inflammation of the border of the proventriculus with the ventricle, inflammation of bursa Fabricius, and swollen kidneys.
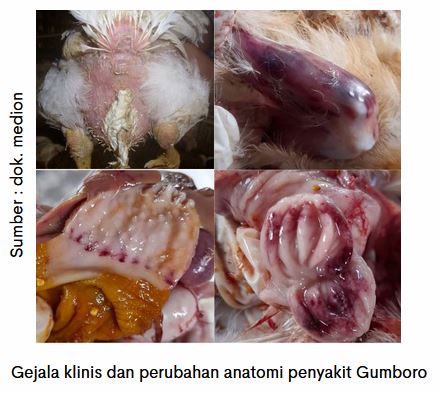
Facts of Gumboro case in the field
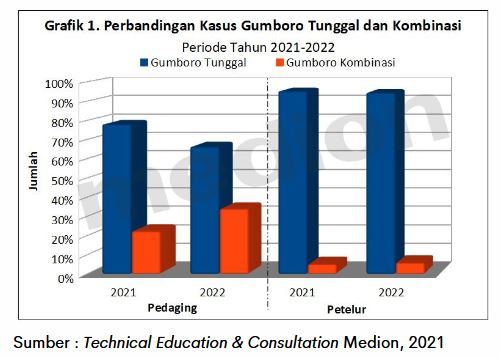
Based on the data collected by the Medion field team in 2021-2022, single Gumboro cases are more often found in the field. However, cases of combination of Gumboro with other diseases such as CRD, Colibacillosis, coccidiosis, ND, etc.can also occur. This is because Gumboro disease is an immunosuppressive disease, meaning that this disease suppresses the immune system so that other diseases are easy to infect.
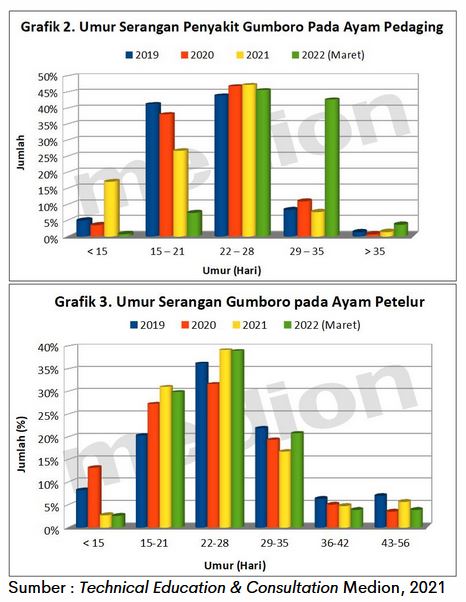
When looking at the comparison of Gumboro attack age data from 2019 to 2022, Gumboro disease in 2022 in broilers most often occurs at the age of 22-28 days and 29-35 days. While in laying hens, the age of the highest attack at the age of 22-28 days followed by the age of 15-21 days and 29-35 days. The time span relates to the development of immune organs that begin to actively work at 3-6 weeks. Current developments bursa Fabricius reaching the optimum, maternal Gumboro antibodies begin to decline so that Gumboro virus is easy to infect. Therefore, it is necessary to increase vigilance, especially at the age prone to such attacks.
