Newcstle disease (ND) is one of the viral diseases that often infect poultry, especially chickens. Diseases caused by viruses Paramixovirus-1 (APMV-1) it causes respiratory, gastrointestinal, nervous, and reproductive system disorders to result in 100% mortality in unvaccinated chickens.
The impact that disturbs farmers in addition to high mortality is a decrease in egg production and hatching, as well as growth disorders. ND disease is one of the endemic diseases in Indonesia, so cases of this disease are often encountered by farmers.
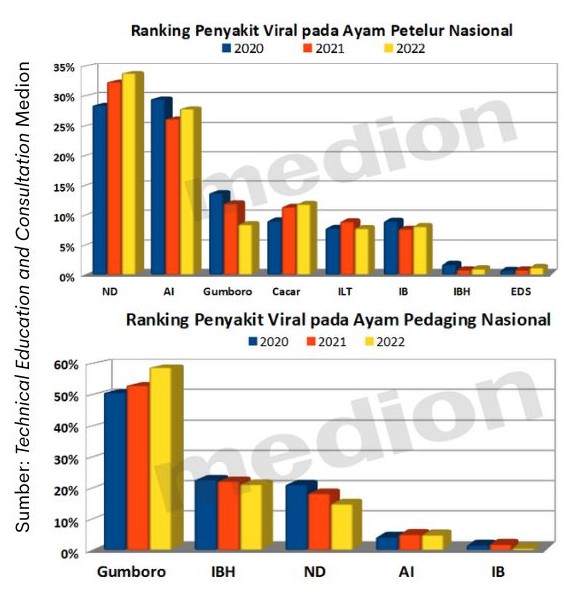
It can be observed from the data collected by the Medion field team, it can be seen that ND disease still ranks first in viral diseases that often appear in chickens layer and the third stage in chickens broiler. ND cases in 2022 in chickens layer increased from previous years. One of the things that affect the occurrence of extreme weather changes so that chickens get sick easily.
Characteristics of APMV-1
This Virus with a size of 150-250 millimicrons is an amplified virus with ss – RNA genetic material. The ND Virus is sensitive to heat, dies at a temperature of 50°, but at a temperature of 37° it can persist for 1 Week, at a temperature of 22-28° it can persist for 2 months, and months on frozen carcasses.
In addition, APMV - 1 is inactivated by ph ° 2 and is sensitive to disinfectants of various classes such as Oxidating Agent (Antisep and Neo Antisep), Ammonium Quartener (QUAT)Medisep and Zaldes) nor aldehyde (Sporades and Formades).
Virus ND memiliki beberapa protein penting yaitu protein Matrix (M), Hemaglutinin-Neuroaminidase (HN), protein Fusi (F), Nukleocapsid (N), Phosphoprotein (P), dan Large Polimerase (L).
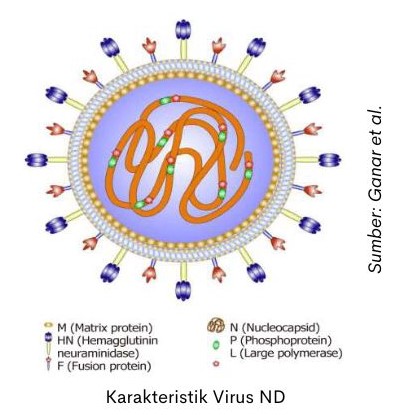
Two important proteins in ND viruses are HN and F. Protein H is a viral surface protein that functions to attach to and bind to host cell receptors. Part N is an enzyme that causes the release of the virus from the host cell. While the F protein causes the fusion between the virus envelope with the host cell membrane so that the virus genetic can be transferred into the host cell.
Classification of ND viruses
By pathotype (degree of malignancy), nd viruses are classified as follows:
- Velogenic: a high level of violence
- Mesogenic: the level of violence is
- Lentogenic: mild degree of violence
- Apathogenic enterotropic: non-malignant nd virus.
