In the process of plant cultivation, farmers do not escape the constraints or problems. Problems can come from both biotic (plant-destroying organisms) and abiotic (soil fertility, drought, flooding, or other climatic conditions) factors. The impact can affect the quality and quantity of agricultural products.
One of the problems in the effort to increase production is plant pest organisms (OPT). Pests are all organisms that have the potential to cause disturbance or damage to plants and affect crop yields. It needs proper and effective handling in controlling pests so as not to reduce production. There are several types of pests, namely pests, diseases, and weeds.
- Hama
Caused by animals such as rats, insects, mites, snails, and other animals
- Disease of
Caused by pathogens such as fungi, bacteria, nematodes, viruses
- Weed
Caused by wild plants such as, grass, puzzle, and other wild plants.
OPT control
Pest control can be done in various ways to suppress the development of pests on agricultural land. Pest control, among others, by means of technical culture, the use of natural enemies, the use of resistant varieties, genetic manipulation, physically, and with pesticides. The selection of control methods needs to be considered so that pest control actions can take place effectively, efficiently, and also safely for the environment.
Pest control with pesticides is the most widely used way by most farmers. A pesticide is a chemical or other substance used to control the growth and development of pests.
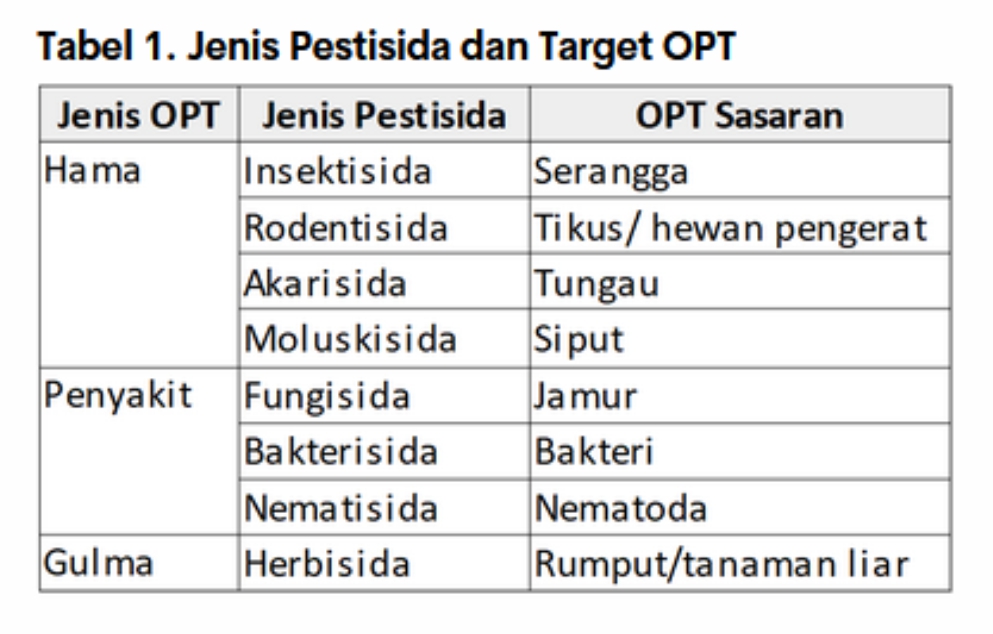
The use of pesticides in the cultivation of chili plants as pest controllers is quite high reaching 87%, compared to using other methods, namely plant destruction 2%, biological agents 1%, and other methods 10% (Directorate of horticultural Protection, 2020). There are many types of pesticides used by farmers and are differentiated based on the target or target of the pest to be controlled (Table 1).
Pest attacks that occur continuously force farmers to use pesticides to control them. The use of pesticides was chosen because it has advantages, namely efficient, effective, practical, easy to obtain, and quick control results in reducing pest populations and disease intensity.
The use of pesticides that are carried out continuously and in a less appropriate way can cause resistance to pests. Resistance is pest resistance to a pesticide. As the example in Scheme 1, the continuous use of one active ingredient can reduce the vulnerable population of the Pest from 90% to the remaining 5% of the vulnerable population of the pest. These conditions cause the pest population to become resistant.
Resistance makes the use of pesticides increasingly increase the number of doses, frequency, and composition of pesticides. The increasing use of pesticides can have an impact also on health, environmental pollution due to residues, and increasing agricultural costs.
