The growth rate of chickens is strongly supported by the adequacy of nutrients consumed. The adequacy of these nutrients is closely related to the nutritional content of feed and the ability of chickens to absorb these nutrients. Poultry includes monogastric livestock where the ability to digest coarse fiber is less good than ruminants. This is because birds only have a single digestive system so they cannot produce cellulase enzymes that function as digesters of coarse fiber.
Chicken feed and performance
The high price of feed resulted in increased livestock production costs. Therefore, efforts are needed to make the use of feed more effective and efficient. Quality feed contains complete nutrients. This is one of the determinants of optimal livestock performance, both layer and broiler chickens.
Poor feed quality will reduce chicken performance. The use of coarse Bran instead of fine Bran will cause the protein content of the feed to drop by 2-3% and the coarse fiber content to rise by about 3-4%. This decrease in protein levels will cause a decrease in egg production that can reach 15% (Wisuku, 2013).
85% of feed raw materials are of vegetable origin
Chicken feed is composed of raw materials of animal origin (animal raw materials) and plant (vegetable raw materials). And the largest component, reaching > 85% of chicken feed constituents is vegetable feed raw materials. This vegetable feed raw material consists of corn, bran, soybean seed meal and others.
Such feed raw materials serve as a source of nutrients that are important for the growth and productivity of poultry. Vegetable raw materials usually have a higher carbohydrate (energy) content than animal raw materials and their availability is abundant. Despite this, this vegetable raw material does not have a complete amino acid content. If you use only vegetable raw materials, then the chicken will be prone to a deficiency of a number of essential nutrients, such as iron, B vitamins12 and omega 3.
High Coarse Fiber, Phytic Acid Increased
The level of coarse fiber in the ration greatly affects the performance of livestock. Coarse fiber is needed by cattle to stimulate the movement of the gastrointestinal tract. Crude fiber requirements in some types of poultry vary, for example, a maximum of 7% Quail, duck maximum 8% while broiler maximum 6% (SNI, 2006). A lack of fiber in poultry feed can cause indigestion, but an excessive amount of coarse fiber can also decrease the digestibility of the feed.
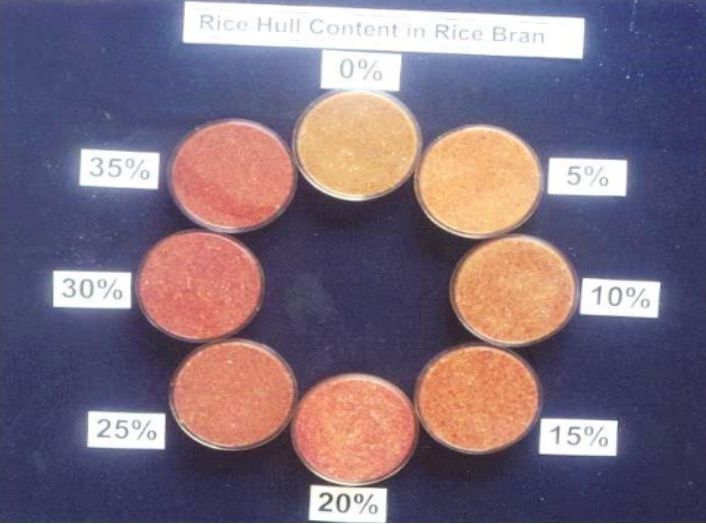
Vegetable raw materials naturally contain phytic acid. This is because phytic acid is found in the epidermis of sesame seeds such as rice, corn, wheat, etc. Chart 1. showed Bran with crude fiber content of 10.2% has the highest phytic acid content.
