CornZea mays) is one of the most important carbohydrate sources in the world besides wheat and rice. Corn is consumed by humans with a variety of processed forms, both in the form of sweet corn, pipil.
Corn is also useful as animal feed, industrial raw materials, compost and other fertilizers. All parts of the corn plant can be utilized, so corn has many uses for various sectors. Corn also occupies an important position in the national economy.

Corn is a plant that has a high adaptability, so it can be grown almost all over the world with different environments. In Indonesia corn can be cultivated in low and high plains. However, for optimal growth more corn is grown in the lowlands. Corn grown in the Highlands has a longer lifespan and relatively less production.
Corn production in Indonesia in 2020 was 25.19 million tons with a Harvested Area of 5.19 million ha. The production has always increased since 2018 (Graph 1). East Java, Central Java and Lampung are the provinces that produce the most corn (Director General of food crops, Ministry of Agriculture).
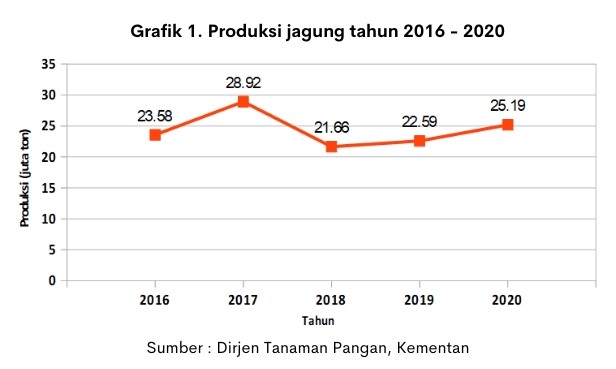
Corn production continues to increase every year, but in 2020 Indonesia still imported 1,242,519 tons of corn. This is because the needs of the Indonesian people are still not met, which are increasing every year.
National Corn productivity in 2020 was 5.57 tons/ha and increased from the previous year. Various ways can be done to increase National Corn productivity. Efforts that can be done, among others, by optimizing the cultivation technology, among others, using superior seed varieties, planting techniques, fertilization, irrigation, pest control (plant pest organisms), as well as handling the harvest and post-harvest.
OPT Corn Crop
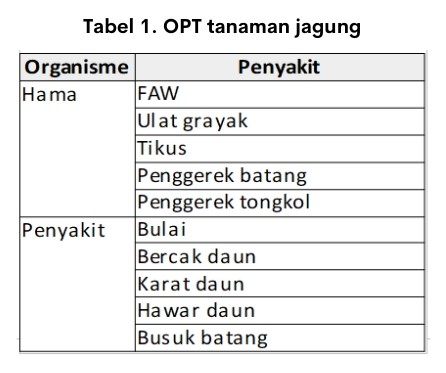
Plant pest organisms (OPT) are one of the factors that can affect corn production. Pest contained in corn plants among other types of pests, diseases and weeds. Pests and diseases affecting corn are presented in Table 1.
Pests that attack corn crops can cause losses if not controlled. Therefore, efforts are needed to provide protection to plants so that there is no loss of crops due to pest attacks.
Hama FAW
Pests will be the most dominant pest in the dry season. One of the challenges that must be faced is FAW (Fall armyworm) or army Caterpillar (Spodoptera frugiperdaJ.E. Smith).
FAW is a pest native to the American continent and attacks more than 80 species of plants, including corn, sorghum, sugar cane, vegetables and cotton. FAW began to spread in Africa in 2016 and continued to spread to Asia until it was found in Indonesia in 2019.

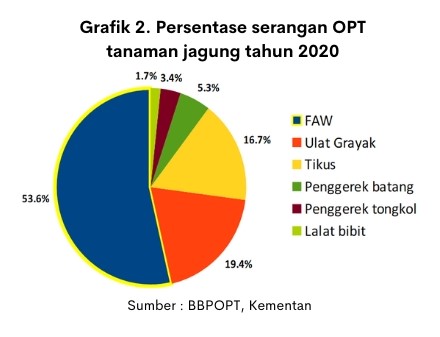
FAW becomes a dangerous pest for corn crops. The ability to breed and spread quickly makes FAW has spread in the territory of Indonesia. FAW became the pest with the highest Attack percentage of 53.6% (graph 2). FAW pest attacks can cause damage to almost all parts of the corn crop so as to reduce production.
FAW life cycle
FAW life cycleSpodoptera frugiperda J.E. Smith) completely metamorphosed, that is, it consists of eggs, 6 instars of larvae/caterpillars and moths.
1. Eggs
Eggs are laid in groups in the amount of 100 – 200 eggs. One moth can lay 1,500-2,000 eggs. Usually eggs are laid on the underside of the leaves. The eggs will hatch after 1-3 days.

2. Caterpillar / Larva
Caterpillar / larval phase for 12-20 days. FAW caterpillars are characterized by a light-colored inverted “Y” shape on the head and four square-shaped black dots on the penultimate segment.

3. Pupa / Cocoon
The Pupa is reddish-brown and oval in shape with a length of 20 to 30 mm. Pupae are usually in the soil to a depth of 2 – 8 cm. The pupal phase lasts 7-21 days.

4. Moth / Imago
The Moth has a wingspan of 3 – 4 cm. The forewings are dark brown while the hindwings are greyish white. The moth begins to lay its eggs at the age of 3 – 4 days and continues to lay eggs until death. Moths live for 2-3 weeks.

Symptoms of FAW damage
FAW can affect all phases of plant growth, from vegetative to generative. Young larvae (instars 1-3) are on the underside of the leaves and feed on the leaves. Young larvae feed only on the epidermal part of the leaves, so the leaves are transparent. When the larvae are getting older (instar 4-6) the leaves that are eaten will have irregular holes.
In addition, the larvae will eat the growth point of the leaves, thus inhibiting the growth of new leaves, eating the stems and corn cobs. Almost all parts of the corn plant are eaten by the FAW. FAW larvae when they grow up are cannibals, so in one plant only 1 – 2 larvae will be found.

Control Way
FAW is difficult to completely remove from the field. FAW pest control should be carried out to suppress the development of pests and reduce the impact of FAW on plants. There are various ways to control pests, including technical, mechanical, biological and chemical culture control (pesticides).
1. Technical Culture
Conducting plant cultivation with certain techniques so as to make the conditions of the planting area less suitable for the development of pests.
- Clear the land and its surroundings of weeds and plant residues beforehand. Pests can live on other host plants.
- Plant in unison to limit pest food sources.
- Soil treatment by turning the soil can kill larvae and pupae that are in the soil.
- Crop rotation
2. Mechanical/Physical
- Collecting clusters of eggs and caterpillars on plants are then destroyed.
- Use light traps to catch moths that will lay eggs.
3. Hayati
Virus SF-NPV (Spodoptera frugiperda – Nuclear polyhedrosis virus) is one of the pathogens that can control FAW. SF-NPV Virus can be obtained from caterpillars that have been infected, then the virus is developed and sprayed back into the field.
4. Chemical (Using Pesticides)
Chemical control with pesticides is the most widely used method. The use of pesticides has advantages, among others, the most effective, efficient, practical, and quickly visible control results. The selection of products used must be appropriate so that the target pests can be controlled effectively.
Emaplus 50 EC is an insecticide with the active ingredient Emamectin benzoate which effectively controls FAW pests. Emaplus has a contact and gastric way of working, so that caterpillars that are exposed to spray or that eat leaves that have been sprayed will die. There are also other insecticides that can control FAW, including Hoowla 5.7 SG and Knocker 360 EC.











