In poultry farming, including free-range chicken / joper, especially breeding, the process of hatching eggs is very important. In nature, chickens have the property of incubating their own eggs. It's just that the success in hatching eggs naturally is not as much when compared with the help of artificial hatching machines because it is considered less efficient, especially in commercial farming.
Getting to know the advantages of hatching machines and Their Types
The hatching machine is a man-made device arranged in such a way as to mimic the nature of a hen to hatch eggs in a large capacity. The use of a hatching machine has several advantages over natural hatching (eggs incubated by the mother), including:
- The success rate of hatching eggs is greater, which is 80-90 % (in nature it reaches only 50-60 %).
- The life expectancy of chicks / ducks hatching with a hatching machine is higher due to temperature changes from the inside of the egg to the outside environment of the egg that is not too extreme.
- DOC produced in large quantities at the same time and the hatching capacity can be multiplied according to the number of eggs ready to be hatched (Nafiul et al., 2014).
- The incubation period in the brood will be lost, so the brood will be more productive and able to produce more eggs during its lifetime.
- Hatching of eggs can be carried out constantly without being distracted by weather changes, since the eggs are placed in a special chamber.
- Control over the quality of eggs is easier to do and avoid contamination with bacteria or other pathogenic seeds.
The hatching machine is divided into three types based on the working system, the capacity to accommodate eggs, and the completeness of the components, here is an explanation:
- Traditional hatching machine

The working system of this machine is still simple with the egg reversal process is still done by hand. In addition, it consists only of a room where the eggs are and a heat source. This machine will be suitable for small-scale production of chicks/ducks (DOC/DOD) or household scale. It usually has a capacity of about 50-200 eggs per unit. The heat source usually comes from simple materials at affordable costs, such as light bulbs, kerosene-fueled petromak or rice husk-fueled furnaces.
2. Semi automatic hatching machine
Semi-automatic hatching machine is a development of traditional hatching machine, where the capacity is larger (about 200-700 eggs). There is even a type of semi-automatic hatching machine with a larger capacity reaching 1,000-1,200 eggs, which is equipped with a temperature and humidity regulator. There is also a more complete semi-automatic hatching machine, namely by using factory-made wire heaters.
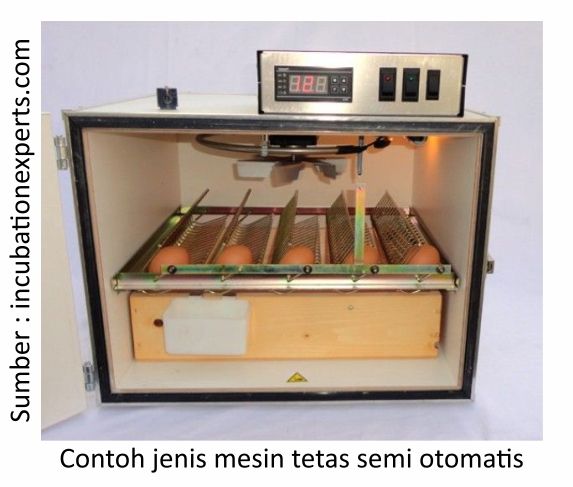

This hatching machine is equipped with a rotary lever outside the machine, so that the reversal of the eggs do not need to open the incubator room because it is enough to turn the lever. This method is relatively more effective and safer than manual hatching machines.
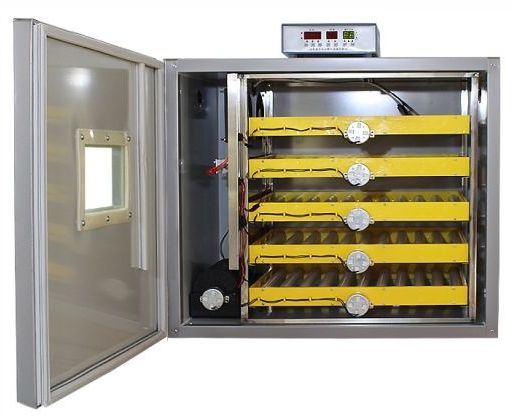
3. Automatic hatching machine
This hatching machine has a working system and component completeness that is more up-to-date compared to the previous two hatching machines, where there is a temperature and humidity regulator that works digitally and automatically. This hatching machine is equipped with a timer and is designed so that the eggs can be rotated automatically based on a preset time. The capacity of automatic hatching machines on the market varies from 100 eggs for household business scale to 1,000-5,000 eggs per unit. With this automatic machine, the hatchability is also getting higher.
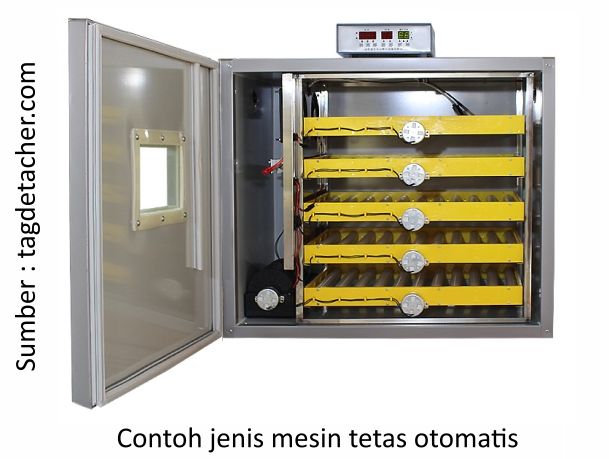

