Variations in the quality of high feed ingredients can drastically reduce the performance of poultry production. In addition, feed accounts for more than 70% of the cost of poultry production. Therefore, accurate feed formulation is essential to ensure poultry get optimal feed and no shortage or oversupply of nutrients. However, this is difficult to do when the nutritional specifications of feedstuffs vary greatly.
Understanding Feed Ingredients
Feed ingredients (animal feed ingredients) are everything that can be given to livestock in the form of organic or inorganic materials that can be partially or completely digested without harming the health of the livestock.
Feed ingredients can be grouped into:
Energy source raw materials
What is meant by energy source raw materials are feed ingredients that contain metabolic energy (EM) > 2,250 kcal/kg. For chicken feed, energy sources can be obtained from grains, especially corn.
In addition to corn, examples of energy source feed ingