Challenges in managing laying hens are common among farmers and often lead to suboptimal egg production. Success in layer management is generally influenced by three factors: the quality of the stock, the quality and quantity of feed, and husbandry management. If any of these factors encounter problems, egg production issues may arise. The primary performance targets for layers include egg production in terms of quantity egg mass, hen day, and long laying persistenc and egg quality, such as shell color, shell thickness, shell strength, and yolk color, among others. Optimal egg production ultimately determines profitability in layer farming.

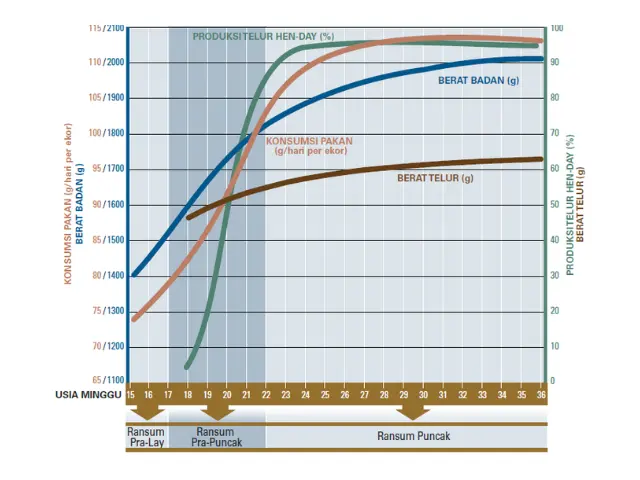
Various challenges in achieving successful layer management must be anticipated by farmers. One of the key issues is the variation in feed and raw material quality, which can result in suboptimal hen performance. Achieving performance targets based on the Hy-Line Brown Max management guide shows a clear correlation between meeting nutrient requirements and attaining optimal feed intake, body weight, egg weight, and egg production. Therefore, high-quality feed must be supported by good-quality raw materials and a properly balanced feed formulation to achieve the desired performance targets.
Egg Production Problems
Egg production problems encountered include a decline in both the quantity and quality of eggs, caused by infectious (disease) and non-infectious factors (feed, pullet quality, and management). This article will discuss non-infectious factors, especially feed. Feed plays a crucial role in achieving layer performance targets. Key feed points to consider are meeting nutrient requirements according to the production phase and achieving target feed intake in line with standards.
Meeting the nutritional requirements of feed is closely related to the nutrient matrix contained in the feed ingredients used in the formulation. Variations in the quality of raw materials can alter this nutrient matrix, leading to unmet nutritional needs. This can affect egg production performance in terms of quantity—such as reduced egg weight, shorter peak persistency, and fluctuating hen day production. From the quality aspect, eggs may exhibit shell issues such as fragility, paler color, and other defects.
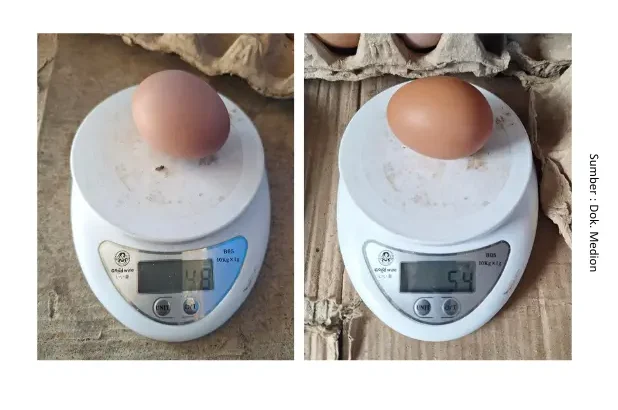