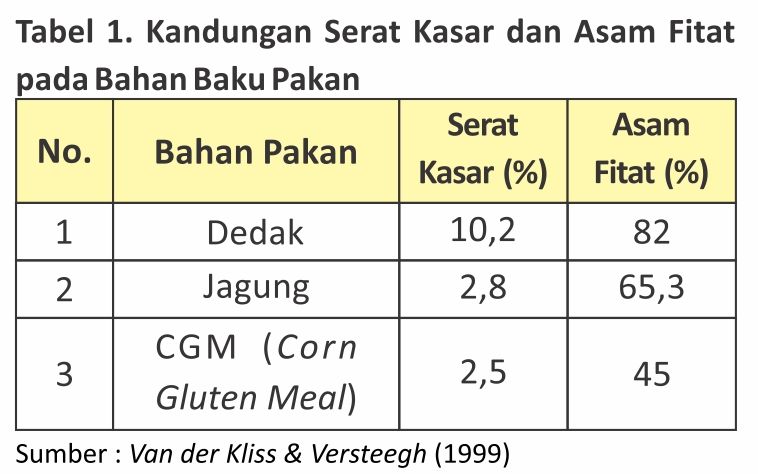
Plus today there is a lot of falsification of Bran with the addition of husks. This will cause the content of coarse fiber in the bran to increase, which will also affect the increase in phytic acid content.
Flouroglucinol test can be one way to identify husk contamination in Bran. When dripped on Bran, within 5-10 minutes a change in color will be noticeable. The more contamination of the husk, the more red it becomes.

Getting To Know Phytic Acid
Phytic acid is a secondary compound that is the main store of phosphorus in plant grains. Its content in grains ranges from 60-80% of total phosphorus (Wu et al., 2009).
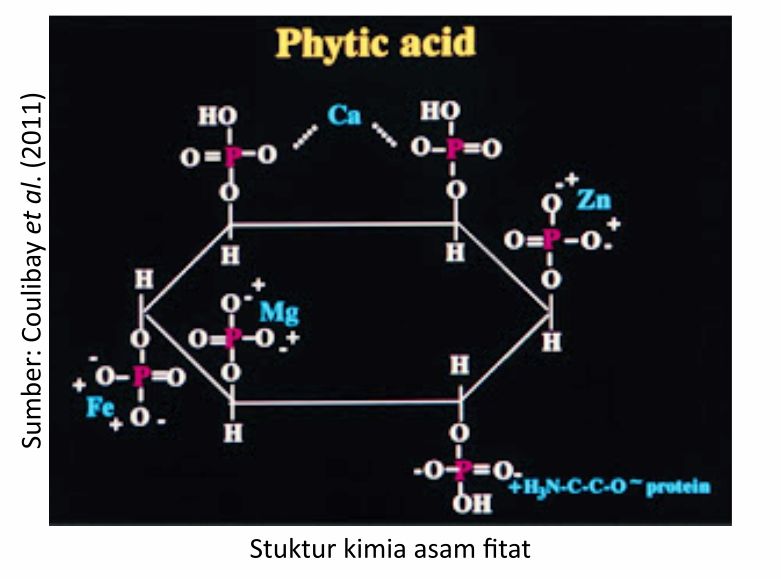
The content of phytic acid in vegetable raw materials varies depending on several factors, namely the type or type, variety and age of the crop. Phytates are found in grains from cereal crops and oil-bearing grains. Phytates in these grains play a physiological role in storing nutrients, especially phosphorus, which will be released with the help of endogenous phytases when germination occurs.
Phytic acid is able to form complexes with nutrients, such as proteins and minerals. This is due to the strong negative charge of phytic acid so that it can easily bind to positively charged components, such as proteins and minerals. The presence of phytic acid causes phosphorus digestibility to be low, which is about 10%, moreover, in the body of poultry there is no phytase enzyme.
