Red onionAllium cepa var. Aggregatum) is one of the vegetable commodities that are widely cultivated and have high economic value. Shallots are spices or flavoring dishes that are used daily and tend to be always needed. Another benefit of onions is as a traditional medicine.
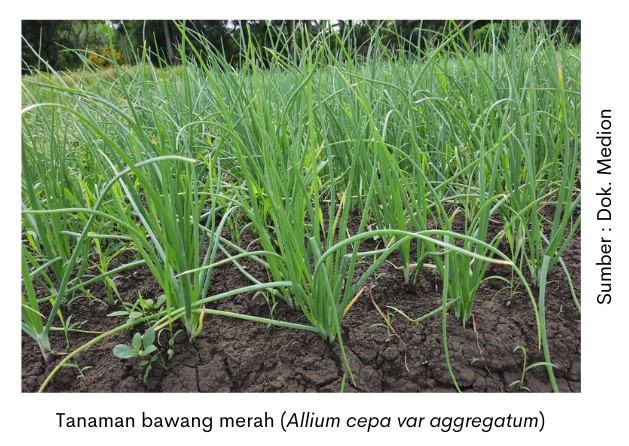

Shallots in Indonesia can be grown in the lowlands to high. However, for optimal growth, planting is carried out in Lowlands (0-450 MASL) with an air temperature of 25-32°C. Onions grown at high altitudes have a longer lifespan of 0.5 -1 months and less production. Onion plants need maximum sun exposure for good yields.
According to the Central Statistics Agency (BPS), onion production in Indonesia in 2021 amounted to 2 million tons with a Harvested Area of 191,201 ha. The production increased by 10.42% compared to the previous year. The largest onion production comes from the provinces of Central Java, East Java and NTB.
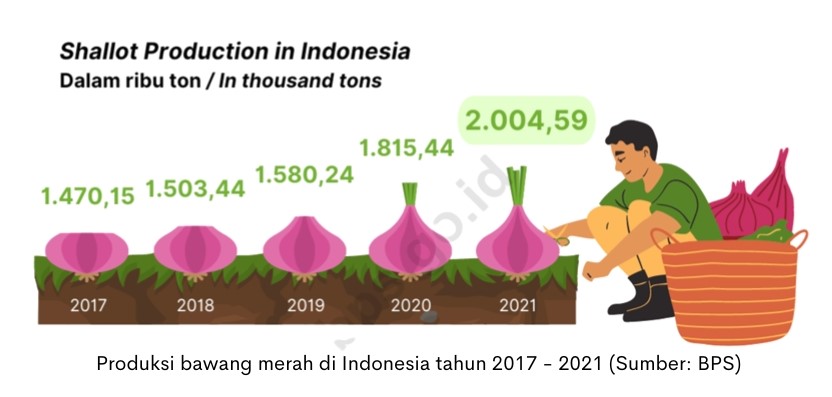
Along with the increasing human population, the demand for Shallots is expected to increase, so efforts are needed to increase production. There are various ways that can be used, among others, with the addition of Harvested Area, the use of superior seeds, cultivation techniques and others.
However, in the cultivation of shallots, of course, there are many challenges that must be faced by farmers, including uncertain climate, expensive fertilizer prices, agricultural land conversion, decreased quality of agricultural land and plant pest organisms (pests) such as pests and diseases.