Some predisposing factors that need to be considered by farmers when they are often exposed to Gumboro attacks even though they have been vaccinated are :
- Management brooding period, less than optimal
- The presence of immunosuppressant factors such as stressful conditions, coccidiosis disease, etc
- The existence of Franky beetles as vectors for Gumboro virus carriers
- Stool cleaning is not optimal and is placed around the cage
- Less than optimal cage rest time
- Vaccination programs and applications are not appropriate
- Implementation biosecurity the less good
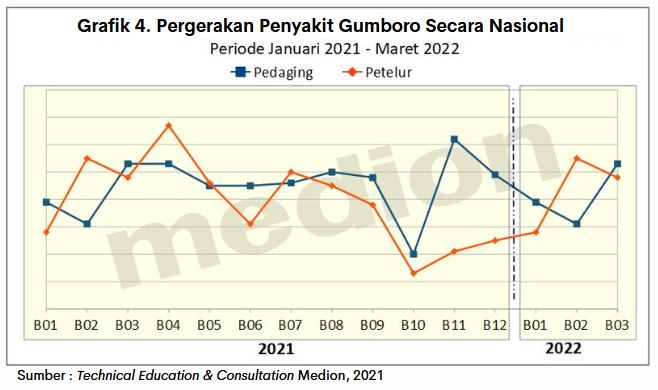
Gumboro disease is one of the poultry diseases that are difficult and difficult to control. When viewed from the movement of Gumboro disease based on data from January 2021 to March 2022, it can be concluded that Gumboro disease is still prevalent in the field with fluctuating movements (graph 4.).
Gumboro Virus found in the field since 2018 until now dominated by very virulent Gumboro (vvIBD), is a group of highly virulent Gumboro virus. This has an effect on higher mortality/mortality in Gumboro cases. In broilers, mortality can reach 20-30%, while in laying hens it is about 30-70%. When compared to the classic Gumboro virus group of virulent strains, vvIBD causes similar clinical symptoms and anatomical changes. However vvIBD causes hemorrhages bursa Fabricius and muscle tissue that is more severe and takes place acutely.
Gumboro Disease Control
The immunosuppressive impact of Gumboro disease encourages farmers to be more vigilant. Preventive measures are the best alternative solution to overcome this disease. Gumboro is a viral disease so the main key to overcoming this disease lies in improving the immune system/immune and minimizing the challenge of the virus in the field. Therefore, the combination of vaccination and biosecurity supported by good maintenance management is the key to success in Gumboro Disease Control.
- Gumboro Vaccination
The accuracy of the type of vaccine used and the accuracy of the vaccination schedule are critical points for successful vaccination.
a. Types of gumboro vaccine
Gumboro vaccine there are several types, including conventional active Gumboro vaccine, complex immune active Gumboro vaccine, vector Gumboro vaccine, and inactivated vaccine.
Conventional active Gumboro vaccine, usually applied to chickens that have entered the cage. Gumboro intermediate plus active vaccines such as Medivac Gumboro A able to penetrate maternal antibodies with an ELISA test titer value of 500. While the active vaccine Gumboro intermediates such as Medivac Gumboro B able to penetrate maternal antibodies with an ELISA test titer value of 125.
The use of this vaccine needs to pay attention to the decrease in maternal antibodies so that the vaccine can work optimally. If the conventional active Gumboro vaccine is given when maternal antibodies are still high, the vaccine virus will be neutralized by maternal antibodies. Therefore, the use of Medivac Gumboro A can be given at least at the age of 7 days, while Medivac Gumboro B can be given a minimum age of 10 days. To be more accurate in seeing the decrease in maternal antibodies and the right time in the first vaccination of Gumboro, it is advisable to test maternal antibodies against Gumboro with the ELISA test method.
Complex immune Gumboro vaccine, usually applied in hatchery or when the chickens are 0-1 days old. Examples of vaccines such as Medivac Gumboplex. The virus is transmitted by a viral infection (coating) by hyperimmune serum, so maternal antibodies are not able to detect the vaccine virus. When it enters the body of chicken vaccine will be trapped in follicular dendritic cell which is in the lymphoid organs (especially the spleen). Slowly hyperimmune serum will be metabolized by the body along with decreased maternal antibodies. When maternal antibodies are low, the vaccine virus will be released and then go to bursa Fabricius to self-propagate and induce antibodies against Gumboro. Usage Medivac Gumbolex it has been shown not to cause lesions in organs bursa Fabicius so it will not affect the organ in its performance of forming antibodies.
Gumboro vaccine is inactivated, usually applied at the beginning of the maintenance period. Inactivated vaccines are an alternative choice because of the longer duration of immunity compared to active vaccines. However, because inactivated vaccines take longer to form protective antibodies, they should still be used in combination with active vaccines. Terdapat vaksin tunggal seperti Medivac Gumboro Emulsion dan vaksin kombinasi seperti Medivac ND T Gumboro Lokal.
b. Gumboro vaccination Program
The preparation of Gumboro vaccination program may vary in each farm. In addition to considering the type of vaccine to be used (if the choice falls on a conventional active vaccine, it is necessary to pay attention to the decrease in maternal antibodies), it is also necessary to consider Gumboro's case history in the previous maintenance period.
Vaksinasi Gumboro aktif konvensional dapat dilakukan minimal 2 minggu sebelum umur serangan penyakit di periode sebelumnya. Jika kasus terjadi pada umur <21 hari atau terdapat kematian >5%, maka bila pilihan vaksin jatuh vaksin aktif konvensional dapat menggunakan vaksin Medivac Gumboro A dengan minimal penggunaan di umur 7 hari. Sedangkan bila kasus terjadi pada umur >21 hari dengan kematian <5%, maka dapat menggunakan vaksin Medivac Gumboro B. For laying and breeding farms with long maintenance life, it can also combine the use of active and inactivated vaccines both as priming or repetition. It can be readjusted to the needs of the farm.
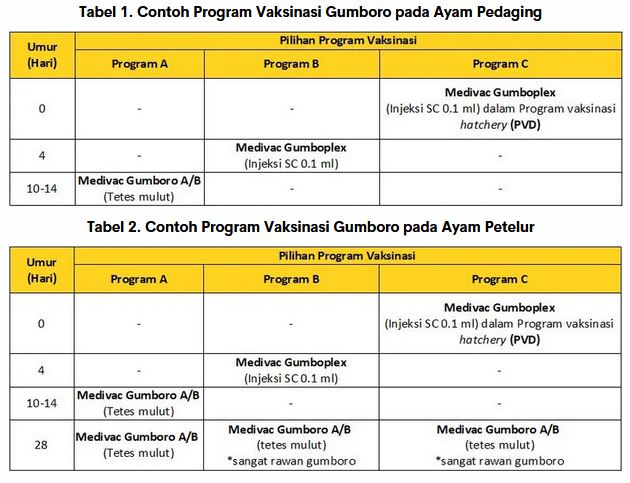
Now it is also no stranger to Gumboro vaccination in hatchery. The advantage is that it is more practical for the breeder and there is no need to consider the decrease in maternal antibodies. However, for laying farms with very high Gumboro challenges, it is necessary to consider repeating the Gumboro vaccine in the cage. Therefore, the Gumboro vaccination program between one farm and another is very diverse and varied. General guidelines for Gumboro vaccination are listed in Tables 1 and 2 (customizable as needed).
2. Tightening Biosecurity
Purpose of application biosecurity that is to minimize the disease agents that are in the cage. Gumboro Virus can survive more than 3 months outside the chicken's body and is still infective. In addition, Gumboro virus has a structure that is not amplified so that not all disinfectants are able to inactivate this virus. Gumboro Virus is relatively resistant to ether, chloroform, trypsin, and organic solvents. However, this virus is very sensitive to formalin-class disinfectants such as Formades and iodine groups such as Antisep, Neo Antisep.
