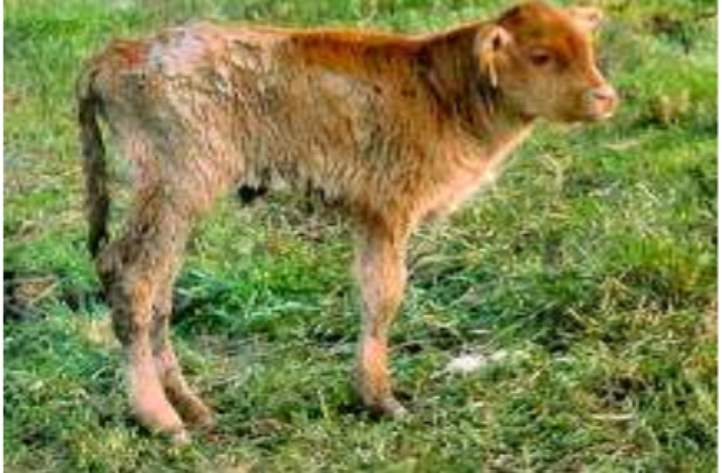
Health problems often cause harm to farmers. For example, digestive disorders, especially diarrhea, often occur in farm animals, both beef cattle, dairy cows, sheep and goats. In Indonesia cases of diarrhea are still often found. Diarrhea is a symptom that indicates a digestive disorder or disease.
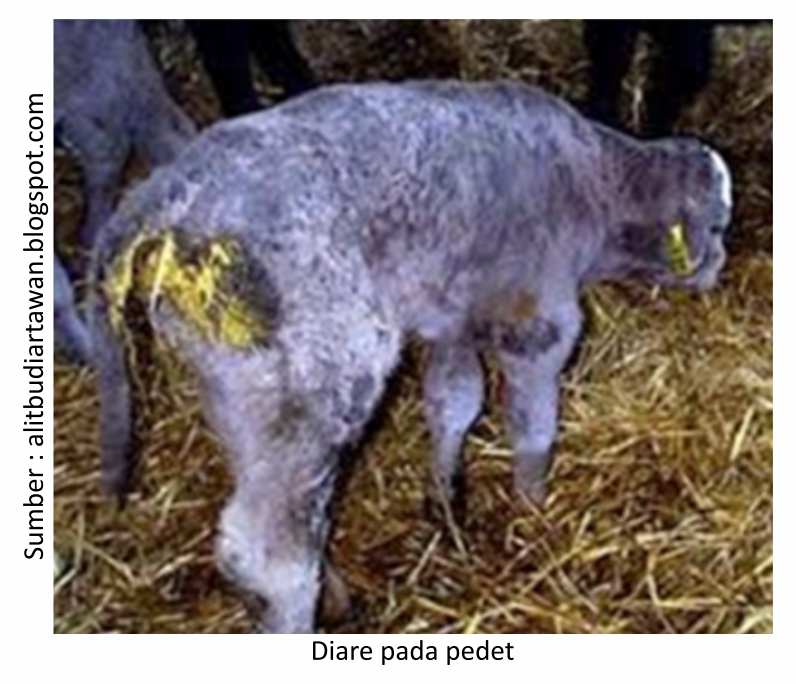

Predisposing factors or supporting factors for diarrhea in livestock include dirty, damp, wet cage floors, cages less exposed to sunlight, crowded livestock populations and accumulated dirt deposits. Diarrhea can be caused by seed infection or infectious or non-infectious diseases. Non-infectious causes such as metabolic disorders due to feed quality, feed turnover, cold air conditions and post-transport conditions. While infectious diseases that cause diarrhea in cattle is the presence of bacterial infections such as colibacillosis, salmonellosis, then viral infections such as Bovine Viral Diarrhea-Mucosal Disease (BVD-MD) or often called malignant diarrhea in cattle and parasitic infections such as worms and coccidiosis.

