Water is very essential for living things including chickens. Water plays a role in maintaining physiological functions to keep them running well. These physiological functions include digestion and absorption of nutrients which also play a role in supporting enzyme function and nutrient transport, for thermoregulation, lubricating joints and organs, dispensing metabolic waste and being the main component in blood and tissue.
About 70-85% of the chicken's body weight is water (Aviagen, 2025). Water consumption in chickens is twice that feed intake or even more at high ambient temperature conditions. When the water iswater intake) decreases it will be very significant impact on chickens. Total water intake must be balanced with the amount of water released (water loss) so that dehydration does not occur. 20-30% of the water consumed by chickens will come out with feces and urine. Water is also used in the evaporation process in chickens. Normally 12% of water is lost due to the evaporation process and can increase up to 50% when the temperature increases.
Good water quality standards
Not only the volume or quantity of water consumption, the quality of drinking water on chicken farms also has an important role in the performance, productivity and health of chickens. Poor water quality can trigger the occurrence of both infectious and non-infectious diseases in chickens (Umar et al., 2014). To understand the good water quality can observe Table 1 the following are related to good water quality standards for chicken farms. Water quality parameters are grouped into three; physical, chemical and biological.
How is the water quality in Indonesia?
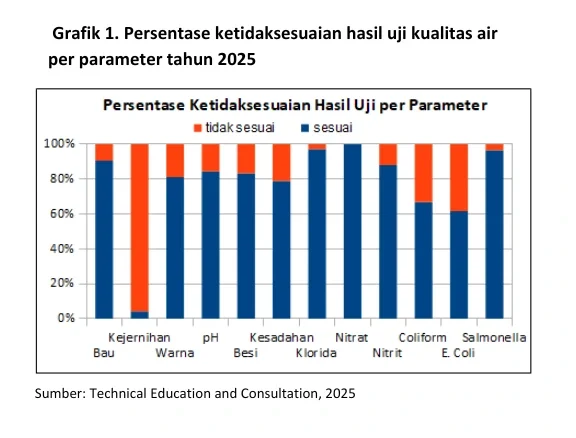
Based on the data of water quality testing in Medion Laboratory in 2025 (Graphic 1), still encountered water quality in chicken farms that do not comply with the standards. The water quality Parameter with the highest percentage of incompatibility of the four in order is clarity, E. Coli infection, coliform and hardness. This shows that not only physical quality, chemical and biological quality is also still found that does not match the standard.
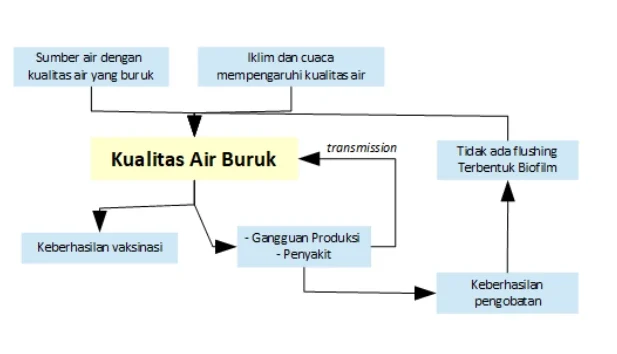
Poor water quality is influenced by various factors including coming from water sources with poor quality. Livestock water sources generally come from drilled wells. To ensure that the borehole gets good water quality, it is necessary to pay attention to its location, which is far from sources of pollution such as faecal dumps, and with a depth of 30-50m depending on the location of the farm. Bacterial contamination of boreholes will be reduced at depths >30m (Susantho, 2022).
Most of the organic contaminants in groundwater come from anthropogenic activities (Raza et al., 2017). These organic contaminants are closely related to contamination of human, animal and other sources. This contamination occurs when manure produced by livestock is exposed to surface runoff during rain and enters groundwater. Therefore, the level of water pollution increases during the rainy season.
