Questions from Bpk. Sodiq – by Email
Would it be appropriate if farm layer revaccination ND live every 3 weeks? What is the advice for the ND vaccination program for layer chickens?
Answer
Thank you Mr. Sodiq for the question submitted. Control of viral diseases including ND is a combination of vaccination and biosecurity. The success of vaccination is influenced by several factors. Among others, the material (chicken conditions and vaccine selection), methods (vaccination programs and vaccination techniques), human (skills and knowledge in the application of vaccination), environment (application biosecurity in the cage and water if the application via drinking water).
Before carrying out vaccination, there are several things that need to be considered related to the selection of vaccines and vaccination programs. The selection of the right type of vaccine is very influential on the success of vaccination in warding off virus attacks in the field.
Then no less important is the vaccination program that is applied according to the conditions farm. Need to consider in advance the history of the disease attack Age, Age of chickens, data monitor antibody titer, the type of vaccine used and the level of vulnerability to ND attacks around farm.
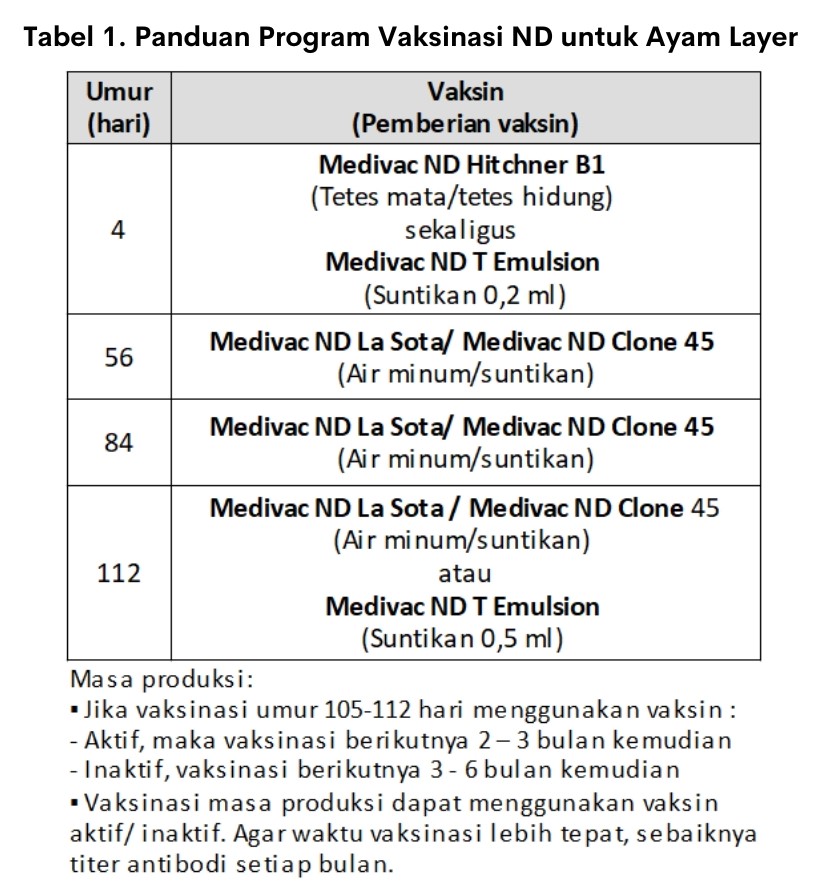
On chicken layer nd vaccination is given 4-5 times before entering the egg-laying period. In the period of laying eggs repeat vaccinations need to be done. Vaccination can use active or inactivated vaccines. If using an active vaccine, the next vaccination is given 2-3 months later.
In the use of active vaccines, it is necessary to ensure that the vaccination is carried out simultaneously in one day with the right dose. This is to prevent the occurrence of rolling reaction (reaction post prolonged vaccination). Whereas if using an inactivated vaccine, the next vaccination is given 3-6 months later.
But it is necessary to consider the degree of vulnerability of ND in farm nor the surrounding area. In order to more accurately determine the timing of the repetition of vaccination, conduct antibody titer monitoring. To optimize the formation of antibody titers vaccination results can be administered immunostimulants (Imustim).
In implementing the vaccination program, it is important to consider the level of vulnerability of ND cases in the father's farm and surrounding farms and the age history of ND attacks. If you have a high level of vulnerability, the frequency of vaccination will be more frequent.
A more precise repeat of the vaccination can be adjusted by the antibody titer on baseline titer. If with a repetition of 3 weeks using the active vaccine, productivity is optimal and chickens are protected from ND, it can still be carried out. Here's an example of an ND vaccination program for layer chickens as a general guide (Table 1).
Monitoring of antibody titers in healthy chickens on a regular basis, especially in the production period can be done every 1-2 months. The protective antibody titer picture will continue to be monitored. So that the timing of vaccination can be scheduled before the antibody titer is below the protective level.
The results of antibody titer monitoring are also useful as baseline titer for early warning system. Baseline titer is the range of antibody titer values based on history to determine the average and protective values in a farm. It is hoped that farmers can detect early if there is deviation of antibody titer from baseline titer of farm the.
Monitoring of antibody titers in healthy chickens on a regular basis, especially in the production period can be done every 1-2 months. The protective antibody titer picture will continue to be monitored. So that the timing of vaccination can be scheduled before the antibody titer is below the protective level.
The results of monitoring antibody titers in healthy chickens are also useful as baseline titer for early warning system. Baseline titer is the range of titer values based on history to determine the average antibody titer and protective in a farm. Through the application of early warning system this, then farmers can detect early if there is a deviation of antibody titers from baseline titer.
The next control that needs to be considered is to increase biosecurity. Tightens biosecurity by limiting the traffic of people and vehicles entering or leaving the cage. Disinfect both vehicles and personnel, especially if they come from other infected farms.
To suppress disease transmission through drinking water, sanitize by providing antiseptics such as Desinsep or Neo Antisep. Perform cage sanitation (cage cleaned, washed and sprayed) with Neo Antisep or Medisep, then prevent wild animals and other pets from entering the cage environment. The water is heated and cooled, and the water is heated and cooled, and the water is heated and cooled, and the water is heated (Medisep).










