Starting in 2022, it is appropriate that we evaluate the performance of the livestock business that has been passed in 2021. There are some important notes that need to be underlined, especially regarding poultry health problems for one year ago. The analysis note is expected to be a learning and evaluation material so that the idea of maintenance business in the next year is better and the productivity and profit obtained is maximized.
Review Of Poultry Disease Cases In 2021
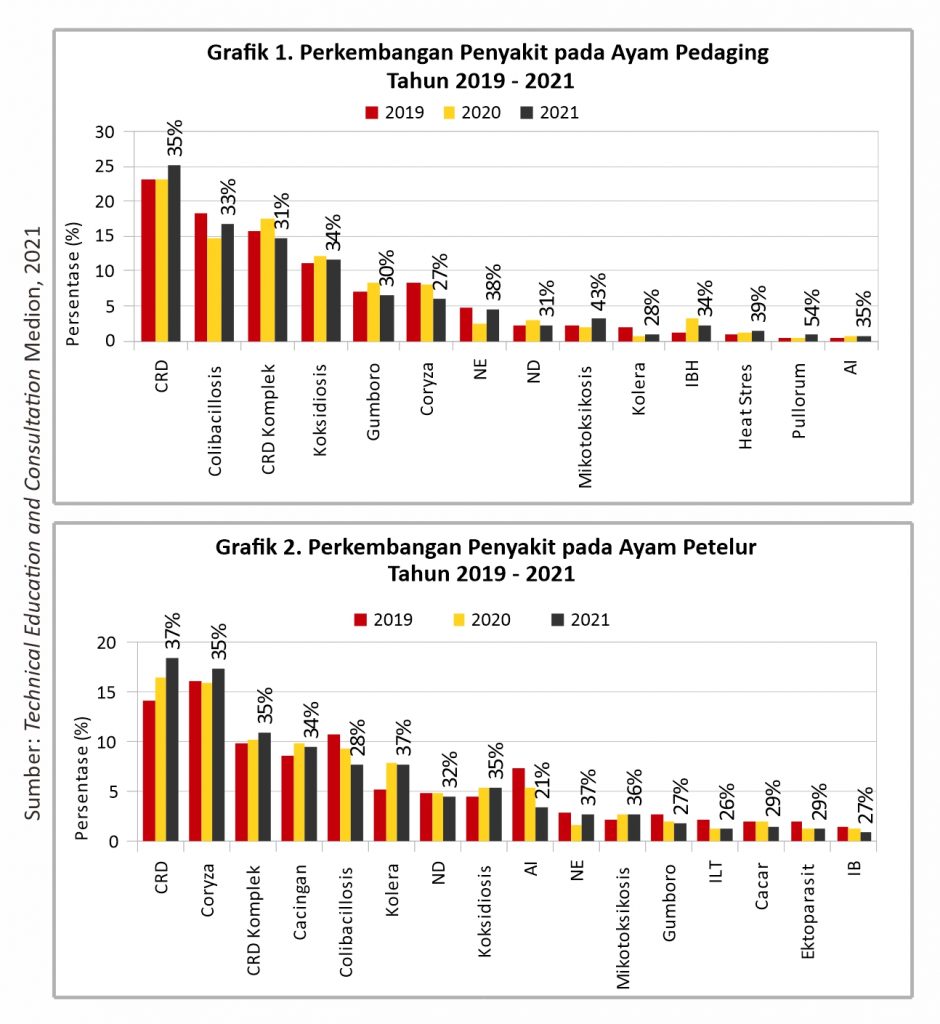
The development of the disease during 2021 in broilers and layers has been summarized by the team Technical Education and Consultation Medion on graphs 1-4. The poultry diseases that occurred in 2021 are still relatively the same as the disease patterns that occurred in previous years.
In 2021, there were no new cases of the disease. The type of disease that exists is still relatively the same as the previous year. CRD became the most frequent disease in broilers and laying hens just like the previous year. Where the predisposition to the disease is due to mismanagement such as air needs are not met properly, cages that are too dense, high ammonia levels, temperature and humidity when brooding period, not as needed, etc.
