Government policy regarding prohibition of use Antibiotic Growth Promoter (AGP) or growth-driving antibiotics in the ration have been in place since the beginning of 2018. Some farmers reported no change in production after the policy was enacted. But not a few also of those who report that since the enactment of the ban on AGP makes the performance broiler (broiler) decreased.
The ban on the use of AGP also makes all feed producers try various alternatives to AGP so that the losses caused by the ban can be resolved. Actually quite a lot of materials that can be used as an alternative to AGP. In addition to the above, there are a number of organic compounds, such as probiotics, prebiotics, organic acids, and essential oils (essential oil), phytobiotics (herbs) and various types of enzymes. On the other hand, the ban on the use of AGP makes farmers have to increasingly focus on various corrective actions in maintenance management. So the negative influence on performance broiler can we press to a minimum.
Tighten Biosecurity
Basically every living thing, including chickens, has a natural body defense system through the work of several organs in the body. Even so, we as farmers must also develop a defense system outside the chicken's body. If the chicken is sick, it indicates that there is an imbalance between the seeds of the disease, the environment and hostels (chicken). This can happen due to the increasing number of disease seeds in the environment or the decrease in the immune system of chickens due to environmental changes such as extreme weather changes. So to minimize the number of disease seeds and prevent chickens from being infected, farmers must be able to apply biosecurity optimally as a protection system from the outside in addition to vaccination.
Maintenance management with the implementation of strict biosecurity is the right combination as the key to successful chicken rearing. The costs incurred for prevention will also be cheaper than the cost of treatment/handling when there is already a disease attack.
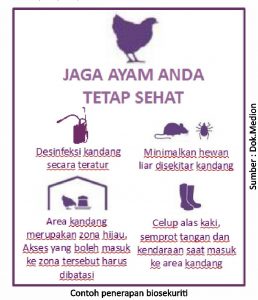
The most common application of biosecurity by farmers is the sanitation of cages by spraying disinfectants. But is this enough to suppress the seeds of the disease in the environment of farms and cages? Of course not. Literally, biosecurity is defined as a series of activities carried out to protect living beings from the seeds of disease. In chicken farming, biosecurity as an effort to prevent the entry and spread of infectious diseases into and out of the farm environment. Therefore, the application of biosecurity must be thorough, continuous and dynamic to keep chickens from disease seeds. Of course, the biosecurity system will not run effectively without involving livestock communities such as owners, manager, workers or employees of the cage and all visitors to the farm.
Although the scope of biosecurity itself is very wide, there are at least 2 important points of biosecurity that can be applied from the beginning of cage preparation, namely the implementation of at least 14 days of cage rest (calculated from the time the cage is finished cleaning), and conducting proper and perfect cage disinfection.
Optimize The Digestive Health Of Chickens
As we already know, that AGP can improve performance broiler. The mechanism of action is by suppressing the development of harmful microorganisms in the digestive tract of livestock so that nutrient absorption is more efficient. The number of bacteria in the gut (eubiosis) can only be achieved when the composition between beneficial bacteria such as Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus sp. and to the detriment of such Clostridium at least 80% versus 20% (Philip, 1993). Therefore, when AGP is prohibited, we must try to maintain the condition of the intestine to keep it balanced.
Digestive tract health and nutrition will later be related to each other. The digestive tract is the organs that play a role in receiving rations, digesting, absorbing nutrients, and removing the remaining unabsorbed rations. The nutrient utilization of such rations can only be optimally achieved if the gastrointestinal tract is in good health.