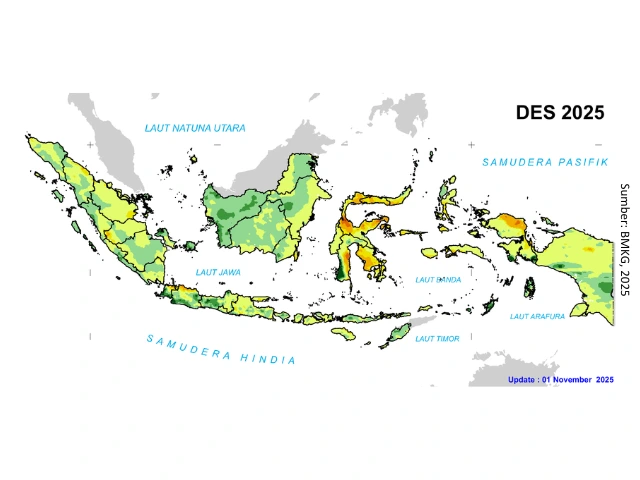
Indonesia has two seasons, dry and rainy. Rain forecast BMKGFigure 2) at the end of this year shows most of Indonesia is predicted to experience high rainfall. This can be a reminder to increase vigilance regarding maintenance management in the rainy season.
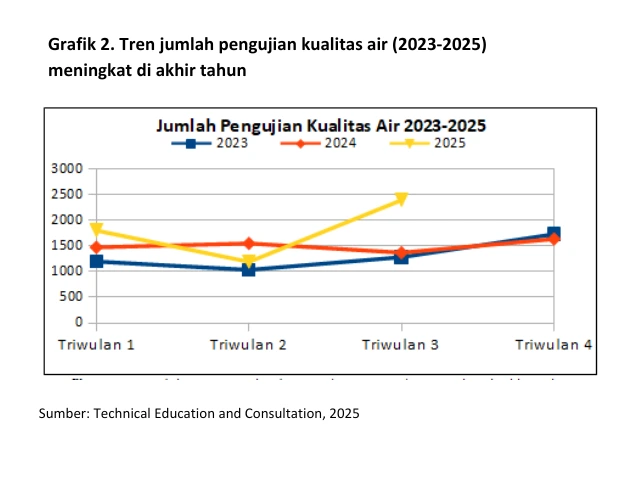
Increased vigilance of farmers in the rainy season is also shown in the vigilance of declining water quality. This is evidenced by the trend in the number of water quality testing increases at the end of the year for the last three years (Graphic 2). Water quality tests are recommended to be carried out at the beginning of opening a new well, at the change of season or during the rainy season and at the beginning of the maintenance period. When there are health problems and the performance of chickens in the cage can also be considered to conduct water quality tests.
Impact of poor water quality
1. Vaccination success
It is not uncommon for vaccines to be given to provide immunity and disease protection from the inside. Some active vaccines are applied mixed with drinking water so that the quality of drinking water also plays a role in the success of vaccination. In water quality parameters that show high pH (alkaline), high hardness, high chloride (Cl) levels, high iron levels or high nitrate levels can affect the effectiveness of the active vaccine. The pH standard of good drinking water ranges from 6.5-8.5. Drinking water with a low pH (acid) can cause perlukaan in the gastrointestinal tract of chickens and corrosion in the waterways. While in water with a high pH (alkaline) can be a factor supporting the development of microorganisms that will indirectly increase the risk of disease transmission. When the pH of the water is not suitable range this will have an impact on reducing the effectiveness of vaccines and disinfectants, chlorine efficacy, water intake, and a decrease in mineral absorption and impact also on the quality of shellfish (Farooq et al., 2025).
2. Production interruption
Decline water intake can be caused due to a mismatch in physical parameters, an alkaline pH, high levels of drinking water hardness or high iron levels. Decrease in water intake will cause dehydration chicken and impact on the decline feed intake. When total dissolved solids (TDS) which is the total amount of all minerals, salts, metals and organic substances contained in water >3000ppm can increase mortality (Cobb, 2021). On chicken layer, poor water quality also plays a role in the quality of shellfish including the formation and coloring of shellfish. This is related to water being a nutrient which contains minerals such as calcium, magnesium and iron.