Here are some things related to biosecurity that need to be considered, namely :
a. Implement three zones in the farm, namely the red zone (dirty area), yellow zone (transition area), and green zone (clean area). Aims to limit between areas on the farm, so as to keep the green zone (clean area) so as not to be exposed to disease agents from the red area (dirty area).
b. Control traffic in and out of the enclosure, including in and out of people, equipment, vehicles, and goods. We recommend that all things that will come in and out of a cage must be cleaned and disinfected first. The presence of disinfection such as dip baths or disinfection Chambers is also recommended.
c. Drinking water sanitation example with Desinsep. This is important to minimize disease agents because water can be a source of infection for both bacterial and viral diseases.
d. Clean and disinfect cages and cage equipment such as drinking water, feeders, egg tray etc on a regular basis.
e. Gumboro eradication vector is Franky Beetle. Regular spraying can be done using Delatrin.
f. Control the wild animals and other pets enter into the cage area.
g. Evaluation of the program already carried out with the results obtained. Make improvements if something is found that is not right.

3. Optimization Of Maintenance Management
Management plays a big role in the successful rearing of chickens. Management factors are also one of the predisposing factors for Gumboro disease. Therefore, if Gumboro is still often attacked, it is necessary to evaluate the maintenance management on the farm. Some things related to management that need to be considered in controlling Gumboro are as follows :
a. Optimization of the cage preparation period. Good Cage preparation will eliminate the Gumboro virus. The cage is cleaned of litter and feces. Try litter and used feces are removed from the cage area because they will be a source of disease transmission from the previous period to the next period. After that, sanitize the cage and equipment. The cage and equipment are washed with pressurized water and detergent. Clean also the remnants of the dirt that sticks. After cleaning, disinfection and lime sowing can be carried out. Then the application of empty cage at least 14 days. It is important to break the life cycle of the disease agent. Three days before use, re-spray with disinfectant.

b. Management optimization brooding period,
Brooding bring a very big influence on the performance of chickens and the occurrence of infectious diseases such as Gumboro. Management brooding period, which will favorably affect the development of chicken organs both digestion, immunity, and regulation of thermoregulation. When there is a break in time brooding period,, then the development of the chicken's body in terms of both weight and organ development will not be maximum. So the disease will easily infect and chickens are not able to fight.
c. Cleaning farm equipment (rations, drinking places, etc. on a regular basis. Thoroughly washed and soak for at least 30 minutes in a disinfectant solution once every 4 days. Advance and reverse the disinfection schedule if it coincides with the live vaccination schedule.
d. Creating a comfortable atmosphere for chickens through the arrangement of cage ventilation, density, etc.
Treatment against Gumboro
There is no effective cure for Gumboro disease because the disease is caused by a viral infection. Actions that can be done is to reduce the death rate due to kidney swelling, loss of energy, or because of clinical symptoms that arise due to Gumboro attack. Here are the steps that can be applied (can be adjusted to the conditions of the case), namely :
- Make a selection of sick chickens. Keep sick chickens separate so that they do not become a source of infection. Selection as early as possible can reduce the spread of Gumboro disease. Culling / reject chickens that are no longer viable / severe symptoms. Consider early harvest (for broilers) when the case mendkati harvest age.
- Disinfect the cage daily as long as there are cases. Use a disinfectant from iodine (Antisep, Neo Antisep).
- On day 1-3, can be given 2-5% sugar water to restore lost energy, can also be combined with Paramed S to reduce fever in chickens.
- On the 4th-6th day, Gumbonal can be given as a urinary tract antiseptic to treat swollen kidneys. In the administration of Gumbonal should not be mixed with antibiotics or other chemical drugs.
- In the case of Gumboro accompanied by a bacterial infection, additional antibiotics can be given according to the disease. Should be selected antibiotics that do not aggravate the work of the kidneys such as Tinolin/Neo Meditril/ Proxan S.
- If Gumboro case is accompanied by infection with coccidiosis, can be given additional anticoxidants that are safe for swollen kidneys such as Toltradex/Therapy.
- Administration of multivitamins or immunomodulators such as Fortevit/Vita Stress/Imustim for recovery (multivitamins / immunomodulators can also be given in the first three days along with sugar water/Gingertol and Paramed S).
Hopefully the information that has been submitted becomes a strategy that can be applied in controlling Gumboro early on.










