Bapak Haryanto – by email
Medan-North Sumatra
Currently, mouth and nail disease (PMK) is rampant in cattle and goats. What efforts can be made so that my livestock is not infected with FMD?
Answer:
Thank you Mr. Haryanto for the question submitted. Previously we explained briefly about PMK. FMD is an acute infectious infection that affects even-toed ungulates such as cows, buffaloes, goats, sheep, pigs, deer, etc. However, FMD is not zoonotic or contagious to humans.
The disease is caused by viruses Foot Mouth Disease (FMD) in famili Picornaviridae and genus Aphthovirus. Masa inkubasi PMK selama 2-14 hari. Virus PMK merupakan virus tidak beramplop dan tahan berbulan-bulan pada materi protein tinggi seperti tulang, susu, darah atau semen. Kelangsungan hidup virus dapat lebih lama dalam kondisi iklim yang relatif rendah, terdapat bahan organik dan terlindung dari sinar matahari. Virus akan mati dalam suhu >50°C atau 70°C dalam 30 menit. Virus ini tidak tahan kondisi asam (<pH 6) dan basa (>pH 9).
PMK transmission can occur through:
- Direct contact with infected animals
- Indirect contact (humans, milk, semen, faeces, urine, cage equipment, contaminated vehicles and vectors/wild animals)
- By air (aerosol) and water
Symptoms that can be observed in livestock affected by FMD are as follows:
- Fever up to 41°C and looks lethargic
- Excessive salivation (hypersalivation) and decreased appetite
- Lie down more often until a limp is found
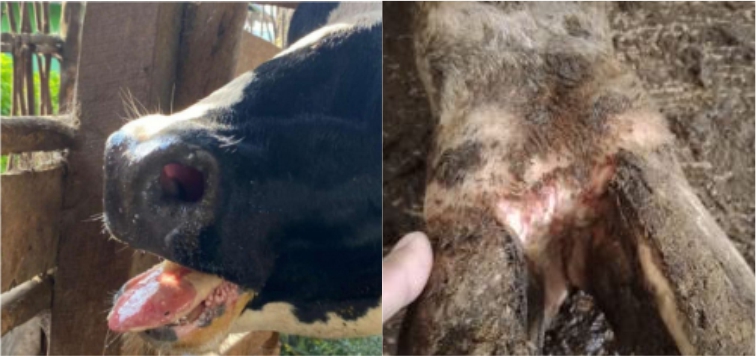
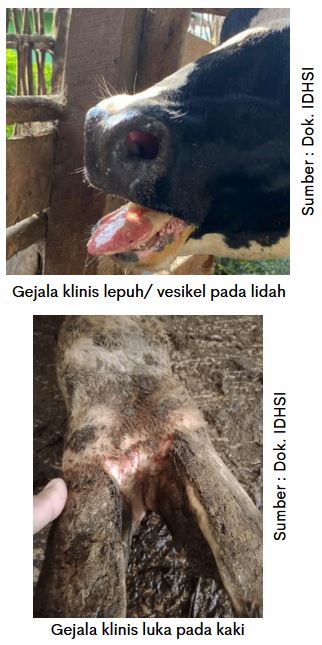
- The appearance of blisters (vesicles) usually filled with fluid around the mouth (tongue, gums, palate).
- On the feet blisters and sores are clearly visible on the nail cracks or ruffled feet
- Injuries to the nipples and a drastic decrease in milk production
- Decreased body weight, miscarriage and infertility
- Morbidity can reach 100% and mortality is high in young cattle (>20%).
- In goats and sheep sometimes less visible lesions on the legs but there can be death in young animals and hypersalivation.
Prevention efforts so that farms are not infected, among others:
- Carry out restrictions and supervision of animal traffic. Protection of free zones by prohibiting the sending / receiving of animals from outbreak areas.
- Conduct a 14-day quarantine when new livestock comes to the farm site for intensive observation of the presence of symptoms of the disease (incubation period).
- Limit the traffic of goods, vehicles and unauthorized persons
- Perform cleaning and disinfection of empty cages, equipment and vehicles using Sporades at a dose of 100-200 ml dissolved in 20 liters of water or Formades at a dose of 500-1000 ml dissolved into 25 liters of water.
- For farms near infected areas, vaccinate susceptible animals with the active virus.
- In addition to vaccination and biosecurity, an increase in the body's resistance of animals with vitamins (Vitamin B Complex Injection, ADE-Plex injection or Vita B Plex Bolus Extra Flavour) is considered important as prevention from within the animal's body.
If livestock is infected with FMD, actions that can be taken include:
- Isolation of symptomatic livestock from healthy animals (in quarantine cages separate from healthy animal cages).
- Immediately report to the local animal husbandry office if you find clinical symptoms of suspected FMD.
- Destroy contaminated materials (carcasses, feed, etc. buried or burned
- Decontamination and disinfection of empty cages and vehicles with Sporades at a dose of 100-200 ml dissolved in 20 liters of water or Formades at a dose of 500-1000 ml dissolved into 25 liters of water.
- Uninfected animals should be placed in dry locations and given adequate and nutritious feed to boost the immune system.
- Do foot dip or dip the feet of animals containing a mixture of water and a 5% solution of cupri sulfate routinely.
- Handling by animal health workers by providing symptomatic therapy to overcome symptoms such as Medipiron Injection as anti-inflammatory, anti-pain and fever-lowering. Treatment with antibiotics (Tinolin Injection, G-Mox 15% LA inj or Tysinol). Vitamins and minerals (Vitamin B Complex Injection, ADE-Plex Inj or Bioselvita) to accelerate healing and increase endurance.