Will we accept AI's presence again in our cage? Of course not, that's a definite answer. There will be no farmer who wants his chickens to be attacked by AI again. Already imagined in the corner of the eye the losses that must be borne by farmers, ranging from the death of chickens, decreased egg production, and the emergence of secondary infections.
Avian Influenza or what we are more familiar with Bird Flu lately began to visit frequently along with the transition into the rainy season. But what we need to explore more deeply is the pattern of appearance of clinical symptoms and anatomical pathology AI has recently undergone some changes.
This certainly requires us to be more sensitive and thorough regarding diagnosis and handling in the field considering the losses caused by AI are still quite large.
How Avian Influenza (AI) at the moment?
Avian Influenza is a disease that affects the respiratory, reproductive, digestive and nervous tracts in some types of poultry. The disease is caused by a virus that belongs to the family Orthomyxoviridae. AI Virus is divided into several subtypes based on the antigenic ability of two surface proteins, namely Hemagglutinin (HA) and Neuraminidase (NA).
As of 2012, 16 subtypes of HA (H1-H15) and 9 subtypes of NA (N1-N9) have been identified in poultry. The HA Protein is an important part of the virus to attach to the chicken's body, while the NA protein is related to the ability of the virus to release virions (the result of multiplication) from the host cell. From its structure, the virus Avian Influenza it is a virus that has an envelope, so it is sensitive to all types of disinfectants without being picky.
Until now in Indonesia we know two types Avian Influenza who attacked the birds, namely High Pathogenic Avian Influenza (Noun) a person who is violent and Low Pathogenic Avian Influenza Which is non-violent. Both types of AI are equally detrimental to breeders.
HPAI that we know so far is Avian Influenza H5N1 subtype that causes high mortality in poultry, while other types classified as LPAI circulating in Indonesia is H9N2 subtype. It is said that LPAI due to a single attack by this type of AI does not cause high mortality but causes a significant decrease in production.
In addition to subtypes, the AI virus also consists of several clade. Clade is the standard term of World Health Organization (WHO) to describe a hereditary, genetic, strain, or group of viruses influenza. Number of clade AI virus in the world including circulating in Indonesia, some clade split again into several subclade and sub sub clade.
AI H5N1 Virus circulating in Indonesia including into High Pathogenic Avian Influenza (HPAI) which is divided into 2 clade they are 2.1.3.2 and 2.3.2.1 c, and have been dominated by the 2.3.2.1 C Clade since 2015. AI disease in poultry caused by AI H5N1 virus clade 2.1.3 has been going on in Indonesia for more than 10 years. After it appeared clade new 2.3.2.
Analysis of organ samples received by the team Research and Development Medion until 2019 showed that H9N2 cases continued to dominate compared to H5N1. The H9N2 Virus belongs to the y280 strain.

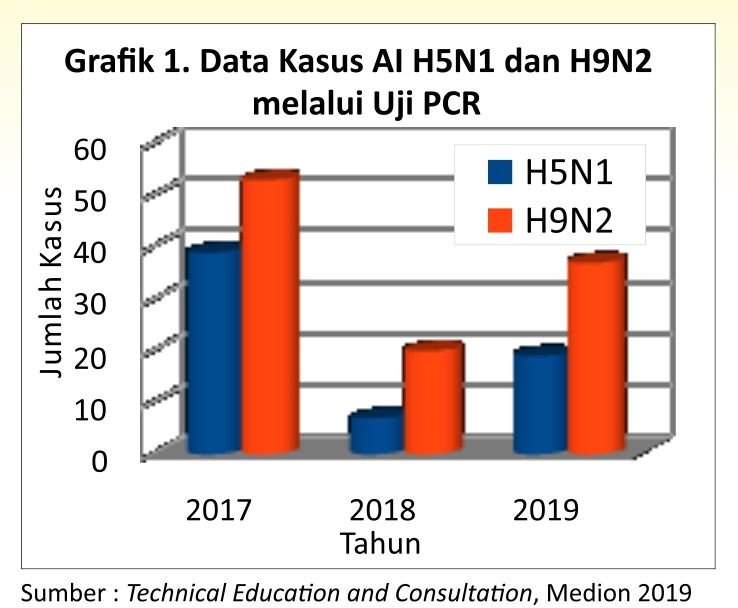
In Graph 1 can be seen the case of AI based on data that goes to the team Technical Education and Consultation (TEC) Medion from all regions in Indonesia. In the last three years, AI cases have been dominated by LPAI cases.
In 2018 the number of AI cases decreased compared to 2017, but in 2019 it increased again and until October 2018 AI cases in Indonesia were dominated by LPAI.

