The use of antibiotics in the poultry world is familiar. The main purpose of using antibiotics is to overcome diseases caused by bacterial infections or to treat chickens from pathogenic organisms that cause disease.
In practice, the administration of antibiotics is sometimes still out of control because of the supervision and knowledge in the use of antibiotics is still limited. The use of antibiotics must be in accordance with the rules of use in order to eradicate disease-causing microbes completely and suppress resistance.
Antibiotics are chemicals that can inhibit the growth or kill microorganisms. Based on its power, there are antibiotics that inhibit the growth of bacteria or bacteriostatics and there are antibiotics that kill bacteria or bactericides.
In addition to the above-mentioned broad-spectrum antibiotics (broad-spectrum) and narrow spectrum (narrow spectrum). Broad spectrum, works against more bacteria, both Gram-negative, Gram-positive, and also Mycoplasma. Narrow-spectrum antibiotics work against certain types of bacteria only. For example: penicillin only works against Gram-positive bacteria.
Use of antibiotics on farms
It is undeniable, many diseases that can attack chickens resulting in losses such as decreased production to death. Efforts are usually made by farmers to prevent and control the disease, among others, with the implementation of good biosecurity, vaccination, and antibiotics.
Prior to the regulation of the use of antibiotics, Antibiotics are not only used for treatment but also for the Prevention of bacterial infections, spur growth and improve feed efficiency. The use of small doses of antibiotics in feed to spur chicken growth can indeed accelerate growth. However, as we all know, there can also be a risk of residue from livestock products.
From the results of a study conducted on laying hens before the regulation on the use of antibiotics showed that 83.3% for the treatment of diseases, 36.7% for Disease Prevention, 26.7% for prevention and treatment and 10% for increased production (Civas, 2016).
In the publication of the Ministry of Agriculture of the survey results on broiler farmers in West Kalimantan showed that the factors that affect the possibility of giving antibiotics to chickens due to increase productivity and growth by 75%, because the chickens do not want to eat 65%, prevent chicken disease 65%, increased mortality rate of 50% and because of the symptoms of the disease 45% (worship, et al., 2019).
There are many types of antibiotics in the field. Many farmers are already aware of the importance of giving antibiotics wisely according to the recommendations and application rolling or antibiotic rotation. But there are also those who give in excess of the recommended dose or less than the dose until there is even given continuously. Some people think that antibiotics can be used to cure all types of chicken diseases so that every sick chicken is immediately given antibiotics.
The use of antibiotics that do not pay attention to the rules of use can result in the presence of antibiotic residues in livestock products and the development of resistant microbes in the body of livestock.
Amr (Antimicrobial Resistance)
Causes of the appearance of antimicrobial resistance (AMR) is the use of improperly dosed, (over-or under-dosed) antimicrobials, prolonged and incomplete treatment that can affect the ability to treat livestock diseases and affect public health. AMR is the ability of microorganisms to survive antimicrobial treatment (antibiotics).
Or microorganisms are able to survive and develop despite the presence of antimicrobial agents, normally these microorganisms will be inhibited or die.
Antimicrobial agents (consisting of antibiotic, anti-fungal, anti-parasitic) are widely used for the treatment and Prevention of diseases in humans and livestock. AMR occurs at a time when antimicrobial drugs become ineffective at killing or are unable to restrain the growth of target microorganisms used in treatment.
Infections caused by bacteria that are already resistant to certain antibiotics will make the disease more difficult to handle. AMR is a global health threat, and the use of antibiotics in the livestock industry is suspected as one of the contributors.
Poultry farms are generally intensively reared that use antibiotics in disease prevention and control, as well as as a growth bully. Antibiotic resistance in products of livestock origin is formed as a result of improper use of antibiotics. Antibiotic resistance to pathogenic bacteria in poultry can result in treatment failure that causes economic losses and is also a source of bacterial resistance that endangers human health.
In the correct use of antibiotics will provide benefits or a positive impact for farmers for treatment. But in its use, if done wisely and irrationally, it becomes a trigger for the emergence of bacteria that are resistant or resistant to the effectiveness of antibiotic treatment. The unwise use of antibiotics in poultry farming, especially broilers, is one of the factors in the occurrence of antimicrobial resistance or AMR. Farmers ' knowledge of AMR is still limited.
The use of AGP
With the Prohibition of use Antibiotik Growth Promotor (AGP) in the livestock business from 2018 has lasted 3 years. This aims to avoid the presence of residues of antibiotics in the body of chickens that will also be consumed by humans. On the one hand, farmers face greater challenges in maintaining poultry health.