3. Predisposition to a disease
Many viral, bacterial and parasitic diseases are transmitted through drinking water. Colibacillosis, salmonellosis and cholera are three bacterial diseases that can be transmitted through drinking water. In viral diseases, nd, IB and AI diseases can be transmitted through drinking water. In addition, protozoan parasites Eimeria causes of coccidiosis and Histomonas causes of Histomoniasis can also be transmitted in contaminated water (do Amaral, 2004).
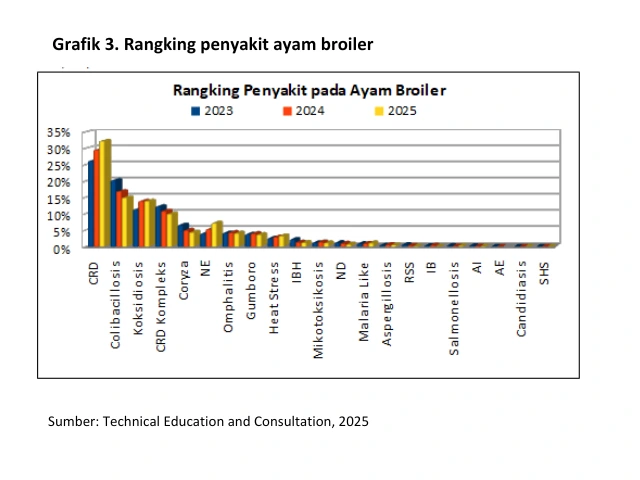
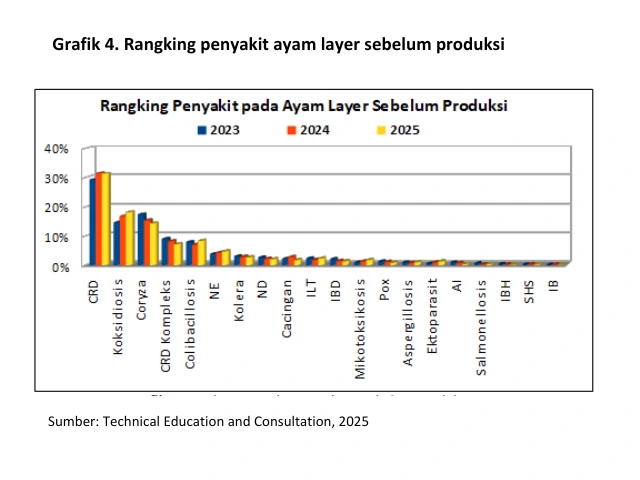
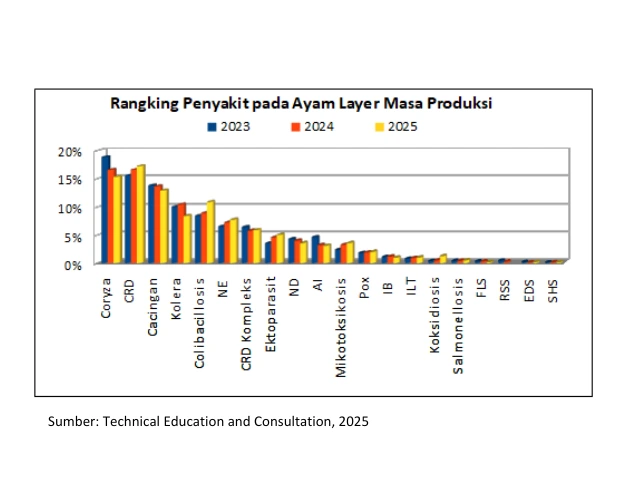
A disease that is very closely related to drinking water is colibacillosis. In the ranking of broiler diseases for the last three years colibacillosis was ranked 3rd (Graphics 3in the 5th grade (Graphics 4 and Graphics 5).