Based on data collected by the team Technical Education and Consultation PT. Medion from 2017 to 2019, the age of the attack varied. In broilers, the predominance of AI attacks occurs at the age of over 2 weeks until harvest. Whereas in laying hens, AI attacks are dominated by chickens during the production period that is above 18 weeks.
However, AI infection in the age before production also needs to be aware of, because in general AI diseases attack chickens of all ages. Infection at the beginning of rearing can also trigger the risk of not achieving weight or skeleton, which will also affect the quality and quantity of eggs during production.

Losses arising in the case Avian Influenza due to high morbidity (morbidity) and mortality (mortality) in cases of H5N1 and a significant decrease in egg production in H9N2, mass depopulation of poultry (stamping out) and increased costs for supportive treatment, sanitation and disinfection of enclosure areas, water and farm equipment.
Due to the considerable losses caused by AI infection, prevention and early detection efforts are very important, plus changes in clinical symptoms and anatomical pathology of AI today are slightly different from before.
How do clinical symptoms and anatomical pathology change Avian Influenza Right Now ?
As we know the disease Avian Influenza it can attack all systems in the chicken's body. But the most visible symptom that usually appears is the presence of respiratory disorders. In the previous AI attack we also found a sudden death in one cage.
As for AI at this time the symptoms have begun to shift, in chickens layer production period symptoms begin with signs of respiratory distress (such as difficulty breathing and snoring), decreased production, chicken weakness, feed intake reduced, pale chicken, then followed by increased mortality.

Another symptom that we used to find often is the presence of bluish red on the skin, jegger, and Wattle, but nowadays these changes rarely appear.

As we see in Graph 1, a positive AI attack based on PCR test results that the current dominance of AI attacks is LPAI, the H9N2 subtype that tends to attack the reproductive system and in a single attack of AI H9N2 this does not cause high mortality.
However, the characteristic of AI H9N2 is that it has immunosuppressant properties that are able to suppress immunity so that other diseases become easy to enter. Based on the data compiled by the Medion TEC team, here are some of the H9N2 AI combination attacks:

In addition to the clinical symptoms that appear from the outside, pathological changes in the anatomy of the chicken organs affected by AI also undergo some changes. Point bleeding or what we often call the term ptechiae at this time heart fat tends to be thinner.

In addition ptechiae in heart fat, in other parts of the body such as fat and chest muscles and abdominal muscles also become lighter.

Changes in the nervous system, namely the dilation of brain blood vessels, still appear as one of the pathognomonic changes (typical) in the case of AI.

In addition to the changes that appeared before, cysts are now often found in cases of AI in the field. Not just a disease Infectious Bronchitis (IB) alone can lead to the appearance of cysts. Cyst size or cystic oviduct this also varies.

Changes that arise and shift from the past and present AI is likely because some farms have applied vaccination, so that immunity has been formed that should be able to protect the chicken's body.
But there are some things that also affect the immune level of chickens, such as immunosuppressant factors, biosecurity, maintenance management and field challenges that must also be considered. Because these factors can cause the formation of antibodies to be less than optimal or antibodies that have been formed to be faster down in a short time.
The following is a summary of clinical symptoms and anatomical pathology of chickens attacked by AI compared to changes in AI then and now:
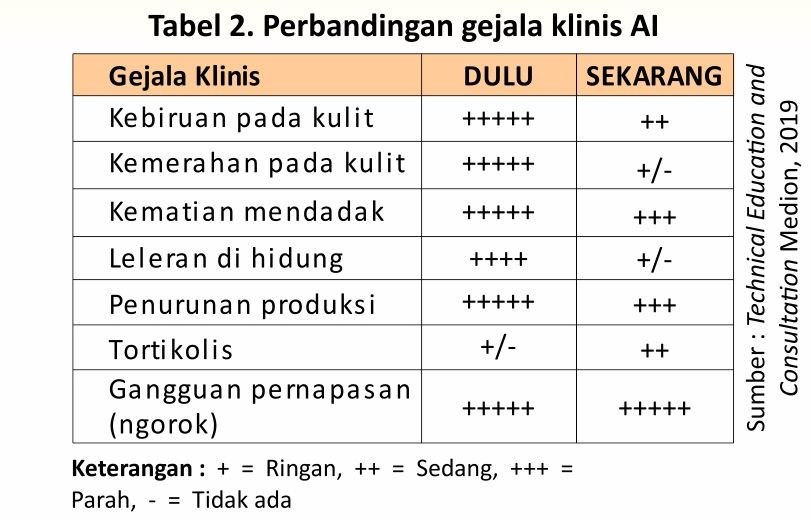