Medion also develops products Mini Incubator with working system full automatic from starting to be turned on to the harvesting process. Its capacity is 100 grains per unit and can be used to process setter (incubation chamber) at once hatcher (hatching room).
Basic Principles Of Using A Hatching Machine
Area hatchery usually consists of egg storage space, egg transport lines, space hatchery and the selection room. Before entering the incubation process, the preliminary activities carried out include: collecting egg, storage of hatching eggs, and preparation of hatching machines. There is a need for special management such as sanitation, disinfection and fumigation of hatching machines to prevent the transmission of pathogenic disease seeds in the hatching machine. Here's the description:
- Storage of eggs before entering the hatching machine
If the eggs are stored for too long, the hatchability will continue to decline. Therefore, in the conditions of the company, eggs are usually hatched 2 or 4 times a week. Thus, the eggs that are inserted into the hatching machine are 3-4 days old. According to some research results, the best egg storage time is around

The egg storage room should not be too hot or too cold. When the temperature of the environment is hot (>27°C) the embryo will develop too quickly, but the development is not normal and most die before or after being in the hatching machine. Conversely, if stored at temperatures that are too cold, the hatchability will decrease.
A good egg storage temperature is about 18.3°C if the eggs are stored for no more than 14 days. When hatching eggs will be stored for more than 14 days, the egg storage is about 10.5°C. Before the eggs are stored, they must be washed and then disinfected or fumigated with a class of quartenary ammonium substances such as Medisep.
Before entering the hatching machine, the hatching eggs need to be heated first (pre-warmed) at a temperature of 24-27°C for 6-8 hours to stimulate the embryo to start its growth and avoid drastic temperature differences from the storage room to the hatchery (Cobb Hatchery Management Guide, 2015).
2. Temperature and humidity of the hatching machine chamber
Temperature and humidity determine the growth rate of the embryo, the successful development of the organs of the body up to the level of hatchability. Moisture also functions to control the fluid in the egg and help break down the egg shell to make it easier for DOC to break the shell. However, if the humidity is high, it can also cause too much water to enter through the pores of the shellfish so that there is a buildup of fluid in the egg. The embryo will develop well at room temperature setter 37.8°C to O 18th and the temperature is lowered by 0.5°C to 37.3°C in Phase hatcher. But the setting temperature of this hatching machine can be set in three stages, namely early (days 1-10), middle (days 10-18), and late (days 19-21) to facilitate the control of embryo death during incubation (Farghly, 2015).
3. Ventilation or air circulation of the hatching machine
The arrangement of air vents inside the hatching machine is made in such a way as to help air exchange. Usually assisted driven by a fan so that the dirty air in the hatching machine immediately changed quickly.
4. Heater stability
The stability of the heating source produced by the hatching machine should resemble the body heat of a hen. The heating source can be from electricity, kerosene, gas or coal. Temperature stability can be assisted by the use of a thermoregulator installed in the machine.
5. Egg screening and selection
The screening process aims to even out the temperature and resist the force of gravity, so that the position of the embryo in the egg remains good and prevents attachment to the membranes. In general, for automatic hatching machines, egg screenings have been done 1 time every hour automatically. It should be noted that the period of the first 1 Week of incubation is a critical period. One of the signs of improper egg screening is the premature death of the embryo. Although there are egg embryos that develop into chicks, they usually fail in cracking the eggshell.
Selection of fertile eggs is done by candling (the egg is highlighted with a lamp then observed) at least after 72 hours the egg is incubated. Fertile eggs show a dark shadow on the yolk with some blood vessels that radiate from the shadow/ larger and darker shadow then the embryo looks more real in it.
6. Long incubation of hatching eggs
The incubation period of different types of poultry differs from each other, depending on the size of the eggs. The larger the size of the egg, the longer the incubation period, here are the details:
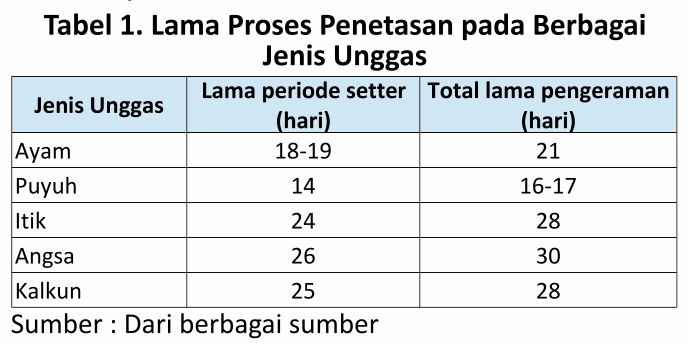
Thus a brief introduction about the hatching machine and its role in supporting the development of poultry farming. May be useful.