Infection E.bra can be encountered with various forms including omphalitis, cellulitis, salpingitis, peritonitis, colisepticemia and coligranuloma. Horizontal transmission of colibacillosis can occur when ventilation and air circulation management is poor; contamination of feed, water and eggs; the presence of other diseases (secondary infection); or can occur due to high density (Khairullah et al., 2024). Poor ventilation management will trigger inflammation to lesions in the respiratory organs which will later become a gap for bacteria E. Coli infection it's in. Furthermore, drinking water plays a major role in the spread of colibacillosis in cages when drinking water is contaminated with bacteria E. Coli infection. Water with good quality is shown with a result of 0 on biological parameters E.bra and Salmonella.
4. Treatment success
Treatment of bacterial infections such as colibacillosis is given antibiotics either via injection or via drinking water. Some classes of antibiotics are sensitive to the quality of drinking water. Such as tetracycline and fluoroquinolone groups when mixed with water that has high calcium or magnesium levels (high hardness) will form water-insoluble compounds.
Water hardness is influenced by the geographical location of a region. Water with high hardness is generally found in areas that have a lot of limestone. The water that crosses the limestone rock will dissolve and carry calcium and magnesium elements which then cause high levels in drinking water. In addition to hardness, high iron levels, too acidic or alkaline pH can also reduce the effectiveness of antibiotics in general. The pH of the water and the pH of the water can affect the working of disinfectants quats (Medisep and Zaldes) and iodine (Antisep and Neo Antisep).
Biofilm threat after treatment via drinking water
After administration of drugs and vitamins via drinking water should be considered related flushing in the water channel. Flushing carried out after each administration of drugs or vitamins. This is to minimize the occurrence biofilm. Biofilm it is an accumulation of microorganisms that adhere to wet or closed surfaces (such as drinking places, water basins, water pipes) and form a thin, slimy film containing proteins and polysaccharides. In addition, it can be triggered by the absence of flushing after administration of drugs and vitamins, the formation of biofilm it can also be triggered by pipes exposed to continuous solar heat as well as high nitrite content in water. High nitrites are closely related to organic contamination in water.
A layer of mucus on water pipes appears normally due to the growth of algae and other microbes including E.Col. Forming process biofilm starting from bacteria carried in water attached to the pipe wall. The bacteria are then attached to the pipe and assemble to form biofilm. Biofilm those that are already large will break and spread more bacteria again.
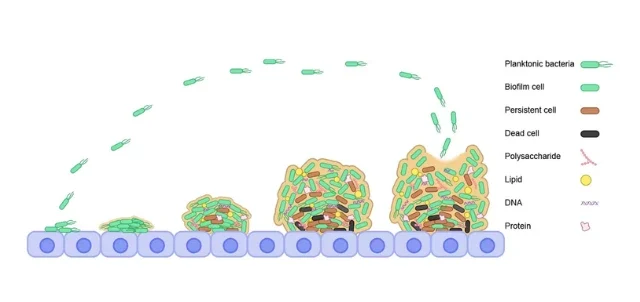
If not addressed immediately, biofilm this can lead to blockages in nipple drinker or water pipes, hiding places for pathogenic microbes from disinfectants (because they are relatively difficult to penetrate by disinfectants) and can reduce the effectiveness of drugs, vaccinations and vitamins given via drinking water.
Addressing Drinking Water Quality Issues
Water quality problems that have not been up to standard affect various aspects of chicken farming. Not only does it affect the performance and health of chickens but also affects a series of operations on the farm including the implementation of routine disinfection. The use of water treatment plant (WTP) helps to treat raw water to be drinkable for chickens. WTP is able to maintain drinking water quality according to standards and minimize the risk of contamination in drinking water. In addition, it can do the following things to control and overcome the quality of drinking water in chicken farms.
a. Water quality test
One of the efforts in the prevention and treatment of poor water quality problems is to conduct water quality tests. By conducting water quality tests we can find out which parameters in drinking water in chicken farms are not suitable. Water quality test samples can be taken from water sources, reservoirs or toren and from nipple or guttering. Thus can be observed and evaluated the mismatch of drinking water quality in the farm is located at the point where the next handling.
b. Handling water quality problems of each parameter
If the physical parameters are not appropriate from the level of clarity, color and Odor then it can be overcome by filtration or filtration. Another method that can be done is to give alum at a dose of 2.5 grams per 20 liters of water in a drinking water reservoir.
When a chemical parameter mismatch is found in the water quality test results, the handling will adjust to which parameters are not appropriate. As in unsuitable water pH parameters either lower (acidic) or higher (alkaline) than the standard range can be given Netrabil to neutralize the pH. Netrabil administered at a dose of 5 grams per liter of water. Netrabil can be given also when the level of hardness found in high water. Whereas if the water quality test results show iron levels higher than the standard can be given Medimilk. Medimilk serves as a stabilizer of drinking water from the presence of heavy metals (including Fe) in drinking water. Medimilk is given at a dose of 10grams per 5 liters of water then let stand for 30 minutes.
In addition to the above-mentioned factors, there is also a lack of evidence for the existence of a significant risk factor for cardiovascular disease (Coliform, E.bra and Salmonella) on drinking water. Handling that can be done on the condition of drinking water is to perform disinfection. Disinfection of drinking water can use Desinsep at a dose of 30ml per 1000L of water. Before use to dissolve drugs and vitamins, drinking water mixed with Desinsep needs to be settled for 6-8 hours. Then after completing the administration of both drugs, vitamins and vaccines via drinking water, do flushing on drinking water channels to prevent the formation of biofilm. No less important source of microbial contamination that causes discrepancies in biological parameters must also be addressed .
c. Eradicating biofilm
In an effort to eradicate biofilm can be started by minimizing the factors that trigger the growth and development biofilm. Immediately flushing when finished administering drugs, vitamins and vaccines via drinking water. Flushing is carried out with high pressure water (1.5-3 bar).
Biofilm also can be prevented by the use of ultrasonic waves with the installation of the device Harsonic. Harsonic it will emit ultrasonic waves that will break down biofilms in pipes and drains and prevent biofilms from growing back.
Other methods that can be used to decompose biofilm is to do flushing combined with chemicals. The active substances that can be used are hydrogen peroxide or citric acid. Hydrogen peroxide (H₂O₂) works by damaging the structure of microorganisms inside biofilm and destroys its protective matrix through oxidation. H₂O₂ releases oxygen then attacks the cell wall, membrane and DNA of the microorganism and causes death in the forming microorganism biofilm the.

Bioflush it is a broad-spectrum disinfectant and is effective in fighting various microorganisms such as bacteria, viruses, fungi and spores. Bioflush has 2.22 x higher effectiveness than phenol coefficient. Although Bioflush effective in eradicating biofilm, Bioflush safe to use on the contents of the cage and has a low level of irritation to livestock and human skin and safe on Cage equipment made of metal/iron. Bioflush does not affect the smell, taste, and color of drinking water.
Dosage Bioflush adjusting eradication goals biofilm on the contents of the cage or empty cage and the severity of the biofilm itself. Following dosage Bioflush:
- Lightweight (fill cage) can use a dose of 10ml/100L of water and can be increased to 20ml / 100L of drinking water
- Severe (empty cage) using a dose of 1-3L dissolved every 100L of water and left for 12-24 hours then rinse with clean water.
Poor water quality can come from poor water sources and/or water management systems. This poor water quality will affect the success of vaccination, trigger production disruptions and diseases, become a medium for the spread of diseases and affect the work of drugs and disinfectants. While the administration of the drug without flushing after it can provoke the formation of biofilm which will worsen the quality of drinking water. The handling of water quality needs to be comprehensively evaluated and improved from upstream to its operational management in the enclosure.










