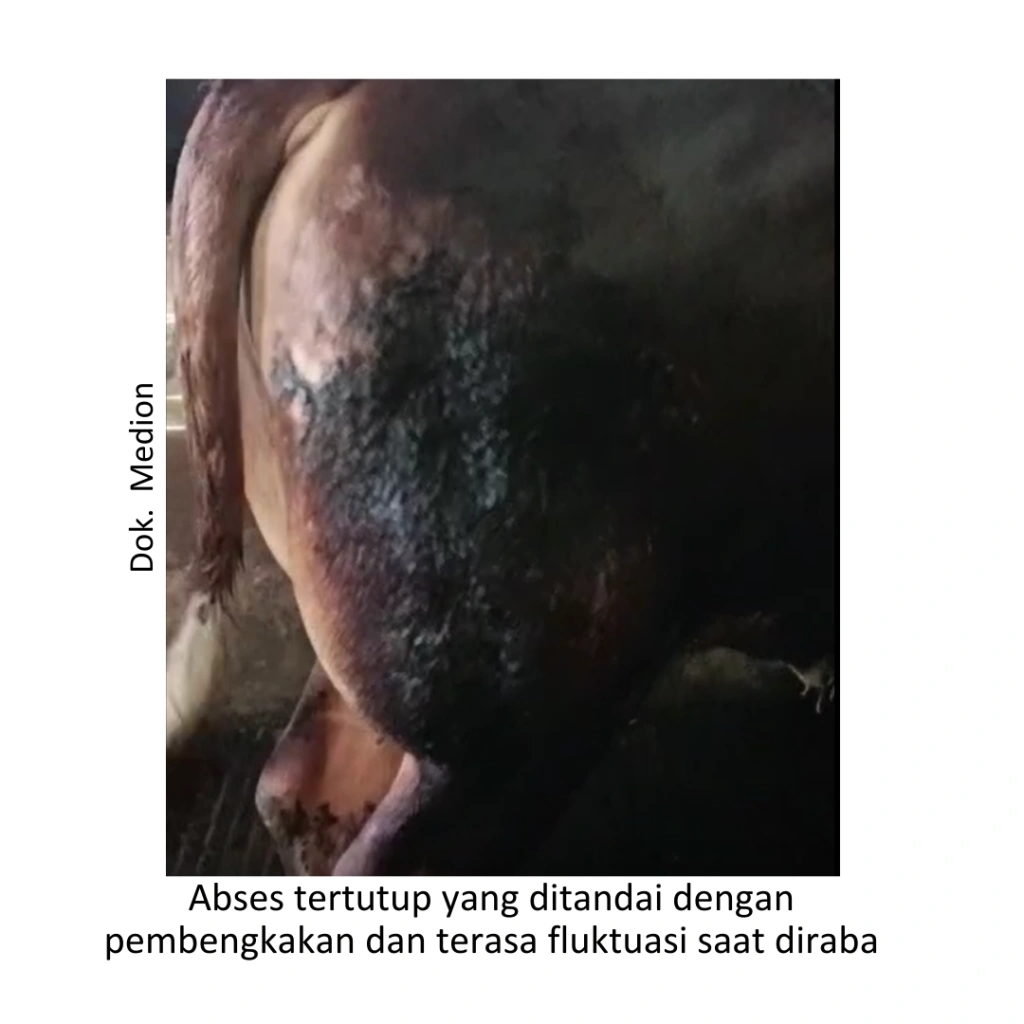
In maintaining livestock productivity, Disease Control is one of the important things to consider. One of the diseases that affects cattle cattle is abscess. An abscess is a collection of pus due to damaged tissue. In cattle, abscesses are often found on the surface of the body. Abscesses can occur in open wounds as well as in closed tissues. A closed abscess is a collection of pus fluid in a body tissue and is protected by connective tissue. The formation of an abscess is a defense reaction to avoid the spread of foreign bodies in the body.
Causes of abscesses
Abscesses can be caused by bacterial infections, such as Staphylococcus aureus, S. epidermidis, S. hycus, Arcanobacterium pyogenes, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Vibrio vulnificus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Actinomyces bovis, E coli maupun Salmonella spp. It can also be caused by parasites ,or foreign bodies (El Tawab et al., 2019).
Triggering factors include Wet pastures, open wounds that are not treated immediately, exposure to sharp objects that cause wounds or limping, uneven housing conditions that provoke wounds. At constant moist conditions around the nail leads to softening and damage to the skin. As a result, surface dermatitis occurs, which allows various infectious agents to penetrate deeper into the soft tissues of the nail.