Both to maintain optimal chicken productivity and to maintain chicken health. Given the policy also resulted in a reduction in the use of antibiotics for preventive purposes for farm animals, including chickens.
With the Prohibition of AGP, it will affect the health of the gastrointestinal tract to prevent digestive tract diseases. It is also widely felt is still high gastrointestinal diseases such as coccidiosis, colibacillosis and necrotic enteritis (NE).
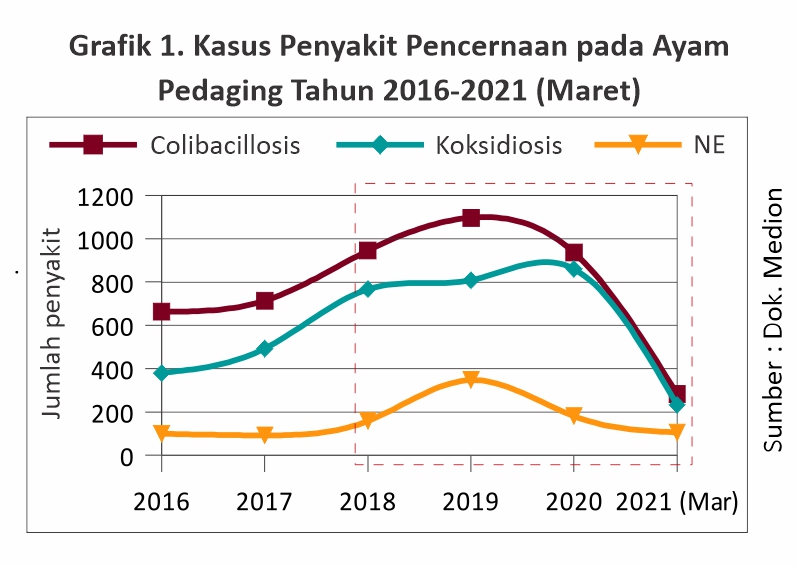
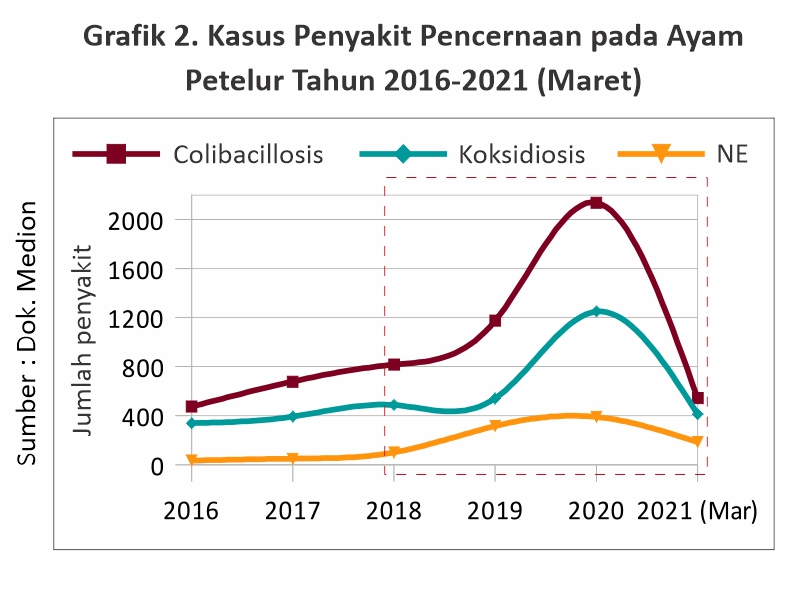
In 2020 to March 2021 colibacillosis and coccidiosis were ranked 3 and 4 diseases that often affect broilers and ranked 5 and 7 that affect laying hens. It is also aligned with the data shown in graphs 1 and 2.
Gastrointestinal diseases colibacillosis, coccidiosis and NE both in broilers and laying hens have increased cases after the prohibition/ restriction of AGP. When compared to the year before 2018 where AGP was still allowed to be used, the cases of gastrointestinal diseases increased after 2018. In broilers in 2020 cases of colibacillosis and NE decreased from 2019.
This is in line with the increasing number of AGP replacement alternative products available on the market. It is also expected that by the end of 2021 cases of gastrointestinal diseases will also decrease from the previous year. A number of efforts were made by livestock industry players to use alternative products instead of AGP. However, these alternatives require some consideration in finding the right product such as being able to reduce the incidence of infection, reduce the number of pathogenic bacteria and be able to increase nutrient absorption.