The impact of pest resistance to pesticides is economically and socially very large. The occurrence of resistance makes the expenditure greater, since it is necessary to use higher doses. Farmers will lose money because the production target is not achieved. The pesticide industry is also losing money because the” life span " or period of time the sale of pesticides on the market is getting shorter. The public bears the risk of harm to health and the environment.
Most resistance is caused by human actions that use pesticides in a less appropriate way. There are many brands and a wide variety of active ingredients to control OPT. However, the lack of information on the use of pesticides is still limited. Therefore, efforts are needed to suppress the occurrence of pest resistance to pesticides and other negative impacts.
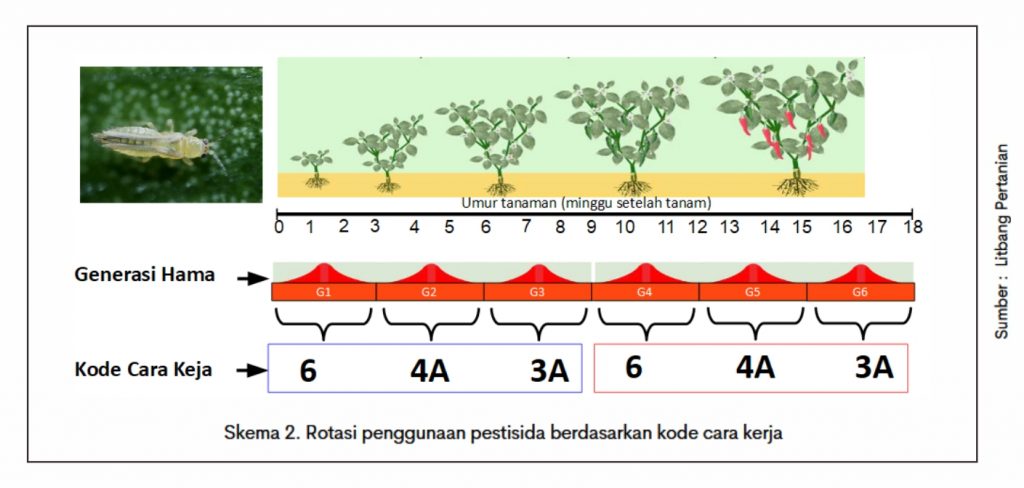
In addition, the use of antiperspirants and antiperspirants in the treatment of erectile dysfunction (Mode of Action). An active ingredient can be used for 3 weeks and the next 3 weeks are rotated with active ingredients that have different ways of working. As shown in Scheme 2. You can find the full list of ingredients on the website at (Insecticide Resistanse Action Committe) for insecticides and FRAC (Fungicide Resistance Action Committe) for fungicides. IRAC and FRAC code each mode of action to facilitate the application of rotating pesticides.
Six Proper Uses Of Pesticides
The use of pesticides needs to be done based on the conception of Integrated Pest Control (IPM). We recommend that the use of pesticides should be done with “six right” (6T), namely right on target, right quality, right type, right time, right dose or concentration, and the right way of use.
1. Right on target
Pesticides used must match the pest that attacks on the plant. Observation is needed first to determine the type of pest that attacks. As in Table 1 presented a list of types of pesticides used based on the target pest. For example, the pest that attacks is a fungus, the type of pesticide used is fungicide. For example, by using fungicides Pyrria to control the fungus Alternaria porri (purple spot)on onion plants.
2. Exact quality
Quality pesticides can be seen from the quality of active ingredients, packaging that is intact, not expired, registered and authorized by the pesticide Commission. Avoid the use of pesticides not registered, expired, damaged or suspected of being fake because their effectiveness is doubtful and can even interfere with plant growth.

3. Exact type
Pesticides used must be known to be effective against target pests and diseases but do not interfere with the development and role of useful organisms. Such information can be obtained by reading the labels indicated on the packaging or through agricultural and Forestry pesticide books.
4. On time
The right time to use pesticides is when the pest has reached the threshold of control and can cause economic losses. Spraying pesticides is better done in the afternoon.
- Morning
It still contains a lot of water vapor which causes the spray granules to be mixed with water vapor and the concentration of pesticides will decrease.
- Daytime
High air temperature that accelerates the evaporation of spray granules.