If we observe the current AI changes become lighter so that it requires more precision in diagnosing. In addition, our ability to detect AI cases is also very important in handling it.
How are AI early detection efforts currently going?
Routine activities that must be done as an effort to early detection of AI cases in the field is to monitor recording or a diary of each cage. Some things we need to be aware of is if some things happen like the following Within 2 consecutive days (Daniel Beltran-Alcrudo et al., 2009) :
- Decreased egg production by 5%
- Decline feed intake a total of 5%
- Increase in death rate 0.25%
If the above happens then we must immediately take action, including :
- Check the condition of the clinical symptoms that appear in chickens whether breathing disorders appear, pale chicken weakness, etc.
- Perform necropsy (chicken surgery), chicken samples are taken from several conditions. Chickens that show symptoms of illness and those that look healthy as a comparison.
- Along with taking samples for necropsy, also take blood samples for serology lab tests with HI test.
- If there is a direction to AI, can be continued to confirm the diagnosis with a PCR lab test.
In addition to these efforts, early detection can also be done by routine monitoring of antibody titers from serological testing with HI test. This monitoring is done by comparing the titer of the test results with the baseline titer or baseline titer.
Baseline titer is the basic titer or standard titer used as a reference. If the serological test results are significantly higher or lower than baseline titer then this becomes early warning or early warning to take immediate action. So prevention and proper handling are very important to reduce losses caused by AI attacks in the field.
How to prevent and treat AI?
Proper prevention efforts can be done with a combination of biosecurity and vaccinations. Here are some explanations to avoid recurrence outbreak AI on a farm:
1. Success factors of AI vaccination
a) proper vaccine
To control AI, the use of a vaccine homologous to the field virus is highly recommended because it will provide optimal protection. Medivac AI Subtipe H5N1 2.1 and Medivac AI Subtipe H5N1 2.3 can be the right solution in this case. Medion also produces vaccines to prevent H9N2 AI diseases that are homologous to the field H9N2 virus, namely vaccines Medivac AI Subtipe H9N2.
Apart from the content, the right vaccine is also judged by its physical qualities. The physical quality of the AI vaccine must be good, meaning that the seal is intact, the shape has not changed, the vaccine has not expired, and the label is still well installed.
b) proper application
In addition to having the right vaccine, the AI vaccination application must also be done appropriately. This includes the preparation of equipment (syringes), thawing (temperature increase process) of vaccines, handling (holding and removing) chickens, how to inject, dose of vaccine administration, and handling of vaccine bottles.
c) timely delivery
This is related to the vaccination program. The AI vaccination Program should be prepared based on the high or low challenge of the AI virus in the field and the baseline titer in each farm. The AI vaccination Program is also compiled based on case histories in the local area. And for AI, the use of vaccines homologous to field viruses is an important point in the preparation of vaccination programs.
The implementation of AI vaccination in broilers, especially during the rainy season is highly recommended. The program is enough to do 1 time at the age of 4 days along with active nd vaccination, or at the age of 10 days using a single AI vaccine. The occurrence of AI in broilers is actually inseparable from the decrease in maternal AI antibodies. At the age of 3 weeks, maternal antibody titers are no longer protective so that age is the most vulnerable time for chickens to be attacked by AI.
In addition, because from field data, AI usually infects broilers aged > 3 weeks, the first AI vaccination in broilers should be done at the age of 4 or 10 days. Although vaccination does not free 100% of chickens from AI, at least vaccination can suppress the potential for contracting the disease and if there is an AI attack, chickens are relatively more resistant. Vaccination will also suppress virus shedding so that AI virus contamination in the field can be suppressed.
If AI vaccination in broilers is enough to do 1 time, then in laying hens vaccination is recommended 3 times before entering the egg production period and at least 2 times after passing the peak of production. Hal ini sesuai pula dengan rekomendasi dari Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO).
2. Monitoring titer
Monitoring antibody titers performed regularly will help farmers monitor the health status of their chickens. In order for the serology test results to provide a representative picture of a cage, take a sample of at least 15 samples per cage. Analysis is done not only look at the value Geometric Mean Titer (GMT) with standard protect, but also seen the percentage of invulnerability and uniformity. Serological test results need to be matched with baseline titer contained in the farm because it is likely that the protective standards for each farm are different.
3. Supplementation
Multivitamins (Solvit, Aminovit, or Fortevit) and premix (Mix Plus) as a supplement to the ration will increase the endurance of chickens. With vitamin supplementation, the condition of the mucous membrane of poultry will be better so that the AI virus that will enter the mucous membrane can be optimally driven away.
In addition to vitamins, the addition of premixes is also important to supplement the nutritional needs of the ration, so that the metabolic process of poultry body defense can run optimally. Give herbal immunostimulants such as Imustim to help improve the immune system work.
4. Biosecurity
Well-programmed vaccination and supplementation will not provide optimal preventive results if not supported by the implementation biosecurity tight. Therefore, increase biosecurity especially in people, equipment and moving vehicles such as vaccinator teams, chicken reject cars, egg boxes etc.
The membrane structure of the amplified AI virus makes it easy for the virus to be killed by all types of disinfectants. Choose and use disinfectants whose working power is less influenced by organic materials such as Formades or Sporades to spray the vehicle or the outside of the cage.
Spray well Antisep or Neo Antisep regularly once a week when the cage contains chickens. Apply a system of 3 zones, namely clean zoa, transition zone, and dirty zone. Isolate sick chickens and do not buy and sell sick chickens. For the treatment of chicken carcasses, immediately burn, Bury and disinfect. In addition, the cage visit begins from the new young chicken coop to the old chicken coop.

