ND disease is still the main scourge in the poultry sector. Though not a few farmers who have routinely vaccinated. Why do ND cases still spread and seem difficult to control?
How is the current incidence of ND in the field?
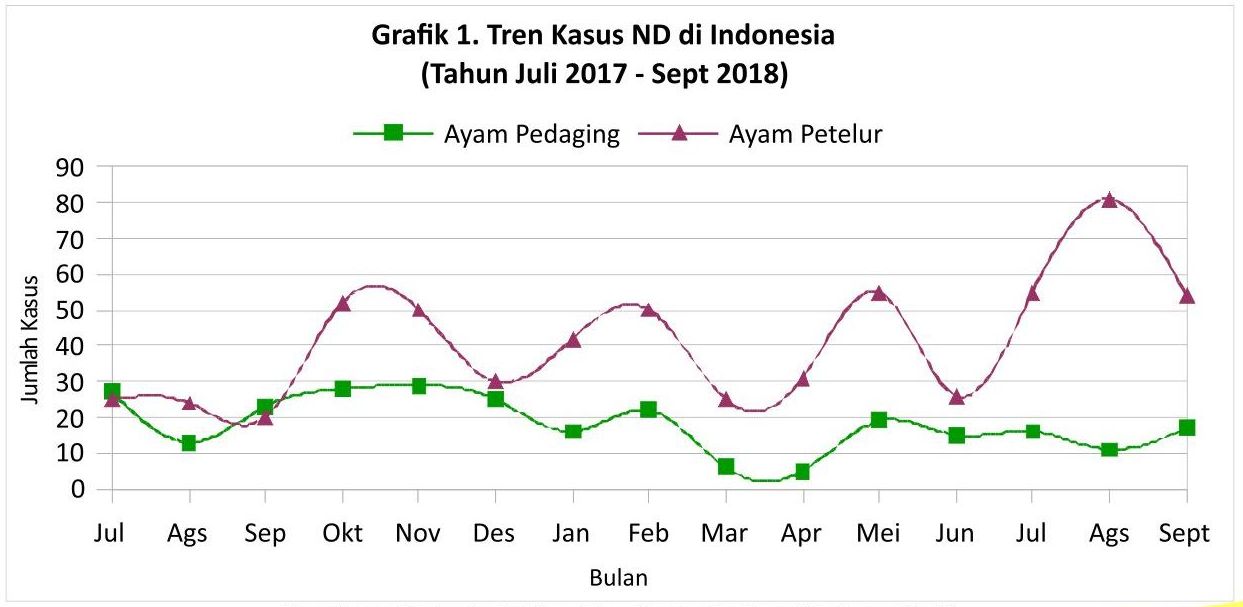
Based on field data from 2016-2018, ND disease always occupies the top 10 ranking of diseases in broilers and layers and attacks all ages of chickens. It is also predicted that the incidence of ND will still experience an increase in the number of cases because it is now starting to enter the peak of the rainy season.
It is also known that the pattern of attacks of ND cases is evenly distributed throughout the year during the rainy season and even towards the transition of the season (Graph 1). This is thought to be due to uncertain weather conditions in Indonesia, causing the condition of the chicken's body to be easily stressed, triggering the emergence of ND cases. In addition, it is suspected that due to the humid conditions of the cage environment, the ND virus is quite stable and easy to develop.
Known since 2009 where the results mapping (mapping) monitoring by Medion has identified nd viruses in the field including velogenic group (malignant) and classified into genotype VIIH (G7H). In 2013, in addition to genotype 7H, genotype 7A (7I) was found. Where in 2018 the number of g7a viruses was found almost as many as G7H. It can be concluded that the ND virus circulating in Indonesia is genotype G7H and G7A. The majority of ND G7 viruses are mainly found in several large islands in Indonesia, namely Sumatra, Java, Kalimantan, Bali, to Sulawesi. This is what breeders need to constantly watch out for. As we know the occurrence of this ND case will cause some losses as follows:
- Respiratory, nervous, digestive and reproductive disorders
- Can attack at different ages of chickens
- The mortality rate of chickens can reach 50-90% while the morbidity rate is relatively high, namely 80-100%
- Barriers to growth
- Decrease in egg production both in quality and quantity and even up to 60%
- Be a predisposing factor to other respiratory diseases
Disease Diagnosis
Sometimes the occurrence of an attacking ND at this time makes it difficult to diagnose due to the features of clinical symptoms and changes in the emerging anatomical pathology is quite difficult to distinguish from attacks of other diseases. For clinical symptoms of ND still looks the same when it was first discovered that is when the chicken looks difficulty breathing and a distinctive sound or commonly called snoring, especially if the night conditions are very cold. In addition, it will be noticeable mucous discharge from the nose of the chicken. Other symptoms that appear such as chicken weakness, decreased appetite, dull feathers, green diarrhea mixed with White Moss and still found chickens experiencing torticollis. Cases of ND also lead to a decrease in egg production, the color of the shellfish becomes pale and sometimes the eggs are small. High mortality is also the biggest disadvantage in the case of ND. Sometimes it can be up to 10-20 heads per day or even in 2 weeks reach ③ 20% of the total population.