While based on the genotype (amino acid composition), nd viruses are classified into two classes, namely Class I and Class II. Type nd class I predominantly attacks on waterfowl with low virulence, while type nd class II attacks on land birds (commercial birds, turkeys, etc.) with low virulence (the majority of virulence).
Based on research conducted by Dimitrov, et al. (2019), currently type nd class II is differentiated into 21 genotypes (genotypes I – XXI). Tipe ND genotipe VII mendominasi di wilayah Asia Tenggara (Pandarangga, et al., 2020).
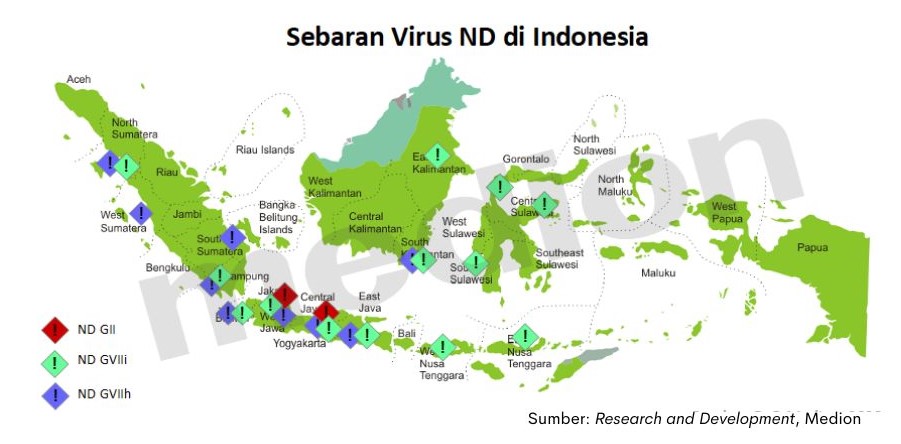
Medion team also actively follow the progress of the deployment and updates nd virus circulating in Indonesia. Based on the findings of the Medion team to date, the dominance of circulating nd viruses is ND GVIIi and GVIIh with a distribution in almost all regions of Indonesia.
Factors predisposing to the disease ND
The cause is still the emergence of ND disease in Indonesia due to several factors, including:
a. Internal factors of chickens
There are a number of ways to increase the life expectancy of a dog, such as by increasing the life expectancy of a dog, increasing the life expectancy of a dog, and increasing the life expectancy of a dog (layer) faster weight gain, and lower FCR (broiler). But it also has disadvantages such as being more sensitive to the environment and getting sick more easily. Therefore, if the management and environmental conditions are less comfortable for chickens, chickens will be more easily stressed. The immune system of chickens is also weaker, so chickens get sick easily when supported by the number of disease agents that also increase.
b. Environmental factors
The current weather conditions are less uncertain. Extreme weather and climate changes greatly affect the stress and endurance of chickens. Rainfall tends to be high (especially in late 2022 to early 2023) causing humidity to increase, decreasing water quality, and disease agents in the environment to be more resistant.
c. Management factors
Some examples of management that need to be considered because it can be a direct or indirect trigger for the emergence of ND disease are Cage sanitation, regulation of faecal discharge (nd virus contamination), and regulation of air circulation in the cage.
d. Factors of vaccine compatibility with viruses circulating in the field and immunosuppressed diseases
The selection of the right type of vaccine is very influential on the success of vaccination in warding off virus attacks. Therefore, the use of homologous vaccines is necessary. In addition, the presence of immunosuppressant diseases such as Mycotoxicosis, CRD and coccidiosis also affect the weakening of the chicken's immune system. As a result, the formation of antibody titers will not be optimal when there are immunosuppression factors.
Clinical symptoms and anatomical pathology of ND
Clinical symptoms of ND disease are still relatively the same as in previous years, namely the emergence of disorders in the respiratory tract, such as gasping or the sound of snoring, chicken weakness, decreased appetite, dull feathers, green diarrhea mixed with White Moss and still found chickens experiencing torticollis.