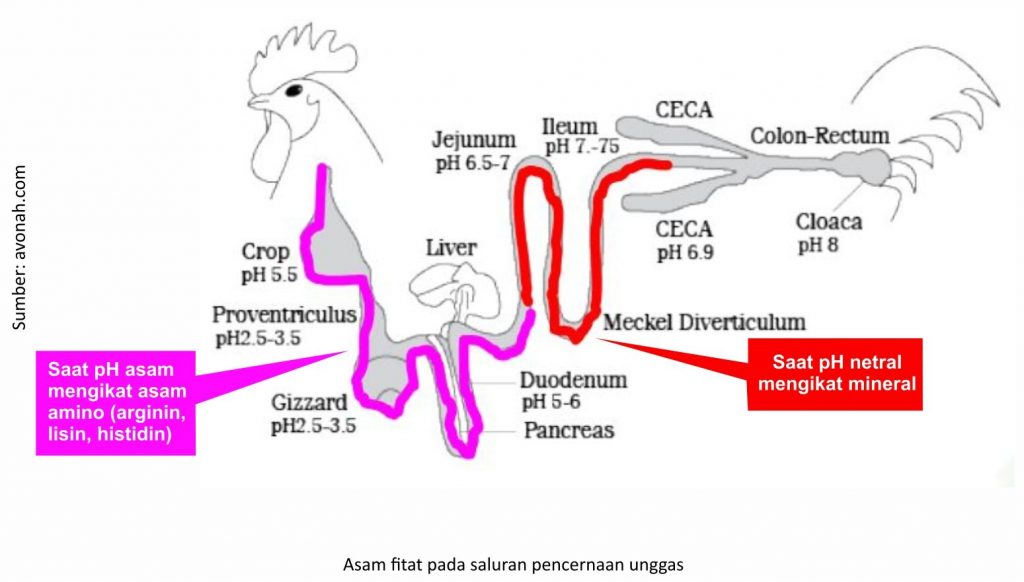
Asam fitat dalam saluran pencernaan mempunyai efek negatif yang mempengaruhi penyerapan nutrisi. Asam fitat ini dalam suasana asam (pH <4) akan mengikat asam amino seperti arginin, lisin, dan histidin. Sedangkan di suasana netral, asam fitat akan mengikat mineral. Nutrien yang terikat oleh asam fitat ini tidak dapat diserap oleh usus. Keberadaan asam fitat mengakibatkan kecernaan fosfor menjadi rendah yaitu sekitar 10%, sisanya diekskresikan melalui feses. Adanya asam fitat dalam ransum ayam pedaging juga mengakibatkan terjadinya penurunan metabolisme energi karena secara tidak langsung asam fitat meningkatkan sekresi natrium (Na) yang menghambat proses penyerapan glukosa pada saluran pencernaan.
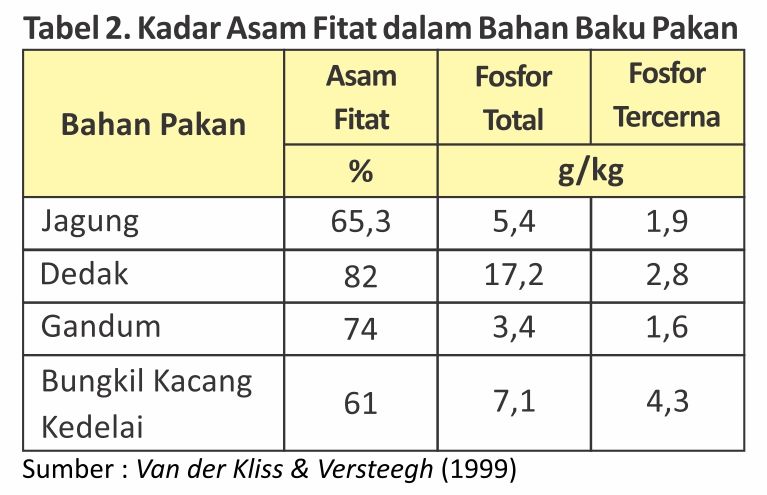
Chart 2. studies show that 60-80% of phosphorus in vegetable feedstuffs will be bound by phytic acid. Undigested phosphorus will come out with feces and cause environmental pollution. Though phosphorus is a very important nutrient. Phosphorus has a metabolic function in the formation of bones and egg shells, plays a role in the process of energy formation and regulates the acid-base balance in the body.
