Worms are diseases caused by the presence of worm infestations in the body of livestock, both in the digestive tract, respiratory, liver, and other parts of the body. Liver fluke disease is one example of a case of worms with a fairly high incidence of the disease. The incidence of disease cases in cattle reaches 60% and even 90% in West Java and 40-90% in Yogyakarta. Undeniably, the facts in the field show that liverworm disease can cause economic losses for farmers, such as:
- weight loss
- weight growth is inhibited
- deterioration in the quality of meat and offal
- decreased milk production
- the human body (Zoonoses)
Causes Of Liver Fluke Disease
Heartworm disease caused by worms Fasciola gigantica, flat leaf-like shape that attacks cattle, buffaloes, goats and sheep. Livestock can be infected from grass contaminated by larvae (metacercariae) of worms where freshwater snails act as intermediate hosts. Worm eggs can survive for 2-3 months in moist feces but quickly break down if they are dry. Adult liver flukes can live for 1-3 years in the liver of cattle.

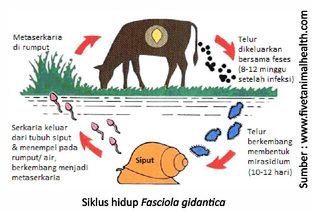
How To Diagnose Liver Fluke Disease
To diagnose liver fluke disease, it is necessary to undergo examinations, such as:
- Clinical symptoms can only be seen in severe cases. While in mild cases clinical symptoms rarely appear. Symptoms that can appear include:
- It is difficult to pass feces with dry feces
- Diarrhea in chronic cases
- Stunted growth
- Decreased productivity

- Laboratory teststhe laboratory test is carried out to confirm the diagnosis by looking for the presence of helminth eggs in the feces. This test can be done in severe or mild cases.
- Carcass surgery / examination of internal organs can only be seen in dead cattle / slaughter. The result of the examination of the organ will be found adult worm infestation of the liver, the liver becomes damaged and thickening of the bile ducts
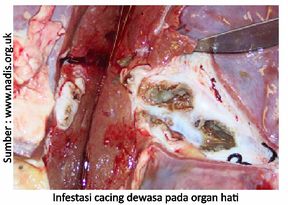
Handling and Prevention
In infected cattle, treatment can be done, among others:
- Administration of anthelmintic drugs that can eradicate liver flukes, such as Wormectin Plus/ Wormectin Plus-B
- Multivitamins such as ADE-Plex Inj/ Vitamin B Complex Injection to increase endurance and accelerate healing
- Cleaning and sanitizing the cage and farm equipment by cleaning, washing and spraying with disinfectants (Neo Antisep, Medisep) every day
- Eradication of temporary hosts, namely freshwater slugsto prevent liverworm disease, some things that must be considered include:
- In addition to the above-mentioned treatment, there is also the treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (Wormectin Plus dosage 1 ml per 50 kg body weight/ Wormectin Plus-B dosage 1 bolus per 200 kg of body weight). Deworming can be given 1 week after weaning and repeated every 3-4 months.
- Routine multivitamin givingit serves to increase the immune system of livestock, making it more resistant to disease (including worms)
- Feeding with sufficient nutrient content to maintain good endurance and add Mineral Feed Suplement S at a dose of 2 kg per 100 kg of feed.
- Improvement of feeding procedures, namely avoid taking grass from rice fields near the cage. When forced, the grass should be taken with a cut of at least 30 cm from the soil surface. Grass that comes from around the settlement or near the cage needs to be dried by drying, at least 3 days in the sun
- Avoid grazing livestock in the morning, so that livestock do not consume the wet ends of the grass that may contain metacercariae
- Eradication of temporary hosts, namely freshwater snails
- Prevent muddy cage, feces accumulate & damp
- Farms are well managed such as arranging cage density and good air circulation. High cage density will be at great risk for getting worms
- Monitoring of eggs and larvae of worms by examining feces regularly every 2-3 months in MediLab (Medion laboratory) so that when the presence of worm eggs in the stool can be detected early.