- Broiler diseases
In 2021, cases in broilers were dominated by bacterial diseases such as CRD, Colibacillosis, and complex CRD. This bacterial disease is dominated by diseases that affect the respiratory and digestive systems. Coccidiosis disease caused by protozoa tends to be high almost similar to previous years. For viral diseases that are still high in attacking broilers, namely Gumboro, followed by ND and then IBH. What is striking in farm broilers are increasing cases of mycotoxicosis from the previous year. This is thought to be due to a lack of attention to feed storage management and control of fungal contamination. NE cases also increased compared to the previous year.
- Diseases of laying hens
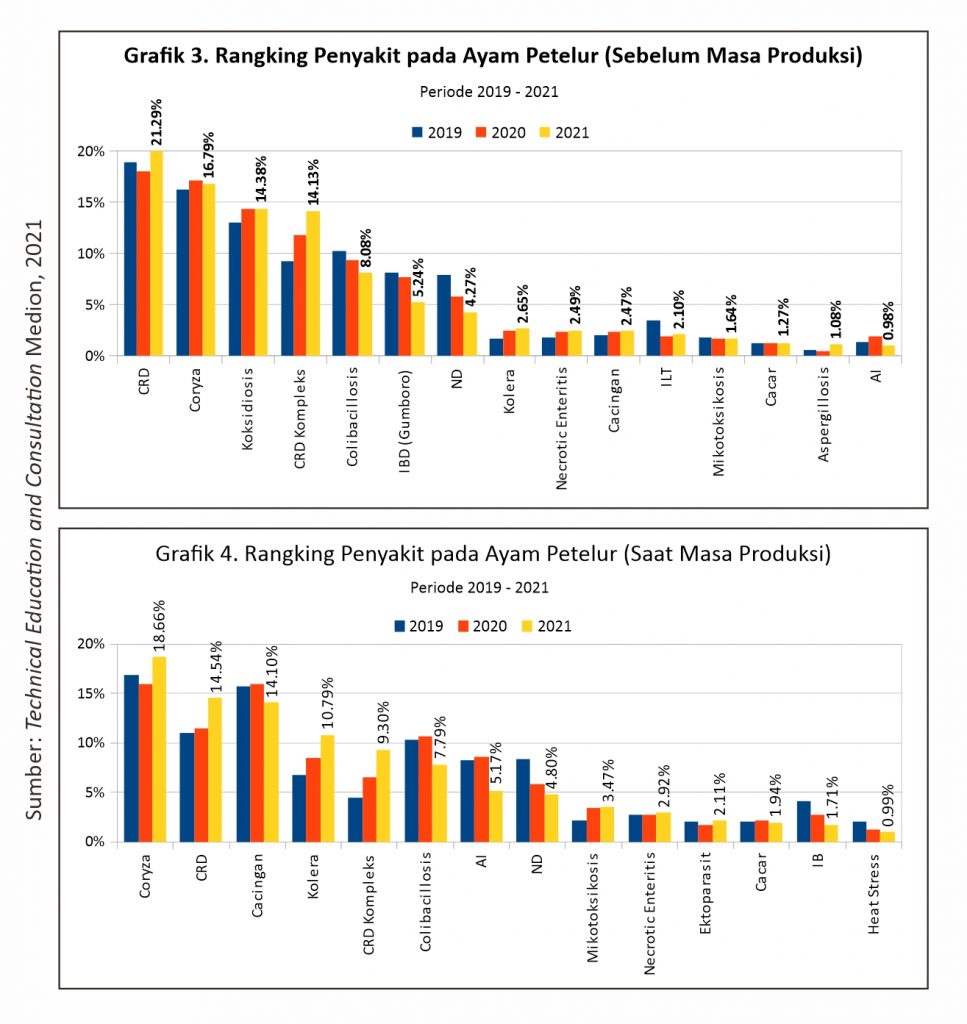
In laying hens the top three diseases have increased quite significantly. Bacterial diseases such as CRD, Coryza, complex CRD, Colibacillosis and cholera are still common. In addition, the disease of worms ranks 4th in diseases of laying hens. For viral cases in laying hens, nd, AI, IB and ILT diseases are the most common in 2021. When stripped in more detail from the maintenance phase, in laying hens pullet period or before production (0-18 weeks) cases of CRD and Coryza predominate. The top viral diseases are Gumboro and ND. In laying hens of the production period (more than 18 weeks) the first rank is occupied by the predominant bacterial disease is Coryza. Then parasitic diseases of worms in the second position as well as other bacterial diseases such as colibacillosis and CRD. As for viral diseases dominated by AI, ND and IB.