According to Woyengo and Nyachoti (2013), the mechanism of phytic acid contained in rations can reduce the digestibility of nutrients in monogastric cattle, namely:
- Forming bonds with nutrients and digestive enzymes in the small intestine, further decreasing the activity of digestive enzymes in the small intestine
- Forms bonds with proteins and digestive enzymes in the stomach thereby decreasing pepsin activity in the stomach
- Forms bonds with nutrients in the body, which leads to a decrease in the rate of absorption of these nutrients in the small intestine.
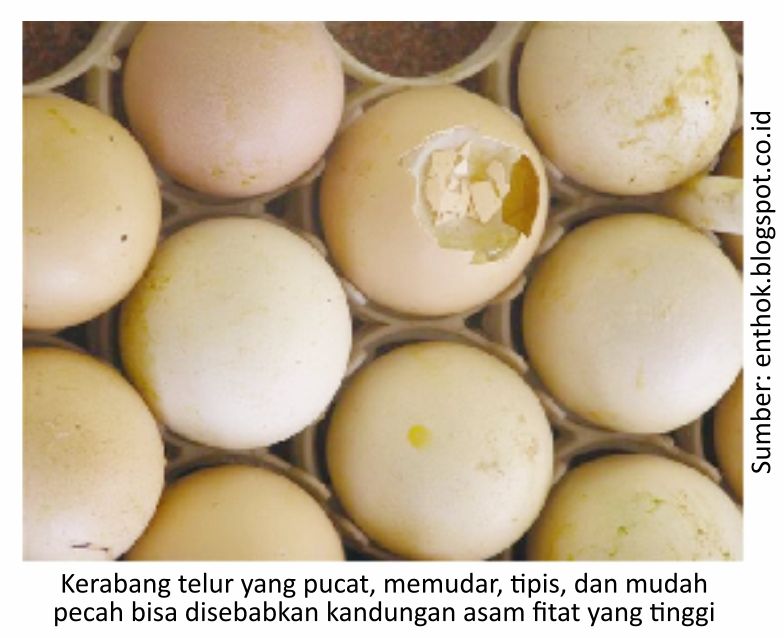
Negative effects that can be immediately seen when phytic acid levels are high include pale egg shells, thin egg shells, easy to crack and break, paralysis and decreased egg production.

Addition of Phytase enzyme as a solution
All livestock use enzymes to digest feed. Enzymes are produced by the cattle themselves or by natural microbes present in the intestines. However, the digestive process of cattle is not 100% efficient. Pigs and poultry cannot digest 15-25% of the feed, since the feed contains anti-nutrient substances that cannot be digested and do not have specific enzymes.
Feed raw materials such as corn, bran (bran), wheat, barley, soybean meal and others, bind phosphorus elements in the form of phytic acid. Whereas phosphorus is an essential element because it is needed for the process of bone development, helps egg production, maintains immunity and helps the growth process.
Poultry itself is only able to digest phosphorus in vegetable raw materials by about 30-40% because birds do not have phytase enzymes in their bodies. As a result, undigested phosphorus will come out with feces and cause environmental pollution.
Phytase is an enzyme that is added to feed to release more phosphorus bound in phytic acid. This situation has a positive impact, namely increased digestibility and more optimal utilization of phosphorus.
In addition to playing a major role in the process of phosphorus absorption, phytase enzymes can also eliminate the negative influence of phytic acid. The addition of this enzyme can also reduce the addition of inorganic phosphorus sources such as calcium phosphate (DCP) and mono calcium phosphate (MCP) so that farmers can streamline feed costs.
Mechanism Of Action Of Phytase Enzyme
Enzymes are functional units of cellular metabolism, as they can help speed up reactions without participating in the reaction itself, either as substrates or products. When an enzyme reacts with a substance (substrate), it chemically modifies the substrate through the action of that enzyme. One of the important enzymes in the formulation of poultry rations is phytase.