Failure to achieve standard feed intake, especially during the pre-layer phase, is a common issue in the field. Several factors contribute to insufficient feed intake, including poor feed quality, improper feed management—such as incorrect feed transition techniques during phase changes—and uncomfortable environmental conditions, particularly during cage transfer or adjustment periods. Inadequate feed intake results in nutrient quantity and quality that do not meet requirements, leading to substandard body weight growth and underdeveloped reproductive organs that cannot fully support egg production. Additionally, below-standard body weight can cause smaller egg sizes and reduced egg production. On the other hand, excessive feed intake also causes problems, such as overweight conditions that trigger excessive fat accumulation. Failure to achieve proper feed intake may lead to nutrient deficiencies, which can alter eggshell quality causing pale shells, cracks, rough textures, or soft shells.
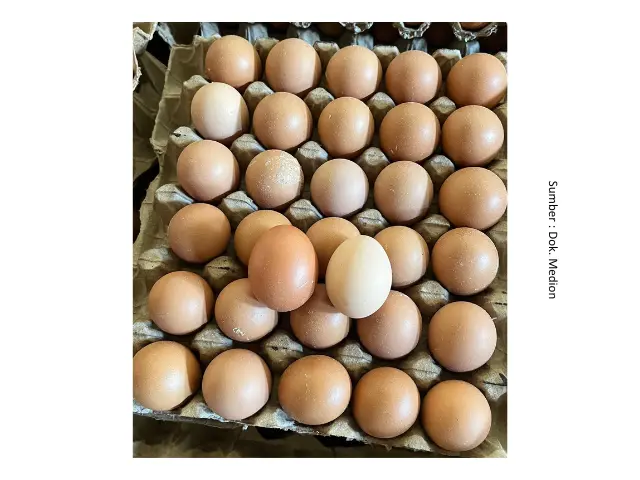
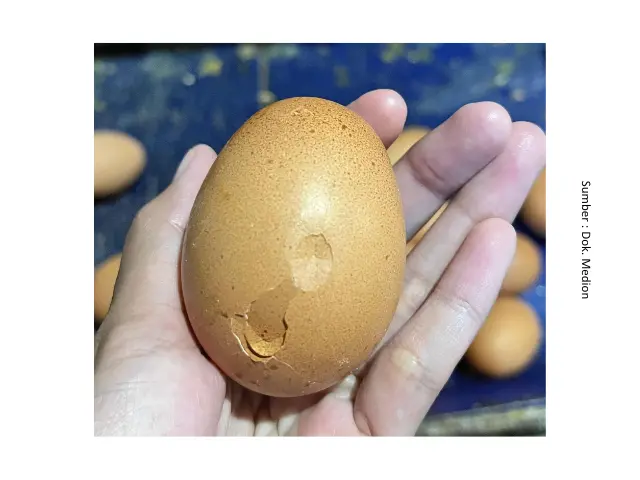
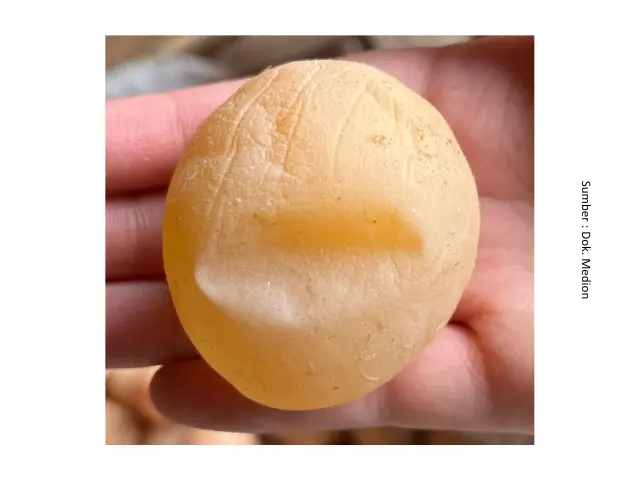
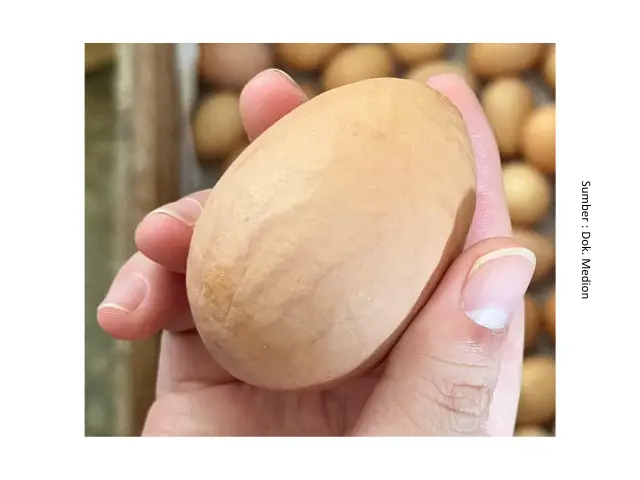





In addition to feed, poor pullet quality can also cause egg production problems. Factors such as below-standard body weight, low uniformity, and suboptimal skeletal development can lead to delayed onset of lay, uneven production age, inconsistent egg sizes, and reduced egg output. Meanwhile, management factors such as lighting, stocking density, temperature, and humidity can cause stress in hens, which in turn disrupts egg production.
Solutions and Prevention
a. High-quality feed
High-quality feed is formulated to meet the nutritional requirements of chickens, ensuring optimal performance. Quality feed is made from high-grade raw materials. Supplementation with premix serves as a backup to fulfill micro-nutrient needs, especially when the raw material quality is below standard due to ingredient variation.The composition of a premix includes feed supplements such as various minerals, vitamins, and amino acids. In addition, feed additives may include alternatives to Antibiotic Growth Promoters (AGPs), enzymes, toxin binders, and others. The use of premix can be adjusted according to the type of feed used, ensuring the composition and dosage match the birds’ requirements.For example, finished or concentrate feeds can use Mix Plus LLK13A, while self-mixing feeds can use Mix Plus LLM3A. These products help optimize egg production, egg weight, and feed conversion ratio (FCR). Additionally, combining with another premix containing trace minerals such as Endomix can help improve eggshell quality, particularly shell color.

optimizes egg production and eggshell quality

using Mix Plus LLM3A + Endomix
High-quality feed must always be accompanied by good feed management. Proper feed management aims to achieve the target feed intake, ensuring that the nutritional needs of the chickens are optimally met. Supplementation to enhance egg production can also be administered through drinking water. One example is Eggstima, an herbal supplement with various benefits that helps increase egg production, improve egg weight, and strengthen eggshell thickness.
b. Check the condition of the pullets
High-quality pullets support the achievement of optimal egg production. Characteristics of good-quality pullets include uniformity above 85% in terms of body weight, skeletal structure (frame size), and sexual maturity (sexual maturity). In addition, continuous monitoring is necessary to maintain the hens’ condition up to peak production. Monitoring includes ensuring feed intake meets the standard, body weight is on target, and uniformity is well maintained.
c. Maintenance management
Maintenance management is the art of raising layer chickens to achieve optimal production. Even when feed quality and bird condition are good, improper feed management can lead to suboptimal feed intake. This is one of the main causes of egg production problems. Therefore, it is important to pay close attention to management factors such as feed distribution, stocking density, lighting, and other environmental conditions.
From the discussion above, it can be concluded that one of the effective ways to prevent and overcome egg production problems is through supplementation either via feed in the form of premix as a nutrient backup or through drinking water using herbal supplements. In addition, these efforts should always be supported by maintaining good flock quality and proper management practices. Hopefully, this information is useful.










