Beef cattle breeding is one of the promising business potential due to high market demand. The success of fattening cattle breeding is influenced by several factors such as seeds, feed, and management or management of maintenance. One of the effects on livestock productivity is health programs. Therefore, it is important to pay attention to the health of cows in order to stay healthy and productive. If the cow is affected by the disease, it will cause losses to the farmer due to a decrease in weight, quality and additional costs of treatment and care. Disease prevention and control efforts are needed to keep cows healthy.
Characteristics of healthy cows and sick cows
Before discussing the health of livestock, it would be nice to know the characteristics of healthy and sick cows. If we recognize the characteristics of sick cows can be immediately taken action. Healthy cows exhibit the following characteristics:
- Good appetite (tends to be gluttonous) and regular drinking
- Active and responsive to changes in the surrounding situation
- Motion of the body is balanced, not stagger/ limp, move not stiff
- Clear eyes and no changes in the mucous membrane/cornea of the eye
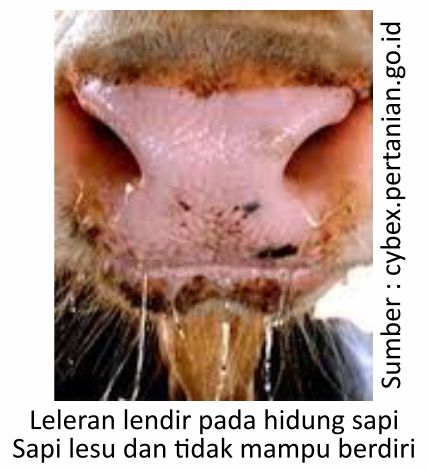
- Moist nose
- Skin / hair shiny smooth, not dull and there are no wounds
- Can rest in peace
- Normal stool density and color
- Regular breathing frequency (20-30 times / min)
- Pulse rate 50-60 times/min
- Normal body temperature 38.5-39 °C
While a sick cow can be recognized by the following changes:
- Decreased appetite and drinking
- Abnormal discharge of mucus from the eyes, nose or mouth or dry nose
- Eyes glazed, sunken and prone to drowsiness
- Drooping ears
- Fur dirty (not shiny) and standing
- Sluggish movements, difficulty standing or walking
- Diarrhea or hard stools
- Inelastic skin, dry nose and mouth
- Fever, abnormal frequency of breathing and pulse
- Cows separated from the herd
Factors affecting the health of cows
Cow health is influenced by several factors such as feed given, environmental conditions and endurance of livestock, the following explanation:
- Quality of feed provided - >Feed is an important thing in raising cattle. Feed that is nutritious, fresh and free of harmful chemicals is a good feed for cattle. Especially those that can meet the basic needs of nutrients such as energy, protein and crude fiber. If the feed given is not appropriate, there will be nutritional deficiencies that cause the target weight is not reached even cows susceptible to disease.
- Environmental conditions and hygiene - >Air circulation and changes in ambient temperature is one of the factors that affect the health of livestock. Extreme temperature changes can result in stress in livestock. In addition, the dirty environmental conditions of the cage will become a hotbed for Disease agents. Even disease agents can spread in the environment through various intermediate media. For this reason, environmental cleanliness must always be maintained.
- Livestock endurance - >Livestock body resistance is the body's defense against disease agents that enter the body. Cattle that have low body resistance will be susceptible to disease.
How to Keep Cattle Healthy?
To keep cows healthy or not susceptible to disease and get fat quickly, things to consider include:
1. Maximize feed management
Feed plays an important role in supporting productivity. Quality feeding with a sufficient content of nutrients and their quantity. The quality of feed, both grass and concentrate, which can help improve the endurance of livestock because the necessary nutrients are fulfilled. If necessary add Mineral Feed supplement s to prevent mineral deficiency and make fattening cows become fatter.