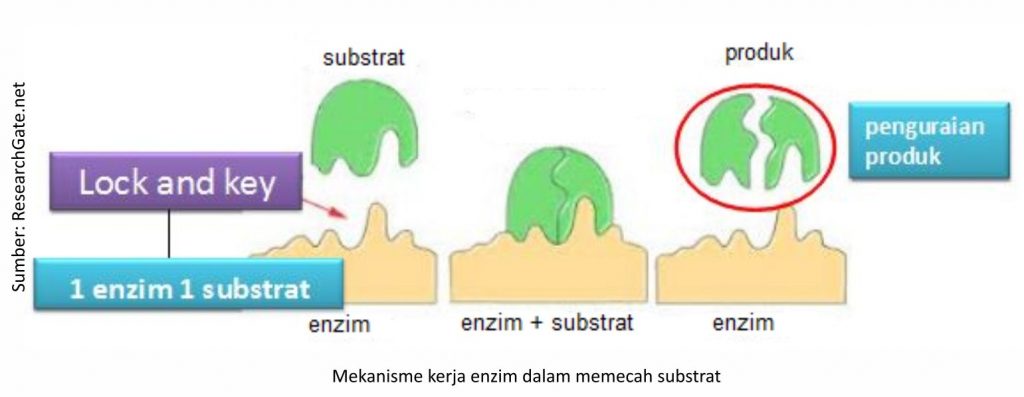
This is a list of enzymes that are responsible for the synthesis of enzymes and enzymes (Lock and Key). The phytase enzyme is described as a padlock that has an active side capable of binding to a substrate (phytic acid) as a key. When the two are matched, a complex bond (enzyme-substrate) is formed which then after reacting, the complex bond breaks free and frees the product and frees the enzyme to work again.
Sources Of Phytase Enzymes
In 1962 the first attempt was made to develop phytase as an enzyme for animal feed ingredients and in 1991 phytase was first commercially available. Phytases sourced from microbes are most widely used for commercial purposes (Khalid et al., 2013). Types of microbes that are widely used include Escherichia coli and Aspergillus sp.
Advantages Of Using Phytase Enzymes
The use of phytase as a feed additive must meet several criteria, namely :
- Has good enzyme activity
- Stable in the pH of the digestive tract
- Effective in releasing phosphate bound phytate in the digestive tract
- Stable in resisting inactivation due to heat from feed processing and storage process
- Cheap when produced (Greiner & Farouk 2007).
Phytase supplementation in rations with a low phosphorus content produces a positive effect on the growth of broilers, that is, it increases the consumption and efficiency of the ration. Another advantage of phytase supplementation is that it has implications for livestock health, as well as having a positive influence on the quality of meat and eggs (Cowieson et al., 2011). This is due to :
- Release of minerals from the phytate-mineral complex;
- Utilization of inositol by chicks;
- Increased starch digestibility; and
- Increased protein digestibility.
Fitase also increases the digestibility of starch in all segments of the small intestine. This increase in starch digestibility is due to the increased absorption of glucose produced by phytase. The use of phytase in broiler rations is also able to increase the energy utilization of the ration.
Betterzym, Enzim Fitase Terbaik
Betterzym is a mixed feed powder preparation containing the latest generation phytase enzyme (6-phytate) that effectively improve the digestibility of nutrients, especially phosphorus (P). Betterzym will break the bonds of phytic acid so as to increase the availability and digestibility of such amino acids, carbohydrates and minerals, especially phosphorus.