In quantity, egg production decreased varies from 7 to 60%, in terms of the quality of eggs from chickens infected with ND is usually pale in color with a small egg size or shaped like a mango (mango shape) in laying hens. As for the death rate from ND infection varies from 5-100% depending on the type of ND that attacks.

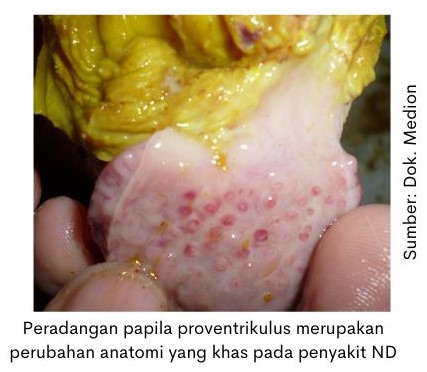
Anatomical pathologies that are seen when surgery is performed on chickens with clinical symptoms leading to ND include the presence of inflammation in the respiratory tract, such as laryng and trachea. In the digestive tract, there are typical changes, namely inflammation of the papillae of the proventriculus and the presence of enteritis accompanied by inflammation of the lymphoid organs peyer patches the caeca tonsil. In the reproductive system, inflammation of the ovaries and their flabby (powdery) shape are found.
Clinical symptoms and anatomical pathological changes in the field are varied and are often confused with other diseases such as AI, IB, CRD, AE, Marek, etc. Therefore, confirmation by lab tests is needed, for example, such as HI serology tests Test to detect the presence of antibodies and help direct the diagnosis. To detect the presence of ND virus can be done using a PCR test and sequencing.
Based on the observation of the Medion team, ND disease can be found singly or in combination with other diseases. During 2022, pure ND disease indeed still dominates. However, compilations with other diseases such as with AI, Gumboro, CRD, Colibacillosis, etc.are also widely found as illustrated in the diagram below.
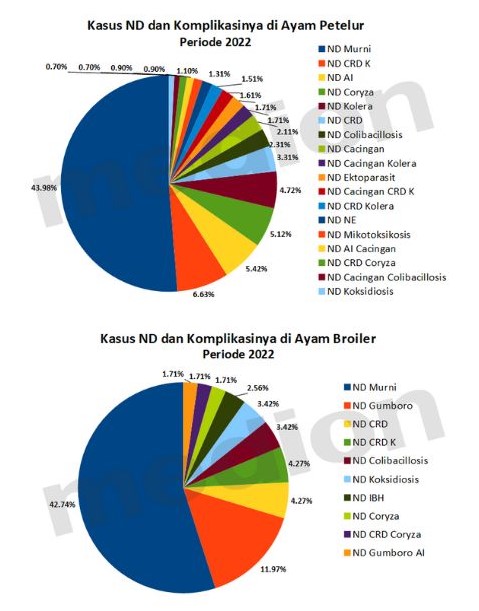
The presence of complications with other diseases, can increase the severity of ND disease that will affect the cure rate.
Nd Disease Control
ND disease can be prevented by combining vaccination and biosecurity. Some things that must be considered in ND vaccination, namely proper vaccine selection, timely vaccination, and proper vaccination application. All three are spelled out in several acts below:
a. The quality of the vaccine is good
Use the ND vaccine whose seal is still intact, the active vaccine does not change its shape, the inactivated vaccine does not freeze and is still homogeneous, the vaccine has not expired, and the label is still properly installed.
b. Use homologous vaccines
Vaccines that are homologous to the airy virus will provide better and optimal protection. Nd cases in Indonesia are currently dominated by type nd GVIIa/i and GVIIh. One of the ND vaccines that are homologous to the ND virus circulating in Indonesia is Medivac ND T Emulsion.