Bacteria will enter the body through wounds that damage the skin or hair follicles. Once the bacteria enter the body, white blood cells will attack the bacteria and nearby tissues die. Then it fills with pus and an abscess forms. The formation of an abscess will contain a mixture of dead tissue, white blood cells and bacteria. Abscesses can become larger as the infection gets worse and more pus is produced.
Clinical symptoms of abscess
Diagnosis of abscesses on the surface of the body or skin and subcutaneous can be done by performing a physical examination. By means of observation and further examination of palpation or touch. The physical examination is to see the swelling and make sure it is likely to contain pus or not. As for the examination of abscesses that occur in internal organs, the diagnosis can be made by ultrasound or radiography.
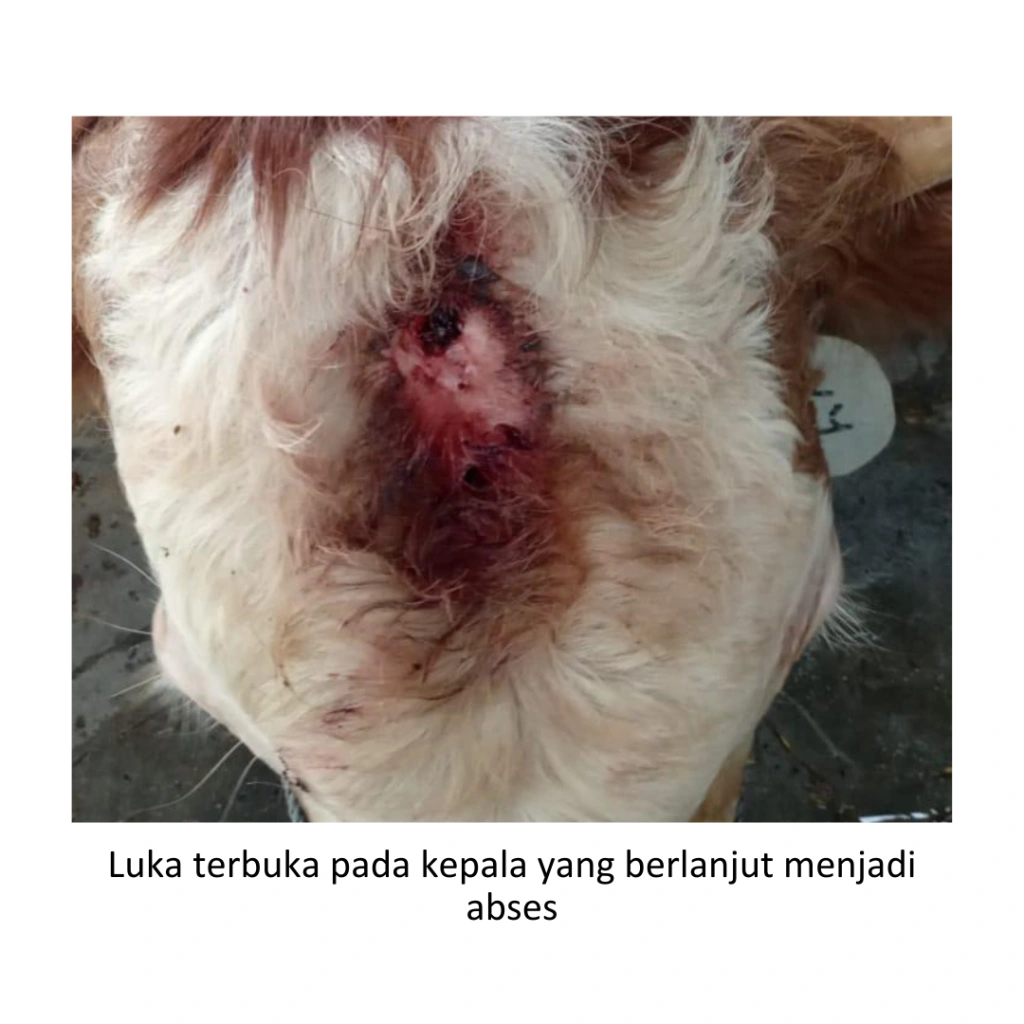
The clinical symptoms of abscesses seen in the field are generally lumps and swelling. The lump has a mushy consistency and if palpated, fluctuations are felt in it. If the lump is pressed, a thick, cloudy and yellowish to reddish liquid will come out. In open wounds pus can come out of the wound opening. Cows will appear restless (look very uncomfortable), appetite and drinking down, cows lie down more often. If it occurs on the legs, the cow will look limping when walking. When further examination is carried out, the cow will feel pain when the abscess is palpated, heat, redness and fever may occur.