1. Betterzym has good enzyme activity
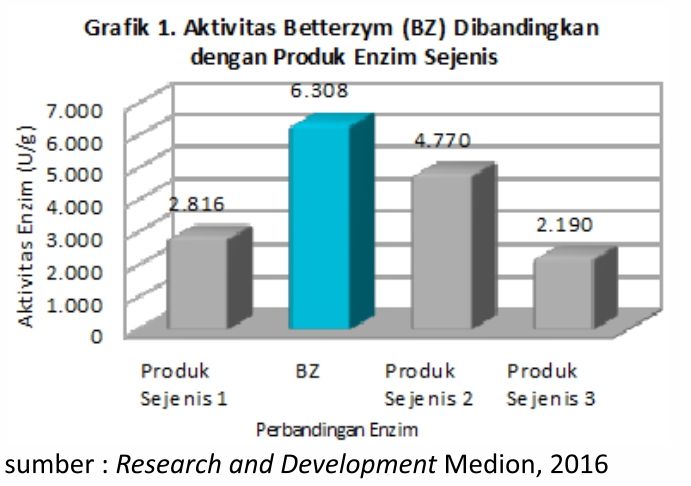
- Enzyme activity testing is one of the determining parameters of enzyme quality. Activity test results Betterzym compared similar enzyme products are shown in Graph 1. This test is performed in vitro at a pH level of 5 with a temperature of 37°C. From these data it is evident Betterzym with the content of the latest generation phytase enzyme has the best enzyme activity than similar enzymes.
2. Betterzym is able to improve henday
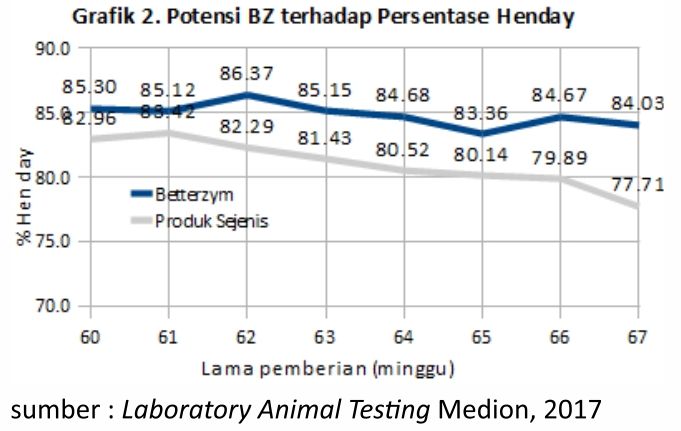
Betterzym able to work under pressure henday, feed conversion ratio (FCR) and cracked eggs. The Trial was conducted in a farm in the Solo area, in laying hens aged 60-67 weeks. Graph 2. shows Betterzym the production of eggs (henday). Decreased egg production after peak production in a given chicken Betterzym still slower than similar competing groups.
3. Betterzym can fix Feed Conversion Ratio (FCR)
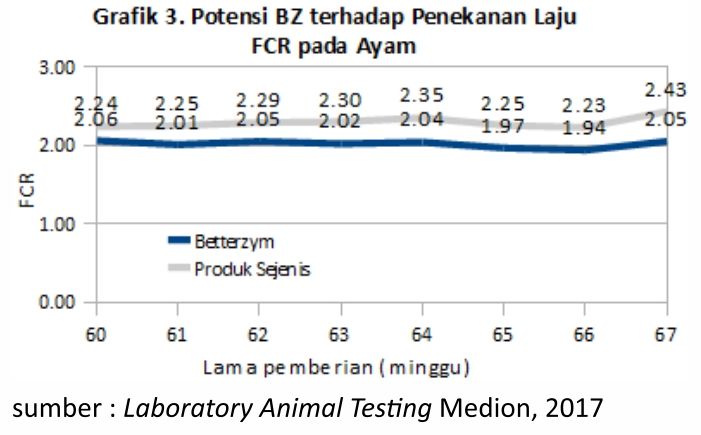
Graph 3. show data Betterzym able to improve the level of efficiency of the ration. Betterzym able to withstand (improve) the rate of increase in FCR from the beginning to the end of the provision of 2.06 to 2.05. The opposite in the group of similar products FCR moves higher from 2.24 to 2.43.