Berulah Breathing Disorder
The anatomical structure of the chicken that does not have a barrier between the nose and the oral cavity and the increase in ammonia causes irritation of the respiratory tract in chickens so susceptible to respiratory diseases. Some diseases that often attack especially during the rainy season such as CRD, Coryza, ND, IB, and AI.
This is supported by the factor of uncertain weather conditions in Indonesia, causing the condition of the chicken's body to be easily stressed, triggering the emergence of respiratory cases. In addition, it is suspected that due to the humid conditions of the cage environment so that viruses and bacteria are quite stable and easy to develop.
Diseases such as AI with viruses that mutate easily require special attention. From 2016 to 2021 the AI H5N1 virus was only found clade 2.3.2. and there is a change in the character of clade (different in amino acid composition) at the end of 2019. While Low Pathogenic Avian Influenza (HPAI) is still found and causes a considerable decrease in egg production. Although it has also spread Low Pathogenic Avian Influenza (HPAI) which has an impact on declining egg production, but farmers still need to be aware of any type of AI disease that can attack chickens.
While in Coryza disease, the team Research and Development Medion has done mapping bacteria that cause coryza in Indonesia. Based on the isolate data collected by Medion, currently the bacteria Av. paragallinarum found in Indonesia, it belongs to serotypes A1, C1 and C4. Especially the dominant serotype C4 was found in 2015-2021 and has been widely spread in several regions in Indonesia such as Bandung, Banjarmasin, Jambi, Kendal, Samarinda, Semarang, and Sukabumi.
The percentage of mortality and morbidity of respiratory diseases is quite varied depending on the malignancy of the infectious agent that attacks, the severity, the condition of chicken immunity and the presence of other diseases that follow. In diseases caused by ND can cause mortality and morbidity up to 100%, AI can cause mortality and morbidity 50-100%, IB with morbidity up to 100% & mortality up to 82%, while ILT with morbidity 50-100% and mortality 5-70% in general 10-20%. In bacterial diseases Coryza morbidity reaches 20-50% and mortality 5-20% (source: Disease of Poultry). The results of the analysis in this field will vary depending on the immune status or vaccination program that has been done before.
IBH events still exist
Based on the results of monitoring the case analysis report conducted by the team Technical Education and Consultation Medion (2021), IBH disease is included in the top 5 cases of viral diseases in broilers in the January-June 2021 period. Cases increased in March and decreased in June. While in laying hens, IBH cases are very rare, but they are still in the top 10 in the ranking of viral diseases in the last 3 years, so you still need to be aware.
IBH disease is widely reported to spread, especially on broiler farms at the age of 3-4 weeks. Chicken and chips (breeder) it can also be attacked. IBH infection in chickens breeder those of a subclinical nature deserve special attention in view of their detrimental effects in particular on the vertical transmission of the virus (from mother to Chick).
