A common problem encountered in chicken farms is the presence of a pungent odor that disturbs the community around the location of the farm. In addition, the pungent odor can be a serious problem for the health and productivity of livestock to interfere with the comfort of cage workers.
Ammonia in poultry farming
Cage environments with strong odor conditions are usually caused by ammonia gas content that is too high. Ammonia (Nh₂) is a form of gas produced from the process of reshuffling the remains of nitrogen derived from chicken feces by decomposing bacteria (ureolytic bacteria). The Protein derived from the ration will be digested and metabolized to produce waste substances in the form of urea and uric acid that are removed along with feces. Urea and uric acid contain elemental nitrogen (N) which will be converted into ammonia (gaseous NHINTEGRATED) or ammonium (dissolved in feces) by decomposing bacteria in the environment.
There are certain conditions that can increase the ammonia content in the cage environment. Some of the things that cause the high smell of ammonia include :
- High salt and protein content
Rations with a high content of salt or protein will cause chicken feces to become wetter. Salt levels that are too high in the ration will disrupt the electrolyte balance in the body and trigger chickens to drink more so that chicken feces become wetter. This is the case with excessively high protein levels. This happens because the remaining undigested protein is converted into uric acid which is high in concentration in the kidneys so that it will trigger chickens to drink more. As a result, chicken droppings become wet and watery. Wet stools will tend to cause a higher ammonia odor.
- Cage construction and poor ventilation
The ideal distance between cages is at least 7 meters or one cage width. Disturbed air circulation due to the distance of the cage is too close, the location is close to a cliff or too many trees, will result in the discharge of harmful gases become obstructed. In addition, it can inhibit the drying of feces, as a result of which the level of ammonia gas will increase faster.
This type of battery cage can reduce the smell of ammonia by 50% than postal cages because the dirt in the battery cage will directly fall down so that it can reduce the smell of ammonia directly. But what needs to be considered from the battery cage is the height under the cage. Preferably the height under the cage is 1.25-1.5 meters. For the maintenance of laying hens in battery or stage cages, the farmer should periodically clean the manure so that the chicken manure does not accumulate too much.
- Too dense cage
The heat of the oven will cause the oven to overheat (heat stress), so that the chickens will drink more than eat. This will cause the resulting stool to become wetter. The high density of chickens can also cause higher cage pressure and air circulation is not going well.
- Quality litter bad
One of the functions litter is to help the absorption of water in the stool so that it dries faster. If the quality and quantity litter less good it will be more quickly damp and wet. This condition will of course favor the formation of ammonia. Management litter it's not good, like there's no turning back litter and the presence of drinking water spills will also increase the formation of ammonia.
Impact Of Ammonia
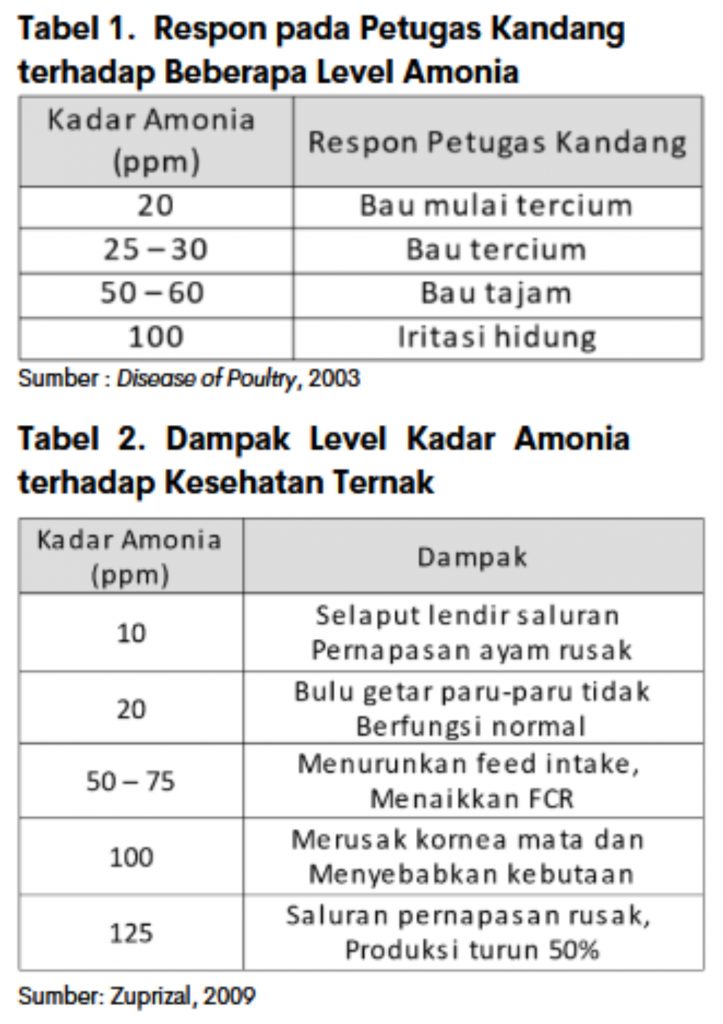
Ammonia levels that are too high can cause livestock health problems. Ammonia levels in the cage can be detected using an ammonia meter. Ammonia meters need to be placed at the right height, which is about 10 cm from the bottom of the cage or at the level of the chicken's head. In addition, the easiest way to find out the smell of ammonia is when we enter the cage and the smell of feces has started to sting, then the ammonia level has been said to be excessive. Here are some of the responses felt by the cage staff and the impact on chicken health on ammonia levels (Tables 1 and 2).