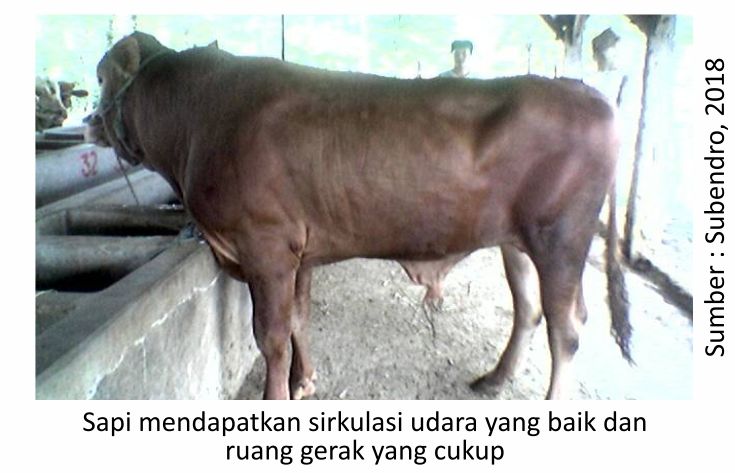
2. Convenient maintenance environment
Cows need to get good air circulation, sufficient space, minimal stress factors such as heat stress, for example by providing shade in the cage area, providing sufficient drinking water and spraying water/ artificial rain so as to reduce the heat of the cage temperature. In extensive maintenance / umbaran prevent heat stress can be done by the presence of protective plants so that livestock can be used as shelter.

3. Minimize Disease-Causing Agents in the Environment
- Maintain the cleanliness of the cage and equipment
Pay attention to cage sanitation and environmental cleanliness by not allowing cow dung to accumulate and cleaning up leftover feed regularly, and avoiding waterlogging on the ground/floor. In addition, plants and weeds around the cage cleaned and disinfected the cage regularly using Medisep, Antisep, or Neo Antisep.
- Quarantine of newly arrived cows and isolation of sick cows
Quarantine aims to ensure newly arrived cows are free from disease and avoid disease transmission. Quarantine cages need to be separate from healthy cattle keeping cages. In the quarantine Cage the cows will adapt to the new environment, including adaptation to the type of feed that will be used in the cattle business. After 7-21 days the livestock is in good health, it is ready to be transferred to the main enclosure. If a cow is positively infected with a certain disease, immediately treat it and isolate or separate it because the cow is sick as a source of disease transmission.
4. Application of health programs
To keep cows Healthy, Health program efforts are important to implement, for example:
- Supplement administration
Giving supplements to cows aims to reduce stress, increase stamina and power of the cow's body, and maintain better productivity. The administration of B-complex vitamins to ruminants needs to be included in routine health maintenance programs. B-complex vitamins can be administered at least once every 3-4 months. For example, by administering vitamins by injection Vitamin B complex or Vita B Plex Bolus. B-complex vitamins can also be given to sick cattle to help them recover from illness. Supplements can also be given to treat muscle disorders and increase energy intake before and after transportation. For example, with the administration of Bioselvita. for the energy supply of cows so that the performance becomes more optimal.
- Deworming
One disease that affects many cattle is worms. One of the control and handling of cases of worms in livestock is with a regular deworming program. Deworming is the main step in the control and treatment of worms in both calves and adult cattle. Anthelmintic/ anthelmintic administration Program should be done from a young age (age 7 days) and repeated periodically every 2-3 months in order to completely eradicate the worms and break the life cycle of the parasite. Medion anthelmintic products that can be used to eradicate gilig worms, leafworms and tapeworms in cattle are Wormzol-B and Wormectin Plus. An example of a health program for fattening cows can be seen in Table 1.
5. Daily health checks
Observation of the health of cows should be carried out at all times. The goal is to be monitored if there are health problems of cows are monitored and find out whether there are abnormalities in livestock so that if found sick cattle or abnormalities can be immediately handled.
Livestock health control is an inseparable part of the livestock business system, especially fattening cattle, because it is an important factor that Spurs productivity in raising livestock.










