Today, farmers often complain about the difficulty of eradicating the disease for their chickens. Over time, disease agents develop more and more and chickens are more susceptible to infection with disease agents.
There is one important factor that determines the success of a treatment is the application or application of drugs. Given the specific nature of the drug, its application must be appropriate, that is, it must be the right indication, the right dosage, the right method and duration of administration. So that the treatment goals can be achieved and the chickens are back in top condition.
Exact Indications
Indication is a condition or disease condition in which medication needs to be used. The indication of the drug will always be on every medicine packaging label. For example, antibiotic drugs to overcome infectious diseases coryza (korisa) with cold symptoms and mucus discharge in the nose caused by bacteria Avibacterium paragallinarum who infects sinus infraorbitalis (nasal cavity) that has few blood vessels. Therefore, only a few drugs can reach the target organs, so it is advisable to use a class of antibiotics that have a higher absorption into tissues. Examples of products are Amoxitin, Proxan-S, Doctril, Neo Meditril, Duoko or Erysuprim. In the selection of antibiotics, special attention should also be paid to antibiotic resistance. Antibiotic resistance is a condition of increased resistance of bacteria to the action of certain antibiotics. As a result, bacteria become insensitive or resistant to one type of antibiotic.
Resistance the first antibiotic occurs as a result of improper dosing, improper selection of antibiotics and incomplete treatment. The second cause, because antibiotics of the same group are used constantly. And the third cause comes from the bacteria themselves, for example due to bacteria having genetic mutations, enzymes and receptor changes in the body of the bacteria.
The right solution to overcome this resistance is to combine drugs synergistically, and most importantly, rolling antibiotics. What is meant by antibiotic rolling is to use or give antibiotics from different groups every interval of 3-4 treatment periods. For example, in the treatment of korisa with Amoxitin of the penicillin group for 4 periods of treatment, then in-rolling with Neo Meditril from the group of fluoroquinolones.
Proper Dosage
Dosage or rules of use are important guidelines for administering drugs. Giving a dose that is less will result in chicken never recover, as well as if the dose given exceeds the limit, this will lead to organ damage and even death. Before giving the drug, the first step we must do is read carefully the instructions on the label on the drug package.

Proper way and time of Administration
A good awarding drugs are important to note, Drug Administration can be optimal if the drug is able to reach the target organ or location of the disease. In general, the drug can be administered orally, by injection (parenteral) or smeared (topical).
- Oral The technique of oral administration of the drug is carried out through the mouth (digestive tract) either in a choke, mix rations or drinking water. The oral technique through drinking water can also be used for vaccination. Examples of drug preparations given orally are water soluble powders or mixed rations, caplets or capsules. Drugs that are given orally will work by directly killing the disease agent in the digestive tract or absorbed through the intestines to then be distributed to infected organs. Administration of drugs through drinking water and feed will minimize stress on chickens but the dose can depend on the activity of eating and drinking chickens, and the stability of the drug may be impaired if the quality of water used does not meet the standards. Another case with the administration through the bite, the dose of each chicken will be more uniform but the chicken will be at risk of stress because it must be caught one by one. The selection of the technique of oral administration of the drug is necessary to pay attention to the condition of the chickens. If the chicken is seriously ill, it will be difficult to reach the place of drinking water. So that the chicken needs to be close to the drinking place or need additional drinking places. For example, in korisa disease with severe conditions (severe), there will usually be swelling of the face and closed eyes. With this condition, the administration of the drug is recommended by injection or injection. The drugs to choose from are Medoxy-L, Gentamin, Kanamin, or Vet Strep.

- Parenteral / Injection
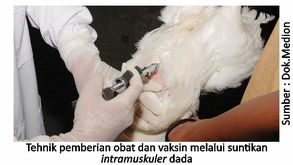
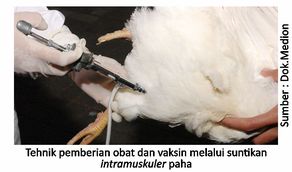
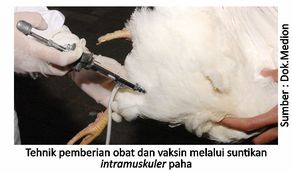
In poultry (chicken), the technique of administering drugs parenterally or by injection is often done in the subcutaneous (under the skin of the lower neck) or intramuscular (translucent flesh or muscle) on the thighs or chest. This technique will produce a relatively fast treatment effect because it does not go through the absorption process in the digestive tract for a relatively long time. Another advantage is that the dosage is more guaranteed and the effect is fast. However, the application of this technique causes the stress level of chickens to be relatively high, takes longer and requires special skills. Parenteral or injection techniques subcutaneous and intramuscular can also be used for vaccination.

- Topical Topical or local administration of drugs is a drug treatment that is applied topically or by other means directly to the skin, eyes, nose or other external parts of the body. An example of a topical medication is an ointment used to prevent infection in smallpox wounds using CIL (Smallpox wound infection) by applying to the wound (scab) smallpox.

In addition to the pattern of administration, the duration of treatment should be important to note the rules of use listed on the drug label (etiquette). If the rules of use are given for 5 consecutive days, the drug should be given within that time range even though the chicken looks healthy. It is intended that the seeds of the disease completely disappear so that the disease is not expected to recur. There are drugs with certain uses, such as drugs Anticancer from the group Sulfonamide to overcome coccidiosis or defecation. In its application, the drug is administered in a 3-2-3 pattern, that is, 3 days of Administration, 2 Days Without Administration, 3 days later it is administered again. It is aimed at breaking the life cycle of parasites that cause coccidiosis, namely Eimeria sp. in the asexual phase. But the class of drugs Sulfonamide has the effect of aggravating the work of the kidneys. So the treatment of coccidiosis with Anticancer not recommended for chickens with impaired kidneys. As an alternative can use Toltradex from the group Triazinethrione.
- In addition, it is also necessary to pay attention to the time of administration of the drug. A good time for administering the drug is 2x a day, for example at 07.00-13.00 then given again at 13.00-19.00. It aims to maintain drug levels in the body, so that the drug will remain effective and disease agents can be eradicated completely.
In supporting the success of disease treatment, the use of appropriate drugs need to be supported by factors of cage management and application biosecurity that's good. Things to do include :
- Regular cleaning and disinfection of the cage using Antisep/ Neo Antisep at least 1-2 times every month. When there is an outbreak, the frequency can be increased to kill the infectious agent of the disease.
- Water quality Test (source, reservoir, faucet) especially during the rainy season. During the rainy season the water intensity is high but the quality is low.
- Perform drain cleaning to prevent growth biofilm (substances in waterways that can trigger bacterial growth)
- Give multivitamins Fortevit / Vita Stress or herbal Imustim to increase endurance and accelerate healing.
Successful treatment and health of chickens is the hope of every farmer. However, disease prevention remains more important than treatment, awareness and good cooperation between employees and farmers are the main keys to successful maintenance. Greetings.