Currently, there are many available and circulating AGP alternatives on the market such as organic acids, probiotics, prebiotics, synbiotics, phytobiotics, enzymes, etc. The main purpose of providing this alternative is the same as AGP, namely maintaining the balance of intestinal microflora and optimizing the digestive process.
Medion, as a livestock industry players also strive to develop alternative products. Organic acids (acidifier) namely Asortin, phytobiotics (herbs) namely Optigrin, as well as enzymes that are Betterzym and Prozyme.
Prohibition Of The Use Of Colistin
The government has issued a regulation banning the use of colistin in animals through Ministerial Regulation Number 09160 / PK.350/F/12 / 2019 as outlined in the decree of the Directorate General of Animal Husbandry and Animal Health on December 9, 2019 in Jakarta. Colistin is one of the peptide class antibiotics that serves to treat bacterial diseases caused by bacteria multidrugs resistence in humans, in widespread use, it has the potential to cause resistant bacteria.
The removal of colistin as a chicken antibiotic has little real effect on poultry health. Bacterial diseases in poultry can still be cured with other types of antibiotics that are as effective as colistin but still adjusted to the type of bacteria. Alternative to other antibiotics that can be used with similar indications.
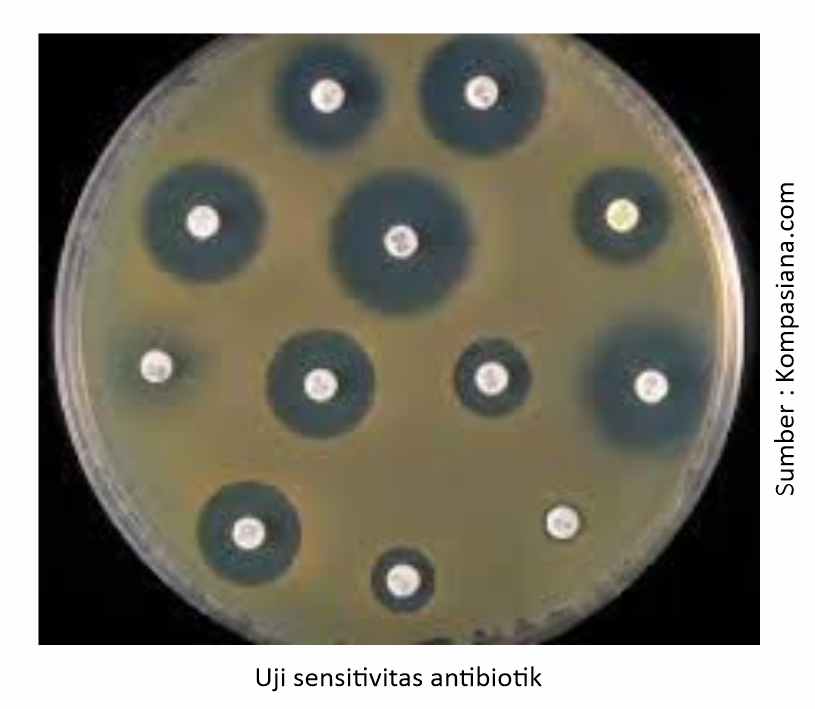
In addition, the right solution to prevent antibiotic resistance is to do rolling antibiotics. What is meant by rolling antibiotics is to use or give antibiotics from different groups every interval 3-4 times the period of treatment or after performing antibiotic sensitivity tests and the results show no sensitivity.
To find out whether the antibiotics used are still sensitive or already resistant to disease agents that attack chickens can be examined with an antibiotic sensitivity test. The test can be carried out in the Medion laboratory, MediLab.