Livestock with diarrhea will show symptoms such as loose stools, increased stool frequency, abnormal stool color, livestock appear lethargic, and even dehydrated. The occurrence of diarrhea can occur in both adult and young cattle and even newborns. Diarrhea in newborn cattle, especially young cattle, is often caused by colibacillosis due to a bacterial infection E. Coli infection. Colibacillosis (dyspnea, heart and liver covered by fibrin) many are reported to attack young livestock such as calves, pigs, sheep, goats and horses. The Agricultural Research and Development Agency, Ministry of Agriculture revealed that colibacillosis cases in calves in Indonesia were reported to reach 21.91% with a mortality rate of 90.92% (Balitbangtan, 2017). Economic losses can occur because diarrhea can cause growth disorders, high medical costs and death.
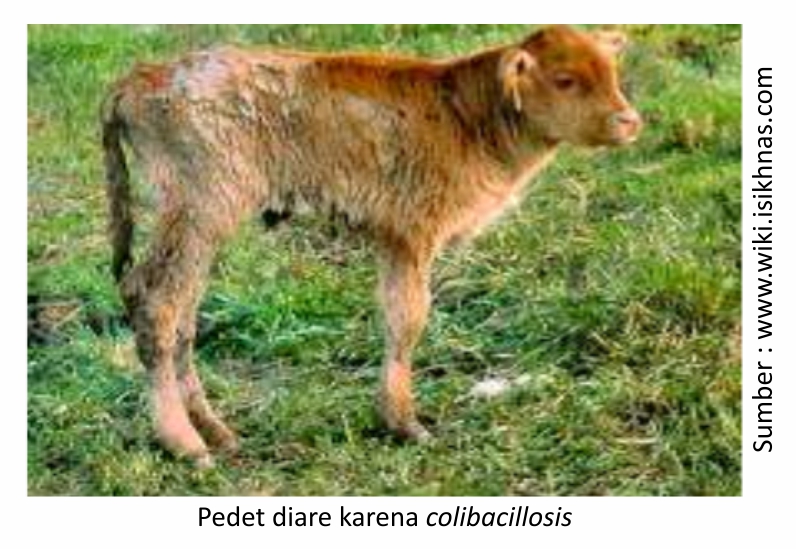
Diarrhea in livestock is a digestive disorder that needs quick treatment because it can cause livestock to get weaker and can even cause death. Livestock with diarrhea can be treated as follows:
- Separating sick cattle from healthy cattle.
- In young newborn cattle immediately give colostrum (milk that comes out first from the mother).
- Provide quality and balanced feed.
- Maintain the cleanliness of the cage and the environment around the cage and avoid dirty and muddy cages and adjust the density of the cage.
- Treatment according to the cause of diarrhea needs to be done. If it is caused by bacteria such as colibacillosis antibiotics such as G-Mox. If the cause is worms, you can be given anthelmintic drugs such as Wormzol-B and if diarrhea due to coccidiosis can be assigned such anticoxidants Toltradex. If it is due to a viral infection, then no treatment can be done causal (for the cause). Symptomatic treatment (treatment of the symptoms of the disease) can be carried out and the administration of broad-spectrum antibiotics directed against secondary infections (infections that follow) for example with G-Mox LA.
- Electrolyte infusions can also be given to prevent dehydration.
To prevent the occurrence of diarrhea some things that can be done include:
- Maintain the cleanliness of the cage environment such as cleaning the feed, drinking place, cage floor on a regular basis. Maintain good Cage air circulation and prevent damp and wet cages. Regular disinfection of the cage is also important to do for example with Medisep or Neo Antisep at least during livestock turnover. The density of the cage also needs to be adjusted so that it is not too full.
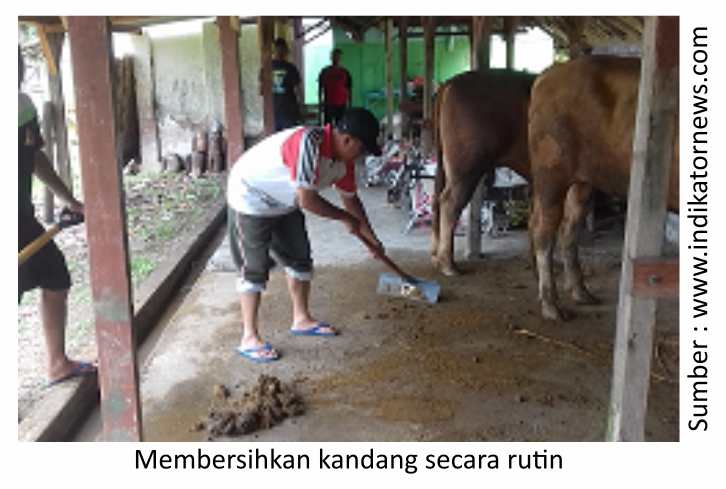

- For newborn cattle immediately give colostrum, feed and drink young cattle regularly cleaned and disinfected every day.
- Provide feed with adequate nutrition and good feeding patterns.
- Regular deworming
- Avoid purchasing livestock from areas affected by the disease, especially diseases salmonellosis, fasciolasis / liver fluke infection and avoid the purchase of young cattle.
- Quarantine for 14 days on newly arrived livestock for health checks and prevent disease transmission.