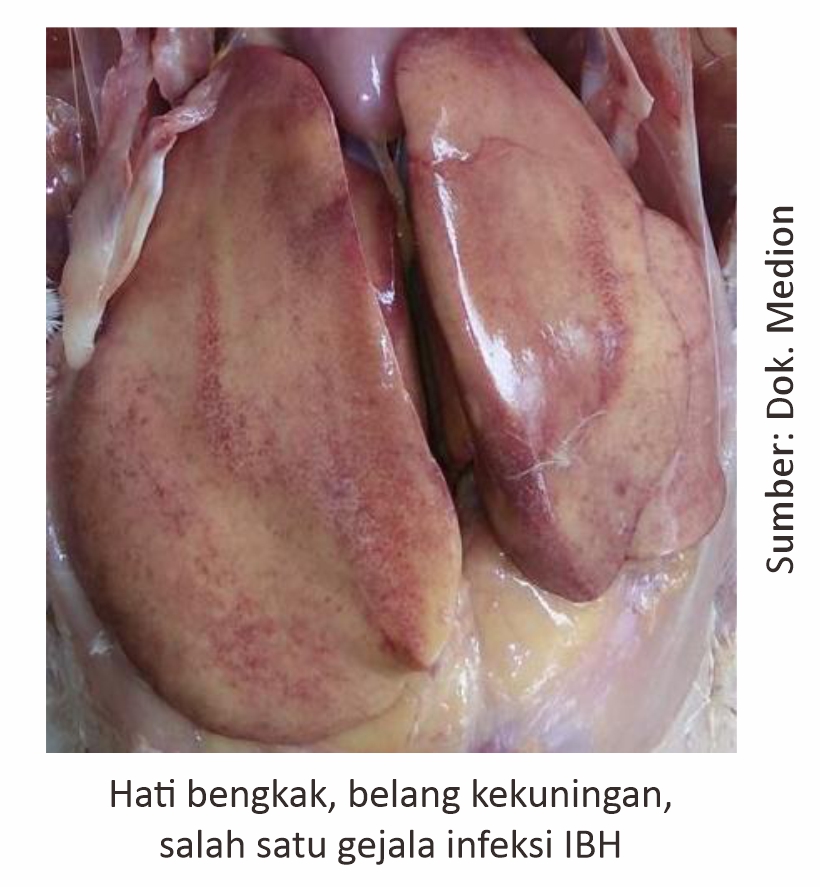
The possibility of IBH can also be triggered from immunosuppression factors such as Gumboro infection or increased mycotoxins in feed that cause decreased immunity. Supported also by uncomfortable environmental conditions that create stressful conditions for chickens (unsanitary environment, overcrowded cages, extreme weather conditions, and the challenge of many disease agents). The persistence of IBH cases can also be attributed to the possibility of uneven implementation of vaccination programs to prevent losses caused by this disease. So it still needs to be adjusted to the program or selection of vaccines that match IBH conditions in the field.
Gumboro Cycle Stop
If you look at the ranking of diseases during 2019 to June 2021, Gumboro disease in broilers ranks first for viral diseases then followed by ND at Rank 2 (Graph 1). In laying hens before production, Gumboro still consistently ranks first in cases of viral disease (graph 3), so this certainly needs to be our collective vigilance.
The Gumboro Virus found in the field is very virulent Gumboro (vvIBD) virus/virus Gumboro yang sangat ganas. The level of malignancy seen in the ability of the virus that can cause high mortality. Clinical symptoms and pathological changes in Gumboro disease caused by vvibd virus are similar to classic Gumboro virus virulent strains. However, the symptoms and changes caused by the vvibd virus attack will be more severe with hemorrhoids bursa Fabricius and muscle tissue and takes place acutely.
Why is the Gumboro case still recurring? Onset outbreak Gumboro in the field is influenced by many factors including:
- Challenge or Gumboro virus challenge in the environment around the high cage like challenge outbreak vvIBD.
- Viral characters are able to survive in the environment for a long time
- Management brooding period, less than optimal
- Sanitation and biosecurity cages are not optimal
- Too short a cage rest period
- Improper Gumboro vaccination schedule
- Gumboro vaccination application is less precise.
Mycotoxicosis lurks laying hens
Cases of mycotoxicosis are starting to spread again on farms, especially broilers, throughout 2021. Mycotoxins, a real threat that cannot be underestimated. Mushrooms develop easily at any time on the storage of raw materials or the ration itself, even in the rainy season as it is today. If this is not anticipated with good ration storage management techniques, mold will grow and mycotoxins will be produced. The shelf life of a good chicken ration generally lasts for 21-30 days from the date of production (batch). While the storage of rations in a damp warehouse will certainly cause damaged rations within 2-3 days. The longer storage of raw materials ration can increase the intensity of fungal contamination. The fungus itself is easily visible, but the mycotoxins / toxins are invisible to the eye. If it is constantly consumed, then even treatment is difficult to achieve.
