The quality of egg shells is one of the parameters that farmers always pay attention to. Egg production (hen day), without being followed by optimal eggshell quality will reduce the success rate of raising laying hens.
The quality of good egg shells is shown from the strength and color of the shells. In other words, shells that are not easily broken or cracked with a shiny brown color are the dream of breeders.
Eggshell Color Quality Standard
The color of egg shells that Indonesian people like is shiny brown. The more brown, the eggs will be assumed to be of good quality. So far, the determination of shellfish color only uses the perception or visualization of consumers.
Egg Shell Color Fan or the eggshell color fan becomes one of the tools to determine the level of eggshell color. The higher the value, the more good quality eggs.

Hendrix Genetics which is a laying hen breeding company ISA Brown uses a reflectometer to measure the color of egg shells. This reflectometer works by taking the percentage of color from black (0%) and white (100%). For a good shellfish color has a value of 25-40%.

Currently, the Lab can also be used to measure the unit of color quality of eggshells. Measurement using chromameter which method in more detail detects the color of eggshells. This tool is also used in general for color measurement, ranging from meat color and vegetable color. The range of Lab values is different from the refrectometer, the lower the Lab value, the darker the color of the egg shell. ISA Brown standardizes the color quality of a good eggshell maximum is 17.0 Lab (the higher the value the more white eggshell).
Determining Factors For The Quality Of Egg Shells
1. Chicken quality
Chicken conditions that need to be considered related to the quality of egg shells are :
- Quality of bone skeleton. This can be seen from the large and long bones of the legs (shank) and the width of the collarbone (os pubis). Two things describe the presence of calcium deposits in large quantities. Chickens with small leg bones and collarbones tend to produce eggs with small sizes and pale colors.

- Cache size and gizzard (Gizzard). These two organs serve as storage (depot) feed. The optimal size (large), will cause the Food Depot to meet the needs of chickens to be more. This is important, considering that the process of shellfish formation occurs longer at night, when there is no more feeding activity. Whereas that's when calcium as the main component of the main constituent of shellfish is needed in sufficient quantities.
2. Feed factor
This feed factor is divided into 4, namely :
- Feed use pre layer
A very high difference in calcium levels, which reaches 400% between feeds grower and layer often an obstacle for chickens to increase feed intake- her. This will be seen during the early to peak production, feed intake difficult to achieve. In addition to a very significant increase in calcium levels, these calcium dosage forms also differ between feeds grower and layer.
Feeding pre-layer it also serves to optimize the development of medullary bone (medullary bone). This medullary bone serves to supply calcium for the formation of egg shells. The development of the medullary bone is not optimal, will result in the quality of the eggshell is not good, ranging from easily cracked to pale color.
Feeding pre-layer this should be done 2 weeks before the chickens start laying eggs. The average farmer is late in changing his feed. Usually when the chicken has laid new eggs the feed is replaced. As a result, chickens do not get the calcium supply as needed. Paralysis of laying hens at the beginning of the production period is one of the consequences of this delay in calcium supply, especially if during the pullet there is a delay in growth.
- Calcium particle size
In addition to the levels in the feed that must be in accordance with the needs of laying hens, the particle size of calcium source feed ingredients such as limestone (flour or stone grit), shells and bones should also be considered. This is related to the long time of the eggshell formation process, which reaches 18-20 hours. In addition, it is also related to the retention period or long-lasting period in the digestive tract (cache, gizzard and intestines).
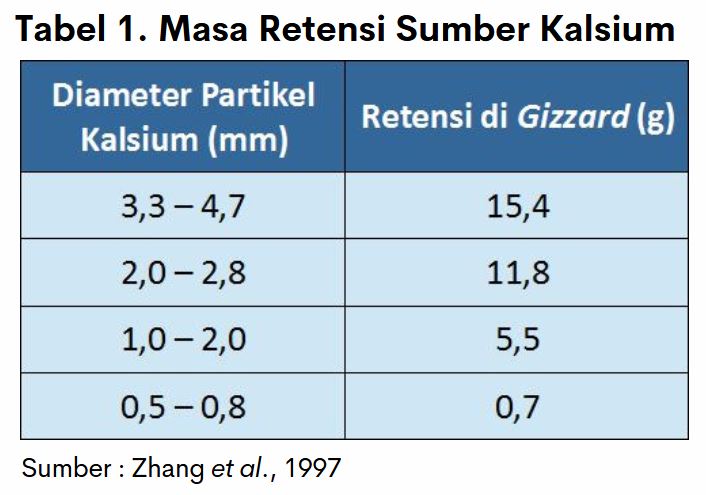
Chart 1. data show that calcium preparations are in the form of mash or the powder will be more quickly removed from the digestive tract. This will result in a lack of calcium supply for the formation of shellfish. While the source of calcium in the form grit or the details will be able to last a long time inside gizzard so it can be digested and absorbed slowly at night for the formation of egg shells.
The source of calcium should be given in a combination of two preparations, namely 30-40% in the form of powder while 60-70% is provided in the form of granules (grit). This is because the source of calcium in the form mash (powder) is also necessary for the re-formation of the medular bone, which takes calcium during the formation of eggshells at night.
Applications midnight feeding or giving rations at midnight can also improve the quality of eggshells.
- Feeding management
Feeding should be done 2 times a day, ie morning and afternoon with a ratio of 30-40% feed for morning feeding and 60-70% for daytime feeding. The purpose of giving more day or afternoon is to help the availability of nutrient supply (especially calcium) at night so that the quality of the shells becomes more optimal.
- Homogeneity
Calcium sources, such as flour or grit stone, bone meal usually has a greater weight than other feed sources. This condition will greatly affect the homogeneity or flatness of the feed mixture. When in mixer, grit stone will go down faster than other raw materials. Therefore, it is necessary to optimize for the most appropriate length of time for mixing.
3. Environmental factors
Environmental conditions that need to be considered are air temperature, CO₂ and O₂ levels. When the temperature is hot, the chicken will tend to decrease appetite so that nutrient intake is not achieved. This will lead to a decrease in egg production (hen day down) and decreased kerabang quality.
In addition to temperature, what needs to be noted is the rate of CO₂ and O₂. These two components must be balanced in the blood. CO₂ levels are very necessary for the formation of eggshells which in fact the main content of calcium carbonate. Calcium comes from feed, carbonate comes from the content of CO₂ in the blood. When chicken panting this causes CO₂ to be lost in the blood. Whereas o₂ levels will help hemogoblin function optimally in carrying feed nutrients.
Although in the cage closed house, noteworthy are wind speed or wind speed. Wind speed is too fast, will cause the chicken to lose O2. And sometimes chicken pantingthis will affect the quality of the eggs.
4. Disease Factors
Disease is a factor that has a lot of influence on the quality of eggs. It's just that usually in addition to the quality of kerabang, hen day eggs will also decrease as a result of this disease. Diseases affecting the quality of shellfish include ND, AI, IB, EDS, Coryza. In addition to the disease, cases of mycotoxins will also cause the quality of eggshells to become pale or white. These mycotoxins, especially aflatoxins will cause damage to the membrane gizzard. If the membrane gizzard the wound, then the grit will not run optimally so that the supply of calcium is hampered. Need to check the condition gizzard in chickens with white shellfish case.
Thus, I hope this article is useful.