OPT shallots
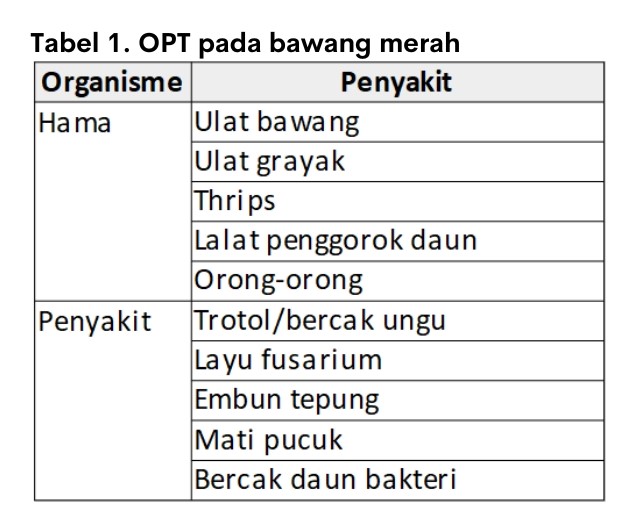
Plant Pest organisms (pest) on onion plants are very diverse from both pests and diseases. Pests that attack onion plants can be seen in the following table.
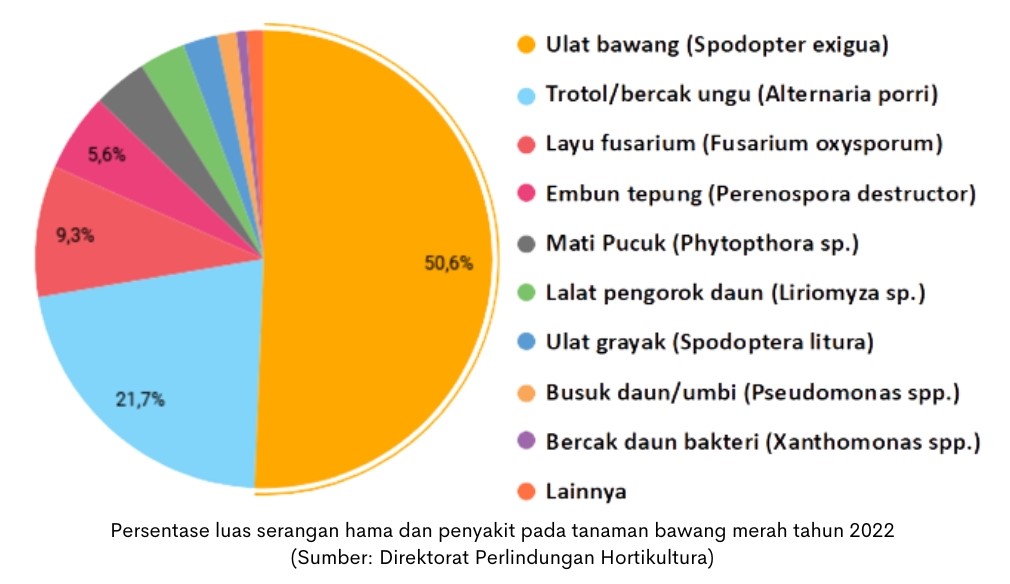
Pests that attack onion plants can cause losses when not controlled. Therefore, efforts are needed to provide protection to plants so that there is no loss of crops due to pest attacks. One of the pests on shallots is the onion Caterpillar pest which has the highest percentage of attack area of 50.6%.
Garlic Caterpillar Pest
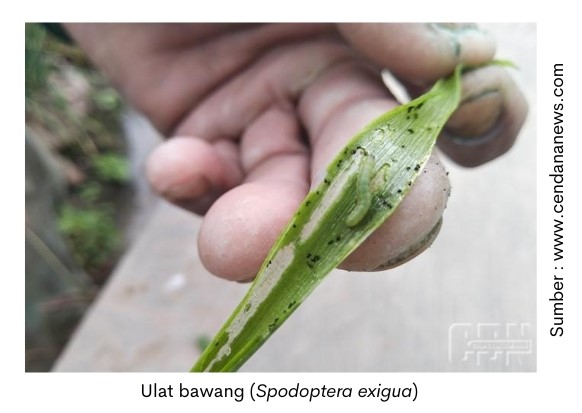
Garlic reportSpodoptera exigua) is one of the important pests due to its high infestation and great losses. Onion caterpillars can attack in the rainy and dry seasons, but high attacks occur in the dry season.
Onion caterpillars can damage plants from the vegetative to generative phase. And the attack of caterpillars is active at night. Attacks can lead to reduced onion production or to crop failure. The high population and the resulting level of damage make the onion Caterpillar pest the most feared pest by onion farmers.

Life Cycle Of Onion Caterpillars
Garlic reportSpodoptera exigua) has a silus life of 21-28 days. The life cycle of the onion Caterpillar consists of four phases, namely egg, caterpillar, pupa, moth. The following is the life cycle of the onion Caterpillar:
Eggs
Egg phase of onion caterpillars for 2-4 days. Onion Caterpillar eggs are laid in groups on leeks. One batch of eggs contains ③80 eggs. One moth can lay 500-600 eggs.