Even broiler farmers who usually use rations need to follow carefully. The reason is because it turns out that there are also many finished rations that as a result of being stored in “potluck” conditions can be an ideal medium for mushrooms to grow and produce toxins. Mycotoxicosis attacks are also immunosuppressive (lower immunity), so they can cause vaccination failure and chickens are susceptible to other infectious diseases.
Digestive problems in the non AGP Era
Farmers who want to get optimal productivity are faced with the incidence of bacterial and protozoan diseases that are still quite high. With the Prohibition of AGP, it will affect the health of the gastrointestinal tract to prevent diseases in the digestive tract. The perceived impact of banning AGP is still high gastrointestinal diseases caused by bacteria such as Necrotic Enteritis and Colibacillosis, as well as due to protozoa that is coccidiosis. This can lead to a decrease in the performance of broilers and laying hens.
Based on data collected by the team Technical Education and Consultation Medion, after the ban on AGP in 2018, there was an increase in cases of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract such as Colibalicollis, coccidiosis, and Necrotic Enteritis. This increase in cases occurred until 2020 in laying hens (graph 2), while in broilers Colibacillosis cases decreased in 2020 (Graph 1). In 2021, Colibacillosis and coccidiosis are likely to decrease, but the incidence of the disease Necrotic Enteritis still experiencing an increase from previous years. Still high enough cases of gastrointestinal disease indicates that the Prohibition of AGP affect the incidence of disease in the digestive system. This indicates that an alternative solution to replace AGP is needed to reduce the incidence of disease. Such as herbal programs that can be used as supporting health programs. The preparation and implementation of the herbal program aims to prevent disease, improve health and accelerate recovery if livestock is attacked by disease.
Poultry Health Projections 2022
From all the data that has been summarized, it is estimated that chicken diseases in 2022 will not be much different from 2021.
- The year 2022 types of diseases are similar to previous years.
- ND, AI, IB, IBD will still show their existence & remain cautious of IBH. Considering that at the beginning of 2022 some regions have entered the rainy season, it is not impossible that events such as ND and AI will increase in number.
- The development of the virus needs to be constantly monitored, especially ND, AI and Gumboro which are easily subject to changes or mutations of the virus. And monitoring of bacteria H. Paragalinarum the cause of Coryza disease where cases of the disease are always repeated on farms.
- Respiratory bacterial diseases (CRD, CRD K, and Coryza) and digestive such as coccidiosis are still predominant. This is related to the weather conditions and the environment of the farm where the air quality decreases. Moreover, the lack of attention to the sanitation of the cage environment can facilitate the spread of disease seeds, especially when the weather conditions are uncertain.
- Also be aware of the decline in the quality of rations in the wet rainy and dry seasons to reduce cases of fungal attack (Aspergillosis) and mycotoxins.
Notes for 2022
Things that must be prepared by farmers whose chickens contract the disease in 2021 so that it does not happen again in 2022 include :
- Carry out maintenance management correctly and appropriately.
- Comfortable conditions must be felt by chickens starting from the moment DOC arrives at the cage. It is necessary to keep the cage clean, especially from feces because in a dirty cage it will be easy to spread the disease and also a high accumulation of ammonia which can be a triggering factor for respiratory diseases. So that the condition litter it also needs to be checked regularly and more often wash livestock equipment such as drinking places, food places.
- Perform flip-flops litter regularly once every 3-4 days. If litter wet and lumpy in a small amount, immediately take out and replace with a new one. Reduce ammonia levels in cages by spraying Ammotrol on feces. It can also be dissolved in drinking water as much as 0.5-1 grams per 2 liters of drinking water.
- Control of coccidiosis is to reduce the number of oocysts and prevent oocysts from sporulating. When the cage is empty, sprinkle the floor with chalk or caustic soda before covering with husks. During the maintenance period, the breeder can also apply lime / caustic soda to the damp and wet surface of the husk, before adding new husks.