- Afternoon
Temperature and humidity are more stable with temperatures
5. Proper dosage or concentration
The dosage or concentration must be in accordance with the product recommendations that are on the package label. Lower or higher use will trigger the emergence of pests that are immune to these pesticides.

6. Exactly how to use
The application of pesticides can be done in various ways, including spraying, smoking, dyeing, smoking, sprinkling, injecting, smearing, sowing, watering, among others. Spraying is the most common way. But not all types of pests can be controlled by spraying. The application is carried out in accordance with the instructions for use indicated on the product label. It is intended that pesticides are effective and optimal in controlling pests.
Use of pesticides by spraying
In the use of pesticides, spraying application is the most widely used way. However, in its application, it is necessary to pay attention to several things in order to control OPT more effectively and efficiently. Some of these include :
a. Spray solution quality
Water is an important component in the preparation of pesticide spraying solutions. Pesticides in general have acidic properties, so in the manufacture of spray solutions required pH of water that is acidic to neutral (4-7) or with an optimal pH is 5. If the water used is alkaline, it can reduce the efficacy of pesticides.
b. Spray Volume
Spray Volume is the amount of pesticide solution used for a given area. Too much spray Volume will cause waste while too little will result in uneven spraying. Uneven spraying can affect the effectiveness for pest control. Calibration needs to be done first to find out the right spray volume for the area of land and commodities to be sprayed with pesticides.
c. Type selection nozzel
Selection nozzel perlu diperhatikan karena menentukan ukuran butiran semprot. Ukuran butiran semprot berpengaruh terhadap efektivitas dan efisiensi penyemprotan. Ukuran butiran semprot 150 – 200 mikron merupakan ukuran yang ideal untuk penyemprotan pestisida. Apabila ukuran <150 mikron, butiran semprot mudah tertiup angin dan menguap. Ukuran nozzel >200 microns make spray granules will easily fall off.
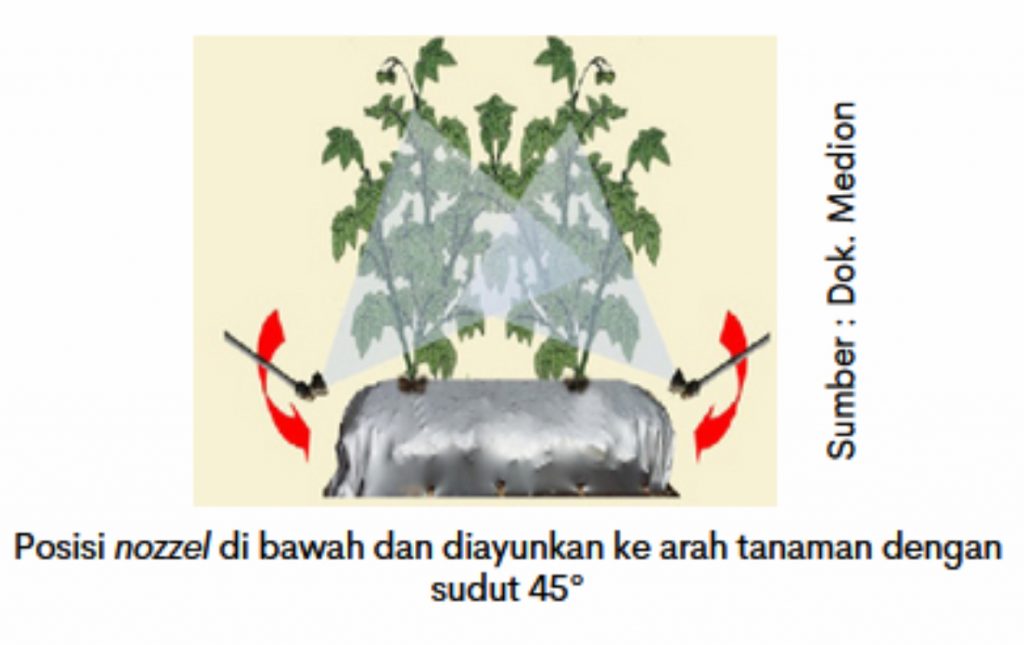
d. Direction nozzel against plants
Plant disturbing organisms (pests) are generally present on the underside of the leaves. Position nozzel below which is directed upwards and swung towards the plant with an angle of inclination of ③ 45° and the distance to the plant is more than 30 cm. This results in higher grain coverage, even grain distribution, and improved pesticide efficacy.