Disease of Foot and Mouth Disease (FMD) or mouth and nail disease (FMD) has spread in various regions of Indonesia. This disease was once endemic in Indonesia in 1887, but was successfully treated and declared free in 1990 by the OIE or World Animal Health Organization.
FMD is a disease caused by a virus, is acute and highly contagious in even-toed or split-hoofed animals. These sensitive animals include cows, buffaloes, sheep, goats and pigs. PCOS is caused by a virus genus Aphtovirus.The transmission rate reaches 90-100%. While the mortality rate is 1-5% in old animals and can be more than 20% in young animals.
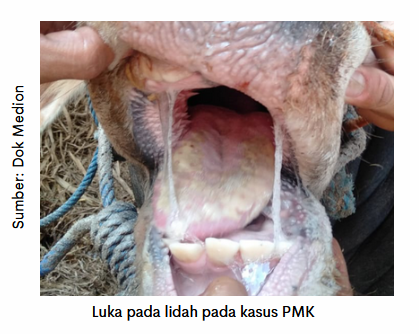
Transmission can occur through direct contact of infected livestock to susceptible livestock, indirect contact through contaminated equipment or humans and spread through the air. Visible symptoms of this disease are fever, decreased appetite, excessive salivation (hypersalivation), blisters on the mouth area (tongue, gums, palate) and nails. Animals may show symptoms of lameness, lying or collapsing, injuries to the nipples, decreased milk production up to death.
Losses due to PMK
FMD is included in the strategic infectious animal diseases (PHMS) because it has a high morbidity rate, causing economic losses and causing community unrest. However, FMD is not zoonotic or contagious to humans. While the impact of economic losses due to FMD is a decrease in livestock productivity such as body weight and milk production, health problems such as fertility disorders, miscarriage, early rejection, and even death. In the case of FMD also requires no small cost for treatment, prevention and control. Of course, with such a big impact, it will cause unrest in the community.

The impact of FMD on a wider scale is the restriction of trade between regions and the loss of export opportunities. Some examples are the presence of closed animal markets and traffic restrictions. This restriction is done to prevent FMD from expanding to other areas that are still free. Until now, the spread of FMD has been found in 19 provinces and there is still a chance of spreading to other areas if prevention is not done properly.
Handling of PMK cases
Animals affected by FMD need to be treated as early as possible from the first clinical symptoms are seen in order to avoid secondary infection and increase the chances of recovery. Here are some case handling actions that need to be done by PMK :
- Isolate or separate sick cattle in separate quarantine pens from healthy animal cages
- Immediately report to the local animal husbandry and health office
- In addition, the use of a variety of dietary supplements such as multivitamins and dietary supplements (Injection Of Vit. B Complex or Bioselvita). The treatment of fever, pain, and inflammation (Medipiron Injection). Antibiotics may be prescribed (Neo Meditril 10-LA or Tysinol).

- Apply antiseptic to wounds in the mouth and nails to speed healing (Antisep or Neo Antisep)
- Do foot dip or dip the feet of animals containing a mixture of water and a 5% solution of cupri sulfate routinely.
- Disinfection of drinking water and cages containing livestock by using Desinsep. Use Desinsep with a dose of 180 ml/ liter of water to spray the cage.
- Carry out decontamination and disinfection of empty cages and vehicles with Sporades at a dose of 100-200 ml dissolved in 20 liters of water or Formades at a dose of 500-1000 ml dissolved into 25 liters of water.
- Destroy contaminated materials (carcasses, feed, waste) by burial or incineration.
- Uninfected animals should be placed in dry locations and given adequate and nutritious feed to boost the immune system.
Preventive Measures
Here are some steps you can take to prevent the spread of PMK :
- Quarantine and monitor traffic. Quarantine is carried out for infected villages or farms and farms that have been in contact. In addition, cattle that have just come to the farm need to be separated from other livestock. The livestock is separated in quarantine cages for 14 days and intensive observation of the symptoms of the disease is carried out.
- Improve biosecurity on farms by conducting regular sanitation and disinfection. Disinfection is carried out on cages, equipment, vehicles and clothing of cage workers.
- Limit the traffic of goods and unauthorized persons in the cage.
- Increase the body's ability to absorb nutrients (ADE-Plex injection/Vita B-Plex Bolus Extra Flavor).
- Vaccinate healthy animals using vaccine isolates homologous to the field virus.
The re-outbreak of FMD has had a huge impact on the livestock sector. So that treatment and Prevention play an important role to be free again from this disease. May be useful.