The optimum condition of the gastrointestinal tract can be described as the intact state of its structure and function or simply the maximum condition of the digestive tract function in digesting and absorbing ration nutrients. It is the management and formulation of rations that can affect the effect of the work of the gastrointestinal tract. Some parameters that can be used to assess the proper functioning of the digestive tract of chickens are:
- Good digestibility and absorption of ration nutrients
- The resulting stool odor is minimal
- Very low incidence of illness or mortality due to digestive disturbances
- Feed convertion ratio (FCR) as per standard
Not only as a place for nutrient absorption, the digestive tract is also where the immune system is formed. Therefore, it is necessary to pay attention to their health in maintaining the working system of Gut-Associated Lymphoid Tissue (GALT). GALT is part of the lymphoid tissue that serves as a site for mucosal immune response to produce antibodies and receive mucosal immune response stimulation (Marsetyawan, 1993). So that chickens are able to produce antibodies to ward off disease.
Poultry has a greater number of intestinal villi with a high ability to regenerate epithelial cells (48-96 hours), and a very fast response to the presence of inflammation. This also makes poultry more sensitive to digestive tract dysfunction in the capacity of absorbing ration nutrients.
Some of the criteria for a healthy poultry digestive tract are long intestinal villi and the integrity of the digestive tract. Intestinal villi are finger-like formations in all parts of the intestine that function to absorb food juices (nutrients) that extend from the bottom of the intestine towards the lumen (cavity) of the intestine where food is digested and absorbed from there. In principle, the longer and/or wider villi will increase the area of nutrient absorption in the intestine so that the absorption of nutrients is more optimal.

Damaged intestinal villi will decrease the ability of the intestine to absorb nutrients. Many factors influence intestinal villi damage such as primary immune system disorders in digestion, intestinal microflora balance and gastrointestinal disease challenges. Some bacterial and parasitic diseases that have an impact on digestive disorders include Necrotic Enteritis (NE), coccidiosis and Colibacillosis (dyspnea, heart and liver covered by fibrin).
Initial management for Optimal performance
On chicken broiler, time brooding period, it'S time for DOC.)chick in) until the age of 14 days (or until the heater is not used). Whether or not the performance of chickens in the future is often determined from how maintenance in the future brooding period,. Broadly speaking, in this period farmers are required to be able to create a comfortable place and conditions for DOC as a first step to achieve optimal performance.
The moment after the chicks hatch to get the first nutrients, is a critical period in triggering good growth for DOC broiler. Although after hatched DOC still has the rest of the egg yolk that serves as a source of energy, but giving rations as soon as DOC comes is still important to do. Not only to provide energy, but to accelerate the absorption of egg yolk and trigger the development of the gastrointestinal tract, so that the initial weight gain and the resulting breast meat are higher.
At this time the chicken will experience very rapid growth and includes all organs that play a role in chicken productivity. Almost all consumed rations are allocated for growth. This can be seen from the level of FCR which reached 1.03 with the growth of body weight broiler the end of the first week reached > 190 grams or 4-5 times the initial body weight (when DOC).
To bring out the genetic potential broiler this extraordinary certainly required extra attention. However, sometimes farmers are not aware of this so that negligence occurs, including:
- The house is not yet ready for the reception DOC (chick in)This condition occurs especially if the rest period (empty cage) imposed is too short, so the farmer has not had time to clean the cage or equipment thoroughly. If this happens, then the DOC will not immediately get a comfortable place to live and the high challenge of the disease.
- Cage brooding period, for reasons of efficiency, the cage brooding period, filled with chicken amount exceeds capacity. As a result, there is competition between chicks for rations, drinking and clean air.
- Chicken overheated or coldwith the assumption that the chicks should get the optimal temperature, it is not uncommon for farmers to constantly turn on many heaters even though the chicks are already rather large. As a result, chicks actually experience overheating and stress. Another case, namely cold conditions usually occur due to farmers saving too much on heating. For example, the capacity of one heater to warm 1,000 chicks, but used for more than 1,000.
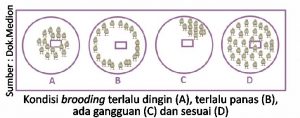
- Other cases, for reasons of fear of cold, there are breeders who completely close the curtains without providing ventilation gaps at all. Though this is not good because the air is clean (oxygen, red) in the cage will decrease and dirty air (carbon dioxide, red) increases. Coupled with management litter which is not good so that ammonia gas increases.
