What are the causes of scabs in the mouth of goats and how are they treated?
Pertanyaan dari Bapak Rafiq – By email
My goat has scabs around its mouth. What are the causes and how are they treated?
Answer
The scab in the goat's mouth area is a symptom of Orf disease or often called bengoran or dakangan. The disease is caused by Pox viruses of the genus Parapoxvirus it can spread rapidly in a single population.
Mainly, Orf disease affects goats or sheep but can also be transmitted to other animals such as cats, dogs and camels. It should also be noted that the disease can be transmitted to humans (Zoonoses).
ORF transmission occurs in direct contact with sick animals or indirectly through media that have been contaminated with Pox viruses. The Virus will enter and infect the body of livestock through wounds on the skin. Furthermore, the process of viral replication (multiply) will occur in the epidermal cells of the skin that cause inflammation.
Perlukaan on the skin will be formed which begins with reddish spots and lumps formed that contain fluid to pus. In the end, the wound will dry out and form a scab. The process of scab formation can occur for 1-2 months.
The incubation period of Orf disease is 3-7 days. In cattle that are young or under the age of 2 months will be more susceptible to contracting Orf with more severe symptoms. The first symptom that occurs is an increase in body temperature in the first week.
This is followed by the formation of wounds that can be found in the area of the mouth, lips and nose. In addition, it can be found also sores in the oral cavity such as tongue, gums and palate. The presence of these injuries causes the cattle to have difficulty eating or drinking due to pain.
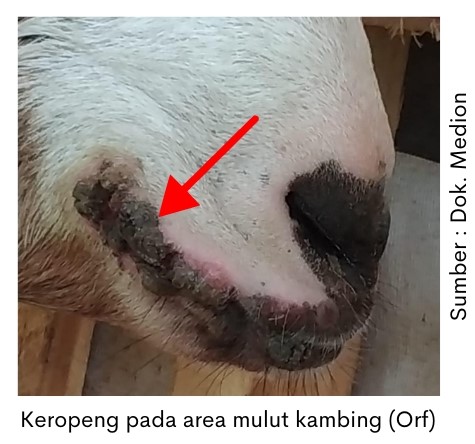
Generally, Orf is a mild disease and can heal on its own. But the healing process takes quite a long time to months. In addition, in young animals this disease can persist and can be fatal because it can reduce the level of suckling in the mother and susceptible to secondary infection by bacteria or fungi. Handling needs to be done as soon as possible so that it can be handled and not transmitted to other livestock.
Treatment of Orf disease is carried out according to existing symptoms (symptomatic) and helps increase the body's resistance to accelerate healing (supportive). In addition, it is also important to treat secondary infections due to bacteria that may occur. Here are some of those handling :
- Isolate sick cattle in quarantine pens to prevent transmission to healthy livestock.
- Clean the scab dry with exfoliated and antiseptic (Antisep) regularly every day.Take a multivitamin (Injekvit B-Plex/Vita B Plex Bolus Extra Flavor) to help the healing process and improve the immune system of livestock.Antibiotics are given to treat secondary infections caused by bacteria (Medoxy LA/Neo Meditril LA). It can be used to treat dry skin and acne (Oxytic) or antiseptic (Antisep).
It is important to take precautions even if the disease is not deadly. Orf can interfere with livestock productivity and risk transmission. Prevention can be done with good biosecurity practices. Newly arrived livestock must be quarantined for 14 days and watched for their health. Then you need to clean the cage and the surrounding environment and perform disinfection (Neo Antisep New Formula/Formades) on a regular basis.