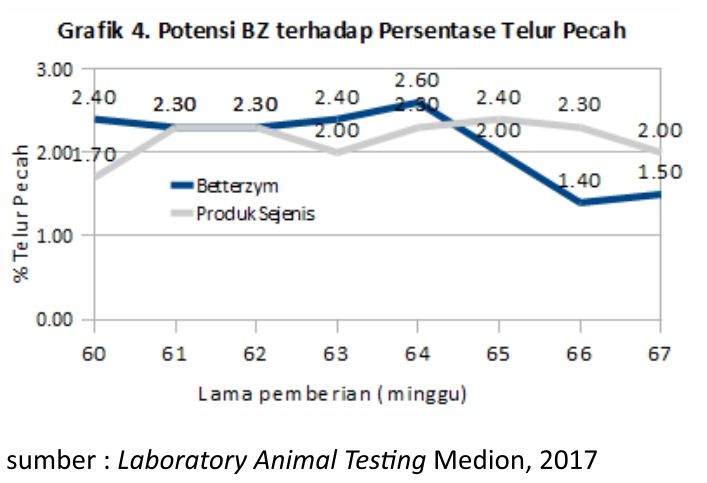
4. Betterzym was able to lower the percentage of broken eggs
Graphic 4. shows Betterzym able to significantly reduce the percentage of broken eggs to 1.40%. This is inversely proportional to similar products that are only able to reduce the percentage of broken eggs in the range of 2.00%.
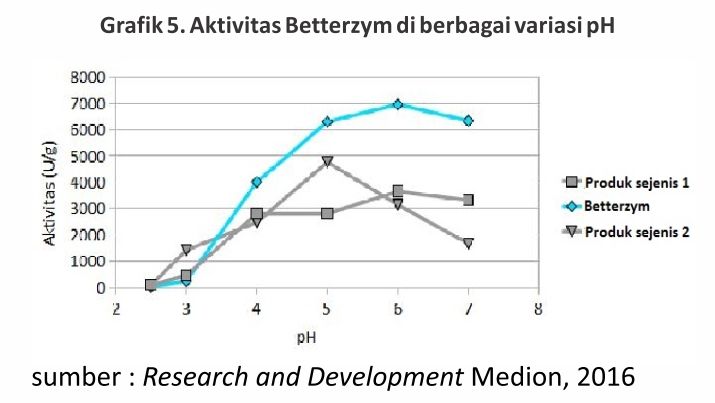
5. Betterzym is stable in the digestive tract
Activities Betterzym it is more stable in the gastrointestinal tract with a pH range of 4 to 7 as in Graph 5.
Panduan Pencampuran Betterzym
1. Mix Using Mixer
There are 2 types mixer, namely mixer vertical and mixer horizontal.
a) Mixer vertical

b) Mixer horizontal

2. Mix Manually
Eg :
- Feed needs in one day is 4 sacks (1 sack @ 50 kg)
- Dosage Betterzym 600 g per ton of feed (for layer) or 0.06%
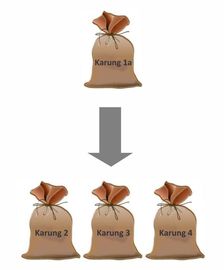
a. Prepare 4 sacks of feed and Betterzym as much as needed

b. Mix 120 g Betterzym into 1 sack of feed

c. 1A sack is mixed evenly with 3 other feed sacks
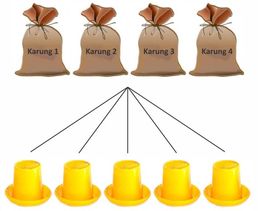
d. The food is mixed with Betterzym it is spread over the food
From all of the above we can conclude that Betterzym has an important role in improving feed quality by binding anti-nutrient substances in the feed so that nutritional needs can be achieved which ultimately the performance of chickens becomes better. Greetings.