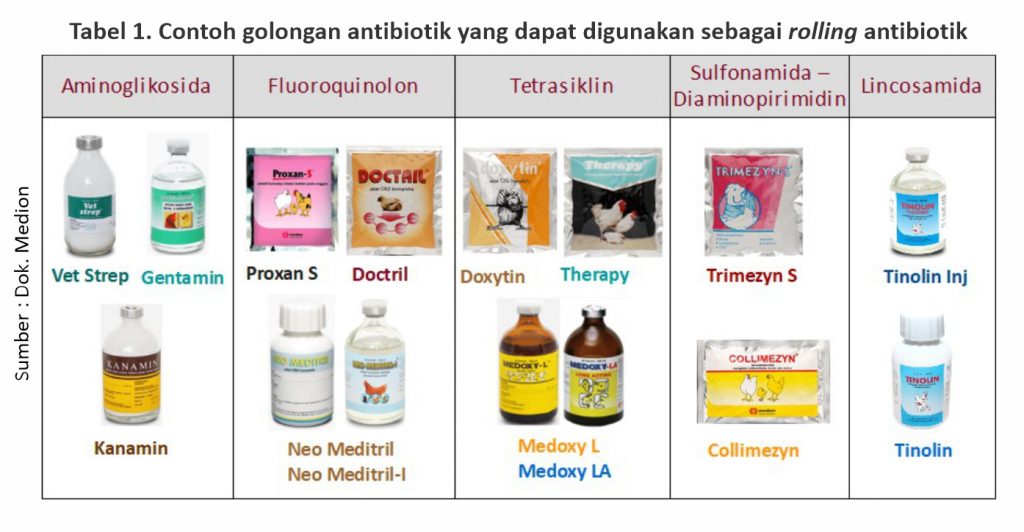
Things to emphasize when rolling antibiotics are different groups of active substances, not just different brands of products. Give the drug according to the indication of the disease that attacks and the right dosage and rules of use. Likewise, you can look for alternatives to other antibiotics that are natural, such as organic acids, probiotics, prebiotics, synbiotics, phytobiotics, etc.
The main purpose of giving this alternative is the same as antibiotics, which can maintain the balance of intestinal microflora and optimize the digestive process. However, these alternatives require several considerations such as being able to reduce the incidence of infection, reduce the number of pathogenic bacteria and be able to increase nutrient absorption.
It is also important to pay attention to biosecurity management in the environment farm strict and disciplined, implementing good maintenance management, doing cage rest for at least 14 days, and trying to maintain the endurance of the chicken's body with vitamin supplementation.
Be wise in the use of antibiotics
The use of antibiotics in farm modern was originally carried out to reduce mortality, improve FCR and improve the growth performance of animals. However, as we know that its use is starting to have less good effects on humans and animals. It is feared by the spread of bacteria that have been resistant from animals to humans through food sources.
In the use of antibiotics need to obey the rules that have been in force as a guideline in the administration of antibiotics. One example is through the use of antibiotics that are only needed for the treatment of serious infections and the existence of certain restrictions on their use. There needs to be a role, regulation, and responsibility from all parties to regulate the administration of antimicrobials to animals and get optimal results.
Many things are obtained from direct learning in farm post antibiotic use rules. Such as learning from the side of operational management, nutrition, and animal health. But actually the use of this antibiotic can still be used.
In some countries the use of antibiotics is still used as treatment to treat diseases. where rational treatment should be encouraged which includes indications, applications, doses and duration of use. In the selection of antibiotics is highly recommended to use antibiotics that have been registered in the Ministry of Agriculture.
Exact indications
Indications will lead to diseases that can be cured with these drugs so that proper diagnosis is necessary. For the direction of proper diagnosis can be done by collecting as complete information as possible from the case of the disease that occurs. Supported by breeder information( Anamnesis), clinical symptoms, observation of changes during carcass surgery (anatomical pathology), to laboratory tests.
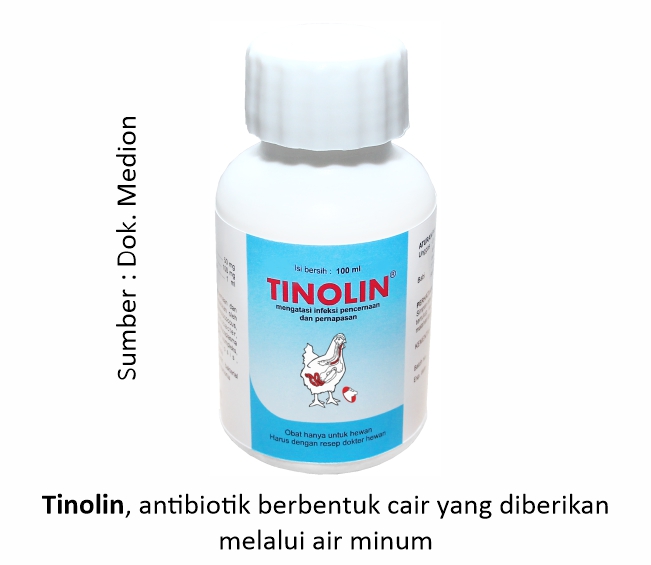
After getting a diagnosis, then look for a suitable drug for the indication. For example, to treat CRD, it is necessary to select antibiotics that can be suitable for Mycoplasma. Examples of Medion products that can be used such as Tinolin, Neo Meditril, Proxan–S, Therapy or Doxytin.