- Lack of regular checkingthe farmer will know that the growth and development of the chicks that are kept running optimally if the farmer diligently checks the condition of the chicks. Is heating enough, is feed intake (consumption) incoming, etc. But sometimes things like this are still ruled out.
- These events must be corrected and we prevent so that optimal chicken performance. How to prevent this so that the critical period of chicks passes well? Here are the important points to do:
During chick in, the farmer is obliged to provide good nutrition and environment, such as the following:
- Nutrition give Gingertol 2 ml / liter of water to drink in advance for the first 2-3 hours after chick in to replace the lost energy of the chicken's body immediately. It is good to drink water in warm conditions (20-24°C). This is to prevent cold shock or traumatized chickens drink water because the water temperature is too cold. At the same time, also give rations. In addition to being a source of nutrition, early ration will spur the development of villi and intestinal elongation. Giving a little at a time is better than giving all at once. The limited capacity of DOC's cache and the preservation of the freshness of the ration are the reasons for the recommendation so that the chicken's appetite remains high. Another advantage when giving rations is that the farmer can simultaneously control the condition of the chickens. Give regular drinking water after Gingertol discharged or 1-2 hours after chick in. It will be better, if the water is added Vita Chick or Imustim so that the development of the chicken body is more optimal. Content of multivitamins in Vita Chick plays a role in supporting and promoting the growth of chicks. While giving Imustim aims to increase immunity through an increase in compounds that play a role in fighting foreign substances that attack the chicken's body. If the condition of the chicks is bad (such as dry feet, dull feathers and so on) give Neo Meditril or Fithera to minimize the risk of bacterial disease cases (Korisa, CRD, Colibacillosis (dyspnea, heart and liver covered by fibrin)) and protozoa (coccidiosis) in chickens broiler.Check the consumption of rations and drinking water, 2-3 hours after the first ration through tactile cache. Consumption of rations is said to be good if at least 75% of the DOC sample is palpable chewy and soft which indicates that the chicken has consumed enough rations and also drinking water. If necessary, the farmer can conduct a re-examination 24 hours after the introduction of the ration with an indicator of 95-100%. Hard gizzards indicate that chickens do not consume enough drinking water or even consume husks (litter). But if the gizzards contain water, it is suspected that the chickens consume too much water but not with rations. If it does not reach 95-100%, the breeder is obliged to evaluate the management chick in for example, the physical quality and nutritional content of the ration, the comfort of the cage, the number of chicken ration places (TRAChicken Soup for the soul (TMA) and so on.

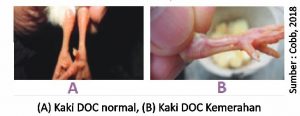
- Modification of the Environmentin 1-3 hours after chick in, perform temperature checks litter whether it is comfortable or not. One of the detection techniques is to see the condition of DOC's feet. If litter too hot, DOC's feet will be reddish and look cracked especially in the nails and soles of the feet. DOC who experience this will usually gather away from brooder. Cage temperature brooder the temperature ranges from 31 to 33 degrees Celsius (Lohman Manual Guide, 2010). On the contrary, if litter too cold, DOC's feet will feel cold (compared to our body temperature). Consumption of rations from cold or hot DOC will also decrease because DOC tends to be silent and curled up.
- No less important thing after chicken chick in is to pay attention to health factors. It is better to take a measurement of maternal antibody titer. Maternal antibodies are antibodies that are passed from a hen to her chicks. Serological tests to measure maternal antibodies can be done when the DOC. The most common test is the maternal Gumboro antibody titer test. This maternal antibody picture is useful for predicting when the right time for the first Gumboro vaccination is done. The study was conducted at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign (Medilab).Good initial growth makes the digestive system develop well and can reduce the risk of developing unwanted pathogenic microbes. In addition, the quality and adequacy of the ration in accordance with the needs of chickens will also help the development of the digestive system to produce optimal performance.
