Ahead of the preparation of Eid al-Adha farmers are busy with the maintenance of livestock to meet market demand. Farmers will give their best so that the results of optimal maintenance by considering the economic value. Both in terms of seed selection, maintenance practices, feeding and in terms of Health.
Health management is one of the success factors of maintenance that affects profits and customer satisfaction. The thing that is sometimes a pity after slaughtering livestock is the discovery of helminth parasites in the internal organs.
Helminth parasites are sometimes not a cause for concern because in mild infections cattle do not show significant symptoms. But actually this parasite can cause health problems that can be economically detrimental, such as inhibiting weight gain, damaging tissues in the body, especially the digestive tract, increasing the risk of diafkir organs and reducing the appetite of livestock.
Frequent cases of worms
Worms in the digestive tract is one type of disease that is often found in animal husbandry. Including during the post mortem examination or after the slaughter of sacrificial animals. This event will certainly reduce the growth rate and health of livestock.
Worms will cause impaired absorption of food juice in livestock to cause damage to cells and tissues. This condition will also cause livestock to become more susceptible to various diseases.
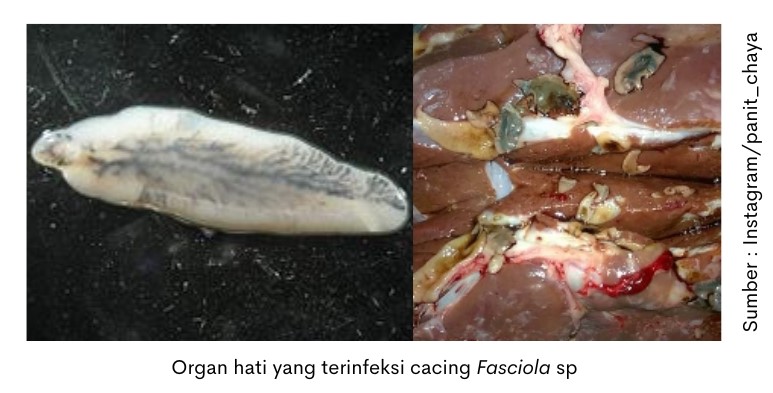
The discovery of worms in the liver of slaughtered cattle, sheep and goats is often found during the examination of sacrificial animals.
Liver fluke infection caused by trematode worms Fasciola gigantica or Fasciola hepatica. The worm migrates inside the liver parenchyma then develops and settles in the bile ducts.
In mild infections cattle can show no clinical symptoms. In severe infections cause impaired growth and weight loss of livestock. In chronic cases, edema or swelling that contains fluid in the lower jaw may appear. Visible changes in the liver organ the presence of bulges or pale stripes. When slashed will be found adult worms.
When inspection post mortem sacrificial animals were later found to have liver worms, many asked whether or not the meat was safe for consumption. The meat of sacrificial animals found liver worms, sacrificial meat is not at risk of becoming an agent of transmission to humans. The part of the liver affected by worms needs to be disinfected and aesthetically unfit for consumption.
If the infection is severe enough or most of the liver is infected, the entire liver needs to be diaphoretic. While the meat remains safe for consumption. Liver flukes can infect humans from water or vegetables contaminated with worm eggs in the form of metacercaria.
Worms are often found also when in cattle, namely Paramphistomum spp. Young worms are in the small intestine, while adult worms Paramphistomum spp. located in the rumen and reticulum. In the rumen and reticulum, these worms will stick and suck blood on the mucosal surface.
Clinical symptoms of infected cattle Paramphistomum spp. is a decrease in weight to thinness. In severe infections can cause severe gastroenteritis in young cattle that can lead to death. On examination post mortem sacrificial cattle can be seen sticking to the mucosal surface of the rumen in red clumps. Infection with worms Paramphistomum it is not zoonotic or contagious to humans.
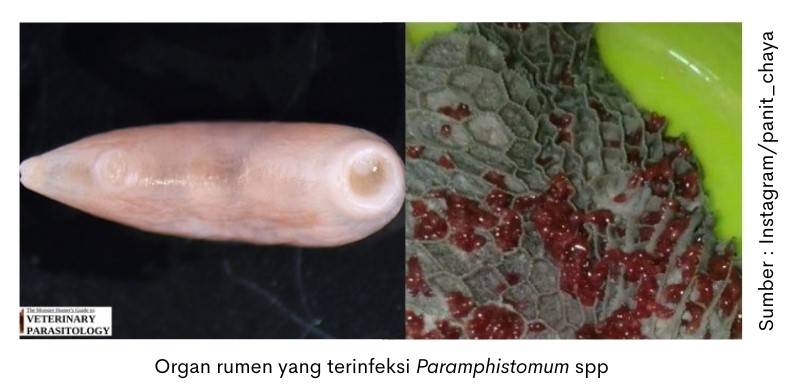
Livestock found worms Paramphistomum the meat remains safe for consumption. If you want to consume tripe, the attached worms need to be cleaned first.
Prevent and treat cases of worms
To prevent livestock from worms, efforts can be made, among others:
Anthelmintic Program
The deworming Program is the main step in controlling cases of worms in both young and adult livestock. Worm medicine is not only intended for cattle that are positive for worms, but can be given as prevention in healthy cows. The deworming Program is repeated once every 3-4 months. Anthelmintic, the dosage form of which is bolus, for example Wormectin Plus-B or Wormzol-B.
Cage and environmental sanitation
Efforts that can be done is to routinely clean the dirt, clean the drain in the cage and prevent the presence of puddles of water so that the cage conditions are not damp and muddy.
Lawn feeding system
It is not recommended to give fresh grass. The grass should be grazed first before being given to livestock. In addition to preventing worms, it can also prevent cases of bloating. Avoid looking for grass too early because at that time the larvae or worm eggs are usually dominant in the grass tops that are still wet.
Elimination of host populations between
The liver fluke needs an intermediate host i.e. a freshwater snail for its survival. Therefore freshwater snails play an important role in the occurrence of liver fluke cases in cattle.
- Examination of eggs and larvae of worms regularly 2-3 months through a stool test. Medion has a laboratory that can serve the test is MediLab which has spread in several regions in Indonesia.
- Increases body endurance
In addition to providing quality food, efforts to increase endurance can be by providing supplements or vitamins. Awarding Vita B Plex Bolus Extra Flavor it can be given once every 3-4 months.