Caterpillar / Larva
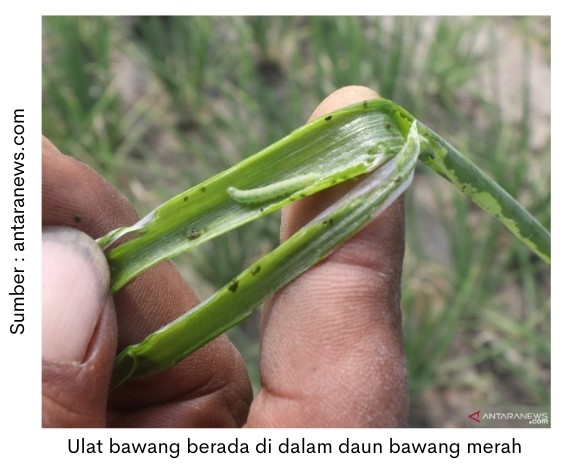
Caterpillar phase for 8-14 days. After hatching the caterpillars will enter the cavity of the leek by making a hole. Caterpillars have a size of 0.1-2.5 cm and are green when young to brownish green when old. The caterpillar phase is the phase that damages the plant.

Pupa/Cocoon
The pupal phase of the onion Caterpillar for 6-7 days. The pupa of the onion Caterpillar is brown with a size of 9-11 mm. The Pupa is usually in the ground (within 1 cm) or on the stem base sheltered under dry leaves.
Moth / Imago
Moth is the stage of an adult insect. The moth begins to lay eggs at the age of 2 – 10 days. The onion Caterpillar moth has a dark brown color of the front wings and whitish rear wings with black stripes on the edges. Moths have a wing span size of 2.5-3 cm.

Symptoms Of Onion Caterpillar Infestation
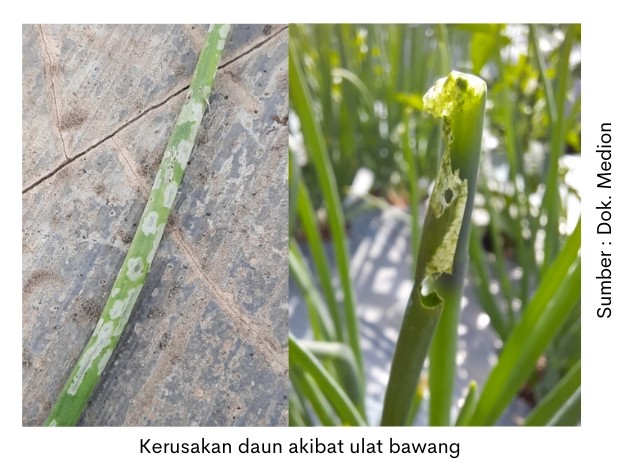
Onion caterpillars attack the leaves of onion plants that are young and old. Newly hatched caterpillars enter the leek by making holes. Caterpillars gnaw or eat the inner surface of the leaf and will only leave the epidermis (outer part of the Leaf) only. Leeks there are white patches that look dreamy translucent (source: R & D Agriculture). The higher the attack rate will make the leaves hollow and broken.

Control Way
Onion Caterpillar pest control must be done to suppress the development of pests and not the reduction of production. There are various ways to control pests, including technical, mechanical, biological, and chemical culture control (pesticides).
1. Technical Culture
Conducting plant cultivation with certain techniques so as to make the conditions of the planting area less suitable for the development of pests.
- Clear the land and its surroundings of weeds and plant residues beforehand. Pests can live on other host plants.
- Plant in unison to limit the food source of the onion Caterpillar pest.
- Intensive tillage by turning the soil can kill larvae and pupae in the soil.
- Crop rotation with non-onion crops to break the life cycle of pests.
2. Mechanical/Physical
Control by taking pests and using physical factors that can affect pests.
- Collecting clusters of eggs and caterpillars on onion plants are then destroyed.
- Use light traps to catch moths that will lay eggs.
3. Hayati
Utilization of biological agents or organisms that can act as pathogens of onion caterpillars. Virus Se-NPV (Spodoptera exigua – Nuclear polyhedrosis virus) is one of the pathogens that can control onion caterpillars. Se-NPV Virus can be obtained from caterpillars that have been infected, then the virus is developed and sprayed back into the field.
4. Chemical / Pesticide
Chemical or pesticide control is the most widely used method. The use of pesticides has advantages, among others, the most effective, efficient, practical, and quickly visible control results. However, the use of pesticides needs to be done appropriately. The selection of products used must be appropriate so that the target pests can be controlled effectively.
Emaplus 50 EC is an insecticide with the active ingredient Emamectin benzoate 50 g / l which is effective for controlling onion caterpillar pests (Spodoptera exigua). Emaplus 50 EC has a contact and Hull mode of action. Caterpillars affected by the spray or caterpillars that eat the leaves that have been sprayed will die. There are also other insecticides that can control onion caterpillar pests, including Hoowla 5.7 SG and Knocker 360 EC.