Nutritious ration
The composition of the ration can also affect the development of microbes in the intestine. The content of nutrients that are not ideal in the formulation will affect the absorption of nutrients and intestinal health. Excess nutrients such as protein will be utilized by bacteria in the intestine so that it can cause infectious diseases such as Necrotic Enteritis (NE).
Antinutrient substances in the ration also need our attention. For example Non Starch polysaccharides (NSP) which is known to bind to many important nutrients in the ration and cause an increase in viscosity in the intestine that reduces the effectiveness of endogenous enzymes and slows down the movement of the ration. The problem with other rations is mycotoxins. Broilers that consume rations contaminated with mycotoxins have shown stunted growth.
The quality of the ration must be maintained from the process of selecting raw materials to storage in the warehouse. Because damage and contamination of nutrients can occur throughout the process. Addition of enzymes and toxin can be done to improve the quality of the ration.

Monitoring Drinking Water Quality
Chickens are able to survive 15-20 days without rations, but without water 2-3 days the chicken can die. At a temperature range of 21°C, today's modern chicken will drink 1.8-2 times more than it eats. This drinking water consumption will increase as environmental conditions change. Some factors that can affect the consumption of drinking water is the environmental temperature (drinking water consumption increased by 7% for each increase in temperature 1°C environmental temperature above 21°C), the freshness of drinking water, water temperature (ideal 22-24°C), the ratio of drinking places and chicken populations, water quality and health status of chickens.
Chicken drinking water consumption can be an indication of chicken health or good / bad rearing management practices. When the chicken's drinking water consumption drops, then we must immediately evaluate the possible causes. Some of them are chickens being infected with a disease, the environmental conditions of the cage are too cold, the number and distribution of uneven drinking places, dirty drinking places for chickens, poor water quality, especially visible from the physical water (clarity and color of water), etc.
So important is water for the achievement of chicken performance. Therefore, it is time we began to realize that water quality needs to be considered properly. Therefore, carry out regular water checks to prevent greater problems from arising on the farm. And pay more attention to the cleanliness of supporting equipment for chicken drinking water supply. In both cases, supported by treatment water according to the problems that occur hopefully optimal chicken performance.
The right vaccinations for maximum productivity
In the poultry farming business, the problem of disease must always be watched out because it will harm farmers. The presence of diseases can reduce productivity and can lead to death. Preventing disease seeds from entering the farm environment and into the body of livestock is a powerful way that can be done. That is, by means of strict biosecurity and vaccination.
The purpose of vaccination is to bully the formation of immunity/antibodies from the body to prevent infection. Vaccines to be given to chickens broiler namely nd, IB, Gumboro, and AI vaccines. In order for optimal vaccination results, several factors that we need to consider are vaccination methods, such as vaccination programs and vaccination techniques. However, it needs to be supported by the quality of the vaccine used, the condition of the chickens, implementers/operators and good environmental management.
Maintenance Evaluation
In a maintenance needs to be done recording or recording. Recording it serves as a” detective " in evaluating the success of a livestock business and knowing irregularities in the management carried out. Many farmers are still ignoring recording this is so that when a case occurs it will be difficult to analyze and the causes and solutions for the next period.
Monitoring it is also important to do prevention before the disease enters and infects into a farm. Because the costs incurred for prevention are less compared to treatment. Things that should be well recorded in recording among them are the population, the number of rations, depletion (shrinkage), body weight, and health programs.
Based on the reviews above, the ban on the use of AGP in the ration has its own consequences. Therefore, we must make improvements to several factors, so that the performance of the chicken is optimal. If we do not do it then the performance of the chicken can not be achieved on target, cost the amount spent on rations is increasing, and eventually the profit from maintenance cannot be maximized. Greetings.