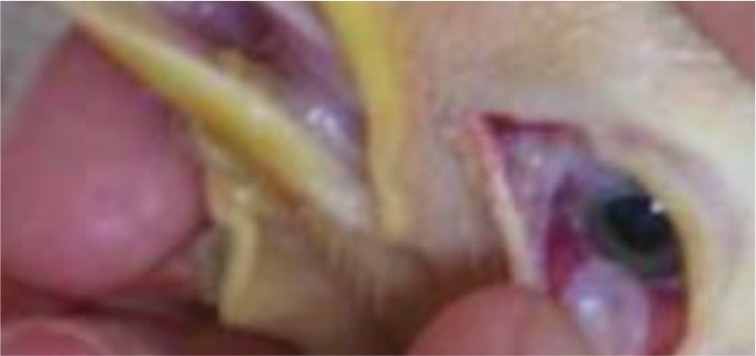
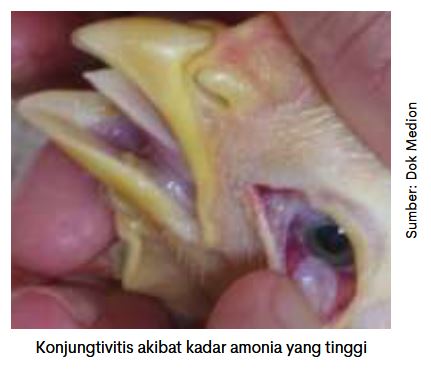
- Eye irritation disorder
Ammonia will dissolve in the eye fluid and produce ammonium hydroxide (NH₄OH), which is a component of alkaline compounds that are able to irritate and cause conjunctivitis (inflammation of the conjunctiva of the eye).
- Respiratory tract disorders
Ammonia levels with levels >20 ppm, can lead to ciliostasis (cessation of cilia movement) and desiliosis (Cilia damage) in the mucous membranes of the respiratory tract. As a result, the respiratory tract will lose its defense against foreign objects, making it vulnerable to cases of respiratory tract infections such as CRD, Coryza, ND, AI, IB and ILT.
- Immune system disorders
Not only damaging the cilia, ammonia can also damage the epithelial cells of the upper respiratory tract so that the production of mucosal immunity (IgA) will decrease. Ammonia whose levels are very high can also enter the bloodstream (due to being sucked in large quantities) and cause stress on lymphocyte cells so that the production of antibodies (IgG and IgM) is disrupted. It affects the immune system and susceptible to disease.
- Reproductive system disorders
Ammonia Gas with levels >30 ppm can cause alkalosis conditions (pH of body fluids, including blood plasma fluids are alkaline) in chickens. If the blood plasma is alkaline, then most of the plasma proteins will bind calcium ions in the blood circulation. As a result, the formation of bone/skeleton of the chicken body was disrupted and the resulting egg shells become thinner.
Ammonia Control Strategies
Peternak dapat menekan kadar amonia pada level serendah mungkin agar produktivitas ayam tidak terganggu. Kadar amonia yang aman dan belum menimbulkan gangguan pada ayam ialah <20 ppm. Beberapa tindakan sebagai strategi mengendalikan amonia adalah :
- Control of salt and protein levels
Provide a ration with the appropriate content of nutrient substances, especially the content of coarse protein and salt. The action that needs to be done is not to give rations with excess salt and protein content to chickens. In addition, make sure the ration intake is also in accordance with ration quality standards.
- Management litter
Litter the one used as the base of the cage must be of good quality (dry, not dusty and able to absorb water optimally). Thickness litter also worth noting is 8-12 cm (postal cage) and 5-8 cm (stage cage). On time brooding period,, it is necessary to perform inversion litter regularly (every 3-4 days) to avoid litter clumping. When many litter which clumps and is very moist, then it is necessary to add litter new that has been sprinkled with lime first to dry quickly. After that just stacked with litter the new one.
- Cage density setting
The density of the shed should be regulated so that it is not too full. Ideally, the density of the cage for broilers is 15 kg/m2 or the equivalent of 6-8 heads and 12-14 heads/m2 for laying hens grower.
- Cage temperature and humidity control
The air temperature in an overheated cage can be lowered with the help of blower or a fan. Installation blower should pay attention to several things such as wind flow direction, wind speed, the volume of the cage room and the chicken population. The air circulation in the cage also needs to be considered by managing the opening and closing of the curtain, adjusting the distance between the cages, and increasing the use of blower or fan (fan). In addition, the cage closed house can be a solution because it can regulate the temperature and humidity in the cage and remove toxic gases from the cage.Control the temperature and humidity of the cage.
- Stool control management
So that the feces become drier can be added materials that can bind water in feces such as the addition of zeolite or lime 1-3%. In addition, to lower ammonia levels can be added certain materials that can bind ammonia. One of the products that can bind ammonia is Ammotrol. Products Ammotrol it is a herbal product that is safe to use every day for a long time to bind ammonia without causing side effects and residues. Awarding Ammotrol also relatively easy, simply sprayed into feces or dissolved in drinking water, and can be given together/mixed with vitamins or antibiotics.
High levels of ammonia will adversely affect the health and productivity of livestock. Therefore, it is necessary to take measures to control ammonia levels.