- In terms of smooth ventilation and arrangement of cage density also affect the health condition of chickens. Uncertain weather conditions, sometimes even changing extremes, coupled with declining air quality demand better management. Also adjust the density of the cage to ensure all chickens get the same opportunity to get rations, drinking water, movement space and oxygen so that growth and productivity are uniform.
- System closed house until now, it continues to grow and become the choice of farmers with better advantages, namely increased density, controlled environment (the temperature in the cage is more stable and can be adjusted as needed), low mortality, efficiency of Human Resources (HR), biosecurity can be controlled and the risk of health problems or disease attacks is lower.
- Recording (recording) on farms it is important to be able to monitor health status of poultry.
2. Application biosecurity strict implementation of biosecurity model 3 zones (clean, transition, dirty) to limit traffic to prevent the spread of disease. Disinfect vehicles and people entering and leaving the cage to prevent contact with disease seeds entering the cage. If it is possible not to keep chickens with multiple age systems in one location (one age one site). When a child is old enough (multiage), it is necessary to pay attention to some things such as organizing the passage of cage traffic from young chickens to old chickens, placing DOC/pullet in cages that are far apart from the production layer cage, and minimize stress conditions on chickens, especially during the cage moving process.
3. Maintaining the quality of the ration
- Improvement of feed quality (feed given must be in accordance with the amount and content of nutrients) according to the needs of livestock to get good chicken performance. If you need to add mold inhibitor like Fungitox to inhibit the growth of fungi. And no less important when humid conditions, especially during the rainy season, you should use toxin to bind mycotoxins in feed. In addition, also provide multivitamin supplementation and premix to optimize productivity and increase the endurance of chickens. Examples toxin Medion production is Freetox.
- Maintain the quality of drinking water given to livestock. The drinking water provided is sourced from clean and safe water and needs to be controlled and checked regularly at least during the change of season.
4. The right vaccination Program
Vaccination needs to be done to form immunity in the body of chickens so that the appearance of cases can be suppressed. Conduct routine vaccination programs according to history, disease challenges, and local farm conditions against ND, AI, IB, IBH, Gumboro and ILT diseases. The selection of the right vaccine and the application of appropriate vaccination conditions in the respective farms are the key points for successful protection from attacks. The most important thing is to be able to apply 4M including materials (chickens and vaccines), methods, Mileu/environment, and humans who play an important role in achieving successful vaccination.
5. Increase the endurance of chickens with supplementation and the right health program
Related herbal health programs have been widely applied in the field as well today. Plant extracts are known to have various nutrients and chemical compounds (bioactive substances) that are efficacious and able to function as supplements, antibacterial, antiparasitic, antiprotozoa to anti-inflammatory. Medion develops herbal products which are standardized and have both the quality of raw materials and finished products. Examples Fithera as an antibacterial and antiprotozoal, imustim to help boost immunity, Kumavit to increase appetite, Heprofit as a supplement to protect chicken liver from damage (hepatoprotector) and Inflagrin to help cope with inflammation in poultry. There are also alternatives in the form of organic acids (for example Asortin) and enzymes (for example Betterzym). In addition, there are also Optigrin which has antibacterial and antiprotozoal properties so that it effectively suppresses the growth of pathogenic microbes that can be used as an alternative to AGP. The main purpose of providing this alternative is the same as AGP, namely maintaining the balance of intestinal microflora and optimizing the digestive process.
6. Monitoring health with laboratory tests
The difficulty of determining the analysis of diseases such as AI, ND or IB is one of the obstacles faced by many farmers in the field. Use of serological tests (e.g. HI test and ELISA), molecular biology test (PCR and sequencing), as well as tests for feed quality and mycotoxin levels can be performed as a means of confirming the diagnosis of the disease. Serological tests are also useful for monitor antibody titers such as AI. Medion presents MediLab (Medion Laboratory) in several major cities in Indonesia, so farmers are expected to be helped by the services of this laboratory test.
Poultry disease trends that tend to be the same from year to year seem to be repeated again next year. Evaluation of livestock business needs to be done in order to determine the strategy that needs to be taken in the future. Success has always been Indonesian poultry farming.