This vaccine contains a virus Newcastle disease (ND) genotipe II (strain La Sota) dan isolat lapang terkini yang termasuk ke dalam genotipe VII yaitu strain MD54 dan MD65 yang mampu melindungi terhadap ND genotipe GVIIh dan GVIIa/i.
In addition to single nd vaccines, Medion also produces inactivated nd vaccines that are homologous in combination with other disease vaccines such as vaccines Medivac ND G7-AI Subtipe H5N1 & H9N2, Medivac ND G7 Emulsion, Medivac ND G7-EDS Emulsion, Medivac ND G7-EDS-IB Emulsion, Medivac ND G7-IB Emulsion, Medivac ND T-Gumboro L Emulsion, and Medivac ND T-IBH Emulsion.
In addition, active vaccines such as vaccines Medivac ND-IB Spray, Medivac ND Spray, Medivac ND La Sota, Medivac ND Hitchner B1, Medivac ND Clone 45, or Medivac ND-IB still it needs to be given to bully the formation of local immunity. Local immunity will protect the mucosa to which the agent of the ND disease enters. So with good local immunity, it will minimize the entry of ND disease infection.

c. Correctness of the compilation of the vaccination program
The preparation of the vaccination program needs to consider the age of the disease, the age of the chicken, antibody titer monitoring data, and the type of ND vaccine used.
The active nd vaccine will bully the formation of antibodies faster than the inactivated nd vaccine. Ie within 2-3 weeks post vaccination. While the inactivated nd vaccine takes 3-4 weeks to provide protective immunity. Nevertheless, the protective antibody titer produced by the inactivated nd vaccine lasts relatively longer than that of the active nd vaccine.
Nd vaccination in broiler chickens can be given 1 time by vaccination hatchery or vaccination in the cage at the age of 4 days with an active vaccine as well as an inactivated vaccine. However, in chicken layer nd vaccination is given 4-5 times before entering the egg-laying period.
First nd vaccination as in chickens broiler. Repetition of ND vaccination in the production period if using an active vaccine can be done once every 1-2 months, while if using an inactivated vaccine can be done once every 2-3 months.
The exact revaccination schedule can also be based on the results of monitoring antibody titers against ND. Medion Laboratory (MediLab) currently has spread in several areas of distribution in various regions, can help farmers provide laboratory testing services, especially for HI serology test Test.
Especially when the first nd vaccination in the cage at the age of 4 days, farmers should provide active and inactive nd vaccinations. The goal is for antibody titers to form quickly and last longer. The first antibody to work comes from the active vaccine, then the antibodies from the inactivated vaccine continue.
Thus, when the antibody titer of the active vaccine begins to fall (the immunity of the active vaccination result is quickly formed but quickly falls), the antibody titer of the inactivated vaccine result (the immunity of the inactivated vaccine is slowly formed but lasts longer) is still above protective (protective).
d. Pay attention to how to handle / handle the ND vaccine from purchase to administration to chickens
- When distribution and temporary storage, the temperature of the ND vaccine should always be conditioned at a temperature of 2-8 ° C.
- Before giving it to chickens, do not forget about the process thawing. Thawing aim to raise the temperature of the vaccine that was previously 2-8 ° C to close to the body temperature of the chicken (41 ° C) or until the vaccine does not feel cold again, that is, with a temperature of about 25-27 ° C. Once in-thawing, nd vaccine should not be put in the refrigerator again/marina cooler because it can lower the potency of the vaccine.
- Previously, 2-8ºC was close to the body temperature of the chicken (±41ºC) or until the vaccine did not feel cold again, that is, with a temperature of about 25-27ºC. Once in-thawing, nd vaccine should not be put in the refrigerator again/marina cooler because it can lower the potency of the vaccine.
- The active nd vaccine must be discharged for a maximum of 2 hours, while the inactivated nd vaccine must be discharged within 24 hours.