The selection of antibiotics is adjusted to the cause of the disease, the location of infection (target organ) and the spectrum of antibiotic action. Choose antibiotics given through drinking water for mild disease conditions. While when the condition of the disease is severe and needs to be overcome immediately use antibiotics given by injection.
Also note the records of medications that have been used. If antibiotics from one group are used too often, for example 3-4 times, choose antibiotics from other groups so that they are not resistant.
Proper application
The drug given must be able to reach the target organ, work site or diseased organ so that the drug can work precisely and optimally. It is associated with the choice of such routes of Drug Administration as oral, parenteral and topical. The choice of treatment route is important to ensure that the drug can reach the desired organ or site of action.
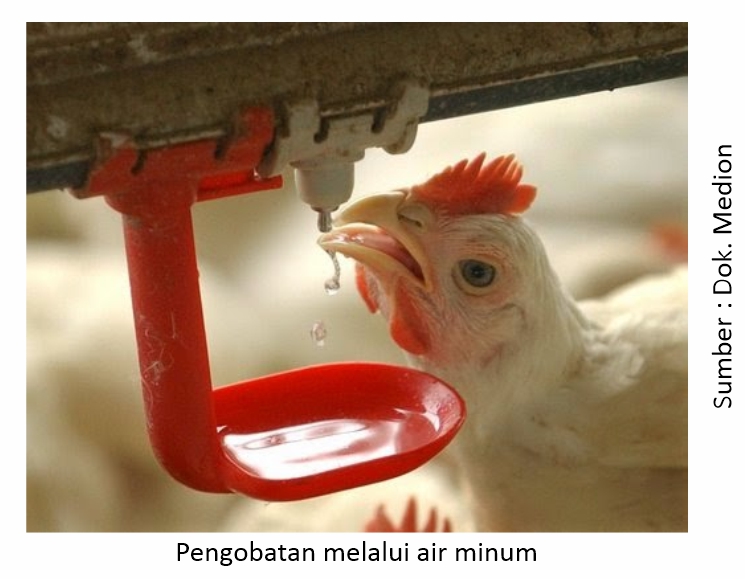

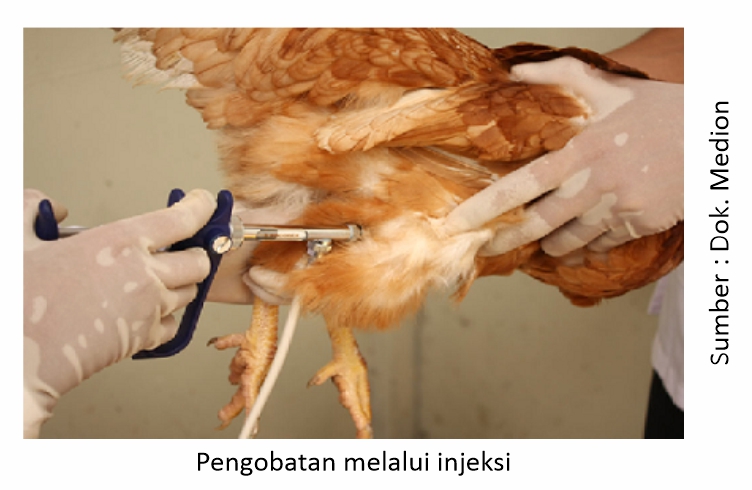
The oral route can pass drinking water, feed, and bite. Parenteral routes include subcutaneous (under the skin), intramuscular (through the muscle) and intravenous (directly into a vein) injections.
