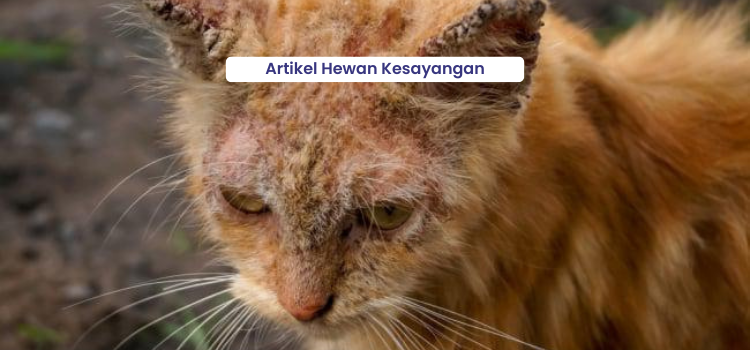
Cats are animals that live side by side with humans. The health of cats needs attention because some diseases are zoonotic or can be transmitted to humans. Parasitic diseases are common diseases found in cats and dogs and some are zoonotic.
Causes Of Parasitic Diseases
Parasites are divided into two namely endoparasites and ectoparasites. Endoparasites are parasites that live in the body of animals such as worms and protozoa. The most common endoparasites found in cats are worms. The average prevalence of worms in cats in Indonesia is 48.97%.
Types of worms that are often found are roundworms (Toxocara cati, T. Leonina), cacing pita (Dipylidium caninum, Taenia taeniaeformis) and hookworm (Ancylostoma tubaeforme, A. braziliense, and Uncinaria stenocephala). While the types of protozoa most commonly found in cats are Toxoplasma sp. and Isospora sp. (Fadhlullah Mursalim et al., 2018).
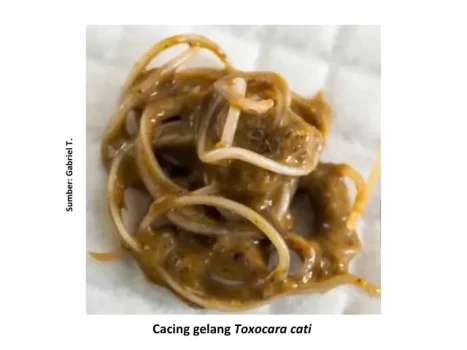
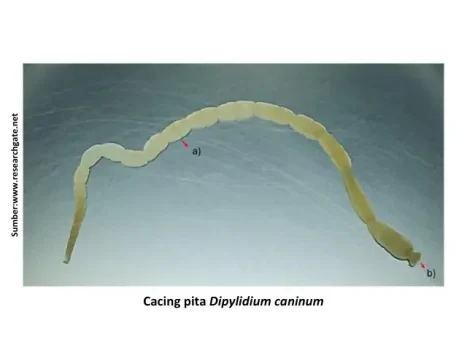
Transmission of helminth infections can be through cat feces containing worm eggs, through brood (intramammary/intraplacenta), contaminated food, and through the environment / soil. In the case of tapeworms, the role of fleas is important to bring worm larvae into the cat's body.
Fleas that have been infected with worm larvae can be swallowed by cats and then the larvae develop into adult worms in the cat's body. In addition, cats can also contract worms from their game animals that have been infected with worms, for example from birds, mice, etc.
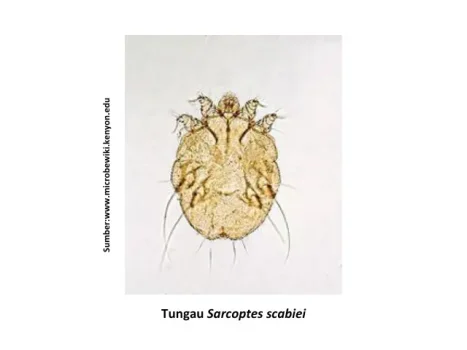
While ectoparasites are parasites that live on the surface of the cat's body, such as hair, skin, ears. Ectoparasites in cats can be mites, fleas, fleas, and ticks. The most common type of ectoparasite found in cats is mites Sarcoptes scabiei, Otodectes cynotis, Notoedres, borrow Ctenocephalides felis, box Lynxacarus, Felicola and ticks Rhipicephalus spp.