- If the ND vaccine is not used up within this period, then the rest cannot be stored for later use again. The rest of the vaccine and the package must first be soaked in disinfectant, and only then removed/buried.
e. Make sure the dose of ND vaccine given is correct
f. Before being vaccinated, chickens are in healthy condition and not in immunosuppressed conditions (eg stress or crd disease, Gumboro, mycotoxins, etc.) which can reduce the optimization of antibody titer formation.
g. The skills of the vaccinator must be good for the vaccination application to be done correctly. In the production period of laying hens, nd revaccination must be given, but it should not only be based on calendar calculations. In order for the determination of the revaccination schedule to be more precise and not too late, you should carry out routine antibody titer monitoring every month. With timely revaccination, the antibody titer in the chicken's body will always be maintained at a protective level.
Other important efforts are being made to support vaccination and the successful prevention of ND, including:
Good management treatment needs to be considered to reduce the possibility of stress and immunosuppression in chickens. Strive for conditions litter keep dry and ammonia concentration low. High ammonia levels cause upper respiratory tract irritation that can trigger respiratory disease infections.
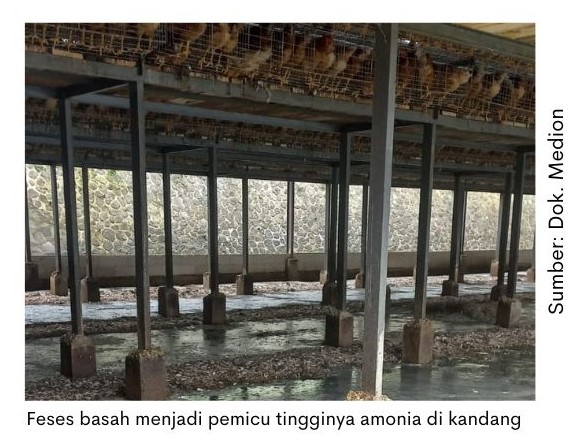

- Also adjust the density in the cage to minimize stress. Make sure the air circulation in the cage is sufficient, wherever possible do the system “all in all out” and the application of cage rest for at least 2 weeks.
- Multivitamins such as Vita Stress or Fortevit plays a role to increase the stamina and endurance of the chicken. Give Imustim, herbal immunostimulants that can help improve the functioning of the immune system. Awarding Imustim before and after vaccination has been shown to work by accelerating the increase in antibody titers from vaccination. Imustim 0.5 – 1 ml per 2 liters of drinking water is given 3 consecutive days before and after the vaccination period so that the vaccination results are more optimal.
- In addition to vitamins, premixes can also be added to the ration so that the metabolic processes of the chicken's body's defenses go to the maximum.
In addition to the vaccine, biosecurity also plays a very important role. The need to tighten biosecurity aims to minimize disease agents present in the environment. Some things to note are:
- Limit the traffic of people / vehicles coming in and out of the cage. If entering the enclosure, disinfect both vehicles and personnel, especially if coming from an infected farm enclosure. It is possible that feces contaminated with the ND virus are carried through vehicle wheels / footwear.
- Perform cage and equipment sanitation (cage cleaned, washed and sprayed) with Neo Antisep or Medisep, preventing guests, stray animals and other pets from entering the enclosure environment. When it is happening outbreak then spraying is done every day because the transmission of the ND virus can occur through the air. Sanitize drinking water by providing antiseptics such as Desinsep or Neo Antisep to suppress disease transmission through drinking water.

- Avoid the presence of other birds in the cage. The existence of other birds of different species can be an infectious agent for the emergence of ND cases.
- Avoid contact or visits to the bird market before entering the farm area. Live bird market (LBM) or live poultry market is one of the potential places to be a source of disease transmission.

Those are some of the things related to the latest ND developments. Vaccinate with homologous ones, tighten biosecurity, and optimize the immune system of livestock by providing supportive such as vitamins or immunomodulators. May be useful.