If you want an immediate effect of treatment in treating severe disease, parenteral route (injection or injection) is the first choice. However, if parenteral preparations are not available, then oral preparations through cekok or drinking water containing drugs that have systemic effects can be an alternative choice. In order for treatment through drinking water to be optimal, it is necessary to take into account the following factors:
- Drinking water quality (pH, heavy metals, chemicals, bacteria)
- Chicken drinking water consumption rate
- Distribution of chicken drinkers
- The water supply system (bell, nipple, open channel)
- Stability of drug solubility (homogeneity of mixing)
Exact dosage and timing of administration
In the administration of the drug, its amount should reach the target organs sufficiently and be sufficient for the therapeutic dose. If less, the seeds of the disease are not completely eradicated. If excess can also be at risk of overdose which can have a negative effect even to death. This is usually already taken into account by the drug manufacturer in the dosage form for each administration. This is the reason why the dose to be administered must be in accordance with the rules of use listed. The dose of the drug will be adjusted to the amount of drinking water or chicken weight. Here is an example of calculating the dose of the drug based on drinking water. For example, a chicken population of 1000 chickens with an average chicken weight of 0.8 kg. Then the need Tinolin per day is:
= Dosis x BB x Populasi
= 0,4 ml/kg BB x 0,8 kg x 1000 ekor
= 320 ml/day
The need for 5 days of treatment is 5 x 320 ml = 1.6 liters
Needs Tinolin per day given in 2 administration time that is morning to noon (hours 07.00-13.00) as much as 160 ml dissolved in drinking water needs for 6 hours, and the next 160 ml given during the afternoon to afternoon (hours 13.00-19.00). It aims to maintain drug levels in the body, so that the drug will remain effective and disease agents can be eradicated completely.
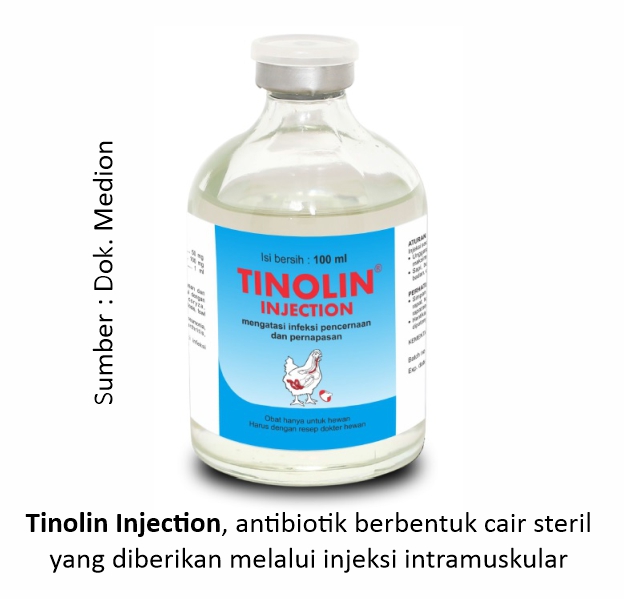
The drug should be administered for at least 5 consecutive days according to the rules for use indicated. Whereas if the administration of drugs by injection as an example Tinolin Injection, it is administered according to the rules of use, namely injection through intramuscularly at a dose of 0.2 ml per kg of body weight.
The rules of use also contain the recommendation “given to chickens for 3 days in a row”. The sentence means that farmers must provide treatment for 3 consecutive days so that the seeds of the disease can be eradicated completely.
Sufficient dosage and the right treatment time are important principles in treatment. The drug needs to be in the blood for a sufficient period of time to be able to eradicate the seeds of the disease. If less than that, it is feared the occurrence of bacterial resistance to antibiotics.
To suppress the contamination of microorganisms including bacteria in the farm environment it is also necessary to be supported by the application of appropriate biosecurity and good maintenance procedures. In the era free AGP, where the use of antibiotics only for treatment, it is necessary to optimize the implementation biosecurity Strictly and disciplined. It is necessary to implement biosecurity model 3 zones (clean, transition, dirty) in the farm area, the implementation of sanitation and disinfection of cages, including carrying out cage rest for at least 14 days.
Some of the actions that need to be done in the application of biosecurity in livestock include:
- Limit guests visiting the farm
- Equipment, personnel and vehicles entering the farm area must be disinfected
- The cage Operator visits the young cage flock first and then to the old age flock
- Provide a place to dip feet and body spray using Antisep or Medisep before entering the cage
- Clean the rest of the feed as soon as possible, wash the ration and drinking place regularly and disinfected by soaking it in Medisep, Zaldes or Neo Antisep.
- Regular cleaning and disinfection of the cage using Antisep or Neo Antisep routinely. When there is an outbreak, disinfection needs to be carried out daily to kill the infectious agents of the disease.
- Water quality Test (source, reservoir, faucet) especially during the rainy season. During the rainy season the water intensity is high but the quality is low.
- Perform drain cleaning to prevent growth biofilm (substances in waterways that can trigger bacterial growth)
- Applying the system all in all out
- Secure the cage from the disturbance of wild animals and eradicate disease vectors
Efforts to use antibiotics need to be applied accurately and wisely. For the purpose of treatment effectiveness in livestock can be optimal and the Prevention of residues of livestock products remain controlled. May be useful