Treatment In The Event Of Illness
AI is a viral disease, so there is no cure. If a farm has been infected with AI, then the things that need to be done include:
Handling on other cages that have not been attacked by AI
- To suppress disease transmission, immediately revaccinate healthy chickens using Medivac AI. The results of revaccination depend on the degree of malignancy of the invading virus, morbidity and mortality
- Do Cage spray to reduce the number of viruses in the field
- Disinfection of drinking water to prevent disease transmission through drinking water
- Scatter lime on the road area around the cage
- Limit traffic employees from sick chicken coops are not allowed to enter or pass through healthy chicken coops
Handling on cages that have been attacked by AI
- Immediately remove dead birds in the cage. Destroy it by the method of burial in previously disinfected chicken carcasses or burning in a location far from the cage.
- Spray the cage that still contains chickens with a disinfectant such as Antisep or Neo Antisep, and on an empty cage can use Sporades or Formades
- Assign immunostimulants such as Imustim to increase the stamina of the chicken. Imustim will help increase the body's resistance optimally so that the healing process will be faster
- Emergency vaccination can be done to reduce mortality. This can be done on laying hens or breeders who are still healthy using Medivac AI.
- Do enough cage rest, which is at least 14 days counting from the cage being cleaned. Then disinfect the cage again before starting chick-in more
Such is the development of AI that we can discuss. So that AI does not increasingly exist in Indonesia, farmers need to implement several AI control measures in an integrated manner between vaccinating appropriately, implementing strict biosecurity, continuing to improve maintenance management, and increasing the stamina of the chicken's body properly.
And do not forget Medion will continue to collect field data and research series to determine the development of the AI virus, as well as study the level of vaccine Protectivity. May be useful. Greetings.