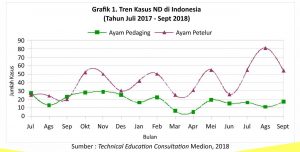
Anatomical pathological changes found in the case of ND include inflammation of the sinuses, larynx, trachea and lungs but these changes are not typical of ND alone. In the digestive tract can be found inflammation of the proventriculus, intestine, peyer’s patches and caeca tonsil. In laying hens that are in production, bleeding can be found in the yolk candidate, The Shape of the yolk candidate is irregular and sometimes there is a broken yolk candidate in the abdominal cavity. You can start with a lab test (MediLab) to help confirm the diagnosis. The laboratory tests in question include serological tests, up to the isolation and identification of the causative agent of the disease through methods polymerase chain reaction (PCR) dan DNA sequencing.
ND control efforts
It is important for farmers to know that it is necessary to carry out integrated control in preventing the proliferation of ND cases. This means that we not only rely on vaccination in preventing ND, but the success of vaccination is also influenced by several factors that we call 4M:
- Material (vaccine and chicken). Make sure the chicken is healthy when it will be vaccinated ND so that the antibody titer formed is more optimal. Use nd vaccines that are still of good quality and have been registered. Apart from the physical aspect, it is also important to consider the use of ND vaccines that are homologous to the field nd virus. The vaccine that will be given for chickens must be adjusted to the type and violence of the disease that often attacks. Medion produces vaccines to prevent nd diseases that are homologous to the field nd G7 virus, namely vaccines Medivac ND G7 Emulsion, Medivac ND G7-EDS Emulsion, Medivac ND G7-EDS-IB Emulsion, and Medivac ND G7-IB Emulsion. Inactivated vaccines are needed to bully humoral immunity (immunity circulating in the blood).Mucosal or local immunity in the area of the upper respiratory tract that is the entrance gate for infection with the ND virus. As a result, vaccines such as Medivac ND La Sota, Medivac ND Hitchner B1, Medivac Clone 45, or Medivac ND-IB it still needs to be administered to stimulate the rapid and protective formation of ND immunity.
- Methods (vaccination programs and vaccination techniques)
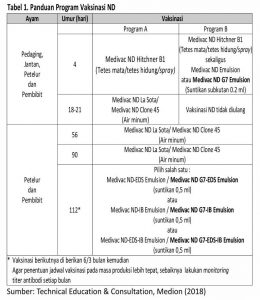
The following is an example of a vaccination program for broilers and layers that can be adapted to local farm conditions (Table 1).
- In order to obtain optimal antibodies, make sure that the first nd vaccination is given via eye/nose drops in order to activate the harderian glands (immune organs) in the eye area. In addition, so that each chick gets 1 full dose. While the injected inactivated vaccine is given according to the age of the chicken, for example 0.5 ml for adult chickens by injection or intramuscular injection, and 0.2 ml for chicks by subcutaneous injection.
- Human (skills, attitudes, and knowledge). If there is a vaccine (vaccine), red) not from vaccine companies, the vaccinator team needs to be given special training in order to have knowledge and skill a good vaccine.
- Milieu / environment (disease agents, biosecurity, and water). Create a comfortable cage conditions by paying attention to the number of chickens in the cage is not too dense, ventilate the cage enough and wherever possible do the system “all in all out” and the application of cage rest for at least 2 weeks.Tighten biosecurity by limiting the traffic of people / vehicles in and out of the cage. It is possible that the ND virus is carried through the wheels of vehicles or footwear of cage personnel who enter and exit the cage. Disinfect both vehicles and personnel, especially if coming from an infected farm enclosure. Sanitize drinking water by providing antiseptics such as Desinsep or Neo Antisep to suppress disease transmission through drinking water.Perform cage and equipment sanitation (cage cleaned, washed and sprayed) with Neo Antisep or Medisep. When it is happening outbreak then spraying is done every day because the transmission of the ND virus can occur through the air. The water is heated with boiling water and heated with boiling water (Medisep) every 2 times a day. It is recommended to take a multivitamin (Vita Stress/Fortevit/Imustim) regularly so that chickens are not susceptible to disease.
ND disease is not a new disease and has appeared in Indonesia for a long time. It is necessary to apply some ND control measures in an integrated manner so that ND does not increasingly exist. And do not forget Medion will continue to collect field data and research series to determine the development of ND. May be useful. Greetings.