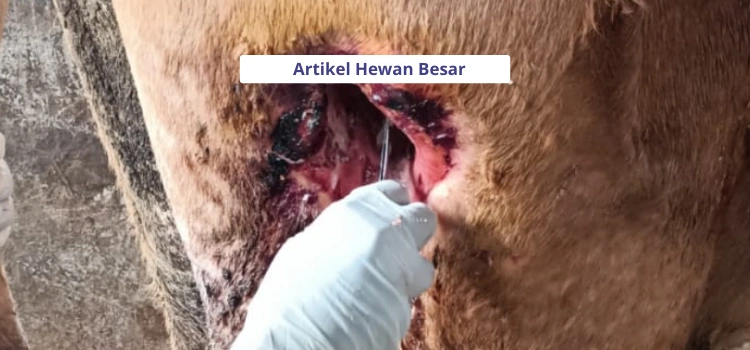
Treatment in case of abscess
When an abscess occurs, early detection and treatment are essential for a good treatment outcome. Abscesses on the surface of the body that are classified as fairly mild can heal on their own and disappear without treatment. But in the case of large abscesses need to require treatment and treatment measures.
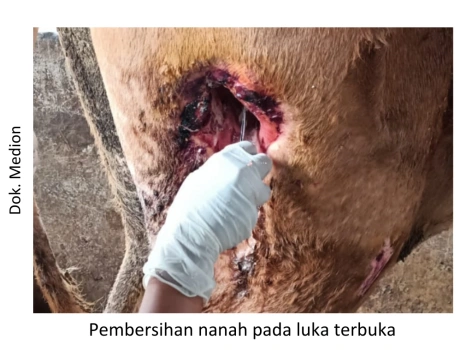
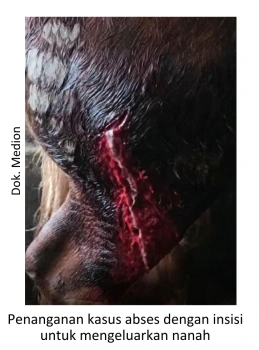
Most cases of abscesses are treated surgically. By making an incision or making a wound in the abscess area to remove the abscess. The goal is to drain or remove the contents of the abscess and clean the abscess cavity from dead tissue using antiseptics. Some cases sometimes need to be anesthetized to overcome the pain. But there are also without anesthesia, especially in small and not yet severe abscesses. The treatment of the abscess needs to be done by a team of animal health workers. Some of the handling steps include:
- Clean the wound first using an antiseptic Antisep.
- If pus in the wound is open. Pus is removed and cleaned with antiseptics Antisep. In pus covered skin, it is necessary to perform surgery to make a hole. Then the pus is gently removed until clean and rinse with an antiseptic Antisep.
- Giving wound medicine Oxytic and proceed each to speed up the dry wound and to avoid flies.
- By looking at the condition of the case, antibiotics can also be given.Antibiotics that are often used in the treatment of abscesses are broad-spectrum antibiotics. Such as injection Medoxy LA, Neo Meditril LA or GMox 15 % LA.
- The pain caused in the case of abscesses also affects cattle lost appetite. Administration of vitamins Injekvit B-Plex or Injekvit B12 needs to be done to speed healing. As well as Medipiron Injection to overcome pain, inflammation and fever.
- After completion of surgery and treatment still need to be treated until the wound is dry and healed.
Prevention of abscess occurrence
To prevent abscesses, several things are done, among others:
- Regular inspection of livestock for possible injuries. If there is a wound immediately clean with clean water and antiseptic Antisep. This is done to reduce the risk of bacterial contamination. Immediately treat the wound with a spray Oxytic until the wound is dry. It is always necessary to have wound medicine available in the cage as a first aid medicine.
- Maintain the cleanliness of the cage and disinfect the cage regularly to suppress the seeds of disease in the cage, for example by Medisep, Zaldes.
- Avoid sharp objects or rough floors in the cage area.
Abscesses that occur on the legs are quite serious events. Because it can have an impact on productivity and in severe cases, death can occur. In this case, the cattle will feel pain so lazy and difficult to move in search of feed.
Pregnant cattle can also be at risk of pregnancy toxemia. Cases of abscesses cannot be ignored. Early treatment is also important to prevent advanced diseases such as arthritis and chronic cases. So that prevention and treatment of injuries as early as possible is important to do.