Ectoparasite transmission can occur through direct contact with cats that already have ectoparasite infestation or indirectly through various media or environments contaminated with parasites.

Impact Of Cats Infected With Parasites
The impact of endoparasites and ectoparasites on cats can lead to various health problems, such as:
- Worms can damage a cat's intestines, causing diarrhea, weight loss and even the risk of death
- Worms, if not treated promptly, cause serious illnesses such as inflammation and intestinal bleeding and pneumonia
- Migration of worm larvae can lead to skin infections, seizures, blindness and pneumonia
- Helminth infections in cats also exist of a zoonotic nature (they can be transmitted to humans). For example Toxocara spp., Taenia spp., Dipylidium caninum, and Dirofilaria spp. (McNamara et al. 2018).
- Ectoparasites cause baldness and skin irritation, destroying the beauty of the cat's skin and hair
- Ectoparasites cause discomfort and anxiety that can be a stressor so that the body's resistance decreases and increases the possibility of secondary diseases, as well as decreased appetite that continues with weight loss
- Ectoparasites are also at risk of zoonoses such as scabies caused by mites Sarcoptes scabiei.

Symptoms of Parasitic Diseases in cats
Symptoms of Parasitic Diseases in cats vary depending on the type of parasite and its severity. Parasites can cause a variety of symptoms, ranging from mild discomfort and diarrhea to more serious problems such as skin diseases, secondary infections and malnutrition.
Symptoms of a cat infected with worms are sometimes invisible, so they are only realized when the worm infection is severe enough. Common features that can be observed in worm infections include:
- Cat hair looks dull
- Decreased appetite
- Looks lethargic
- Vomiting
- Discharge from the nose to difficulty breathing
- Diarrhea / feces look mushy to watery and dirty anus
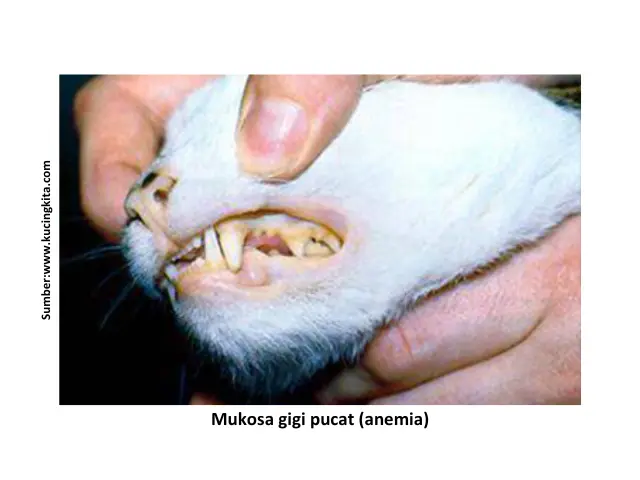
- Pale oral mucosa
- Weight loss
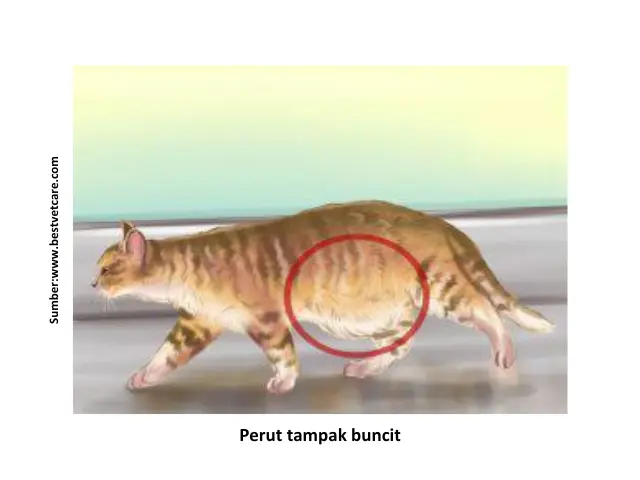
- Belly looks distended

Symptoms of ectoparasite infection in cats vary depending on the species of ectoparasite that infects. In general, cats infected with ectoparasites will show the following symptoms:
- Itching, frequent scratching
- Hair loss
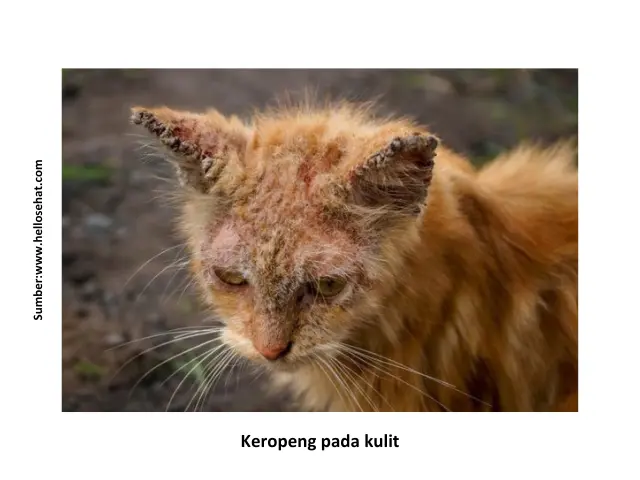
- Skin irritation, rash appears, redness
- The skin is peeling, there are open wounds, ulcers, or scabs / scabs on the skin
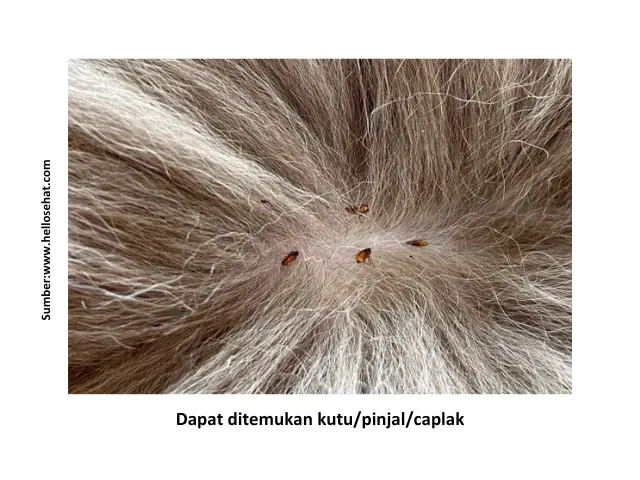
- Small black-brown spots that move between the cat's fur
- Sand-like flea droppings appear in cats, especially on the back and tail
- Cats appear lethargic with pale under-eyes and gums
- If ectoparasites are left untreated, cats can develop anemia characterized by weakness, lethargy, rapid breathing, or even death.


Preventing Parasitic Diseases in cats
Good care and maintenance must be done so that the cat is protected from worm endoparasites and ectoparasites. This is done by:
- The quality of the food is excellent (Kadofu, Delicats)
- Maintain the cleanliness of the environment by cleaning the cage and the environment regularly. Regularly clean the environment, feces and litter box. Also clean the cat's living environment (carpet, chair bedding). Control of rodents such as rats that act as vectors.
- Maintain cat hygiene by bathing / grooming regularly every 4-6 weeks. By grooming regularly cats will avoid ectoparasites that can infect cats.
- Give anthelmintic and antiectoparasites according to the health program with Golden Pet Deworming to prevent worms and Golden Pet Anti Flea & Tick For Cats to eliminate ectoparasites. An example can be seen in Figure 1.
- Golden Pet Deworming it can prevent and treat tapeworm, roundworm, and hookworm infections in cats. Golden Pet Anti Flea & Tick For Cats it can eradicate all stages of fleas (eggs, larvae, and adult fleas), fleas and ticks in cats.
- Keep your cat healthy and increase endurance by giving vitamins and checking your cat's health regularly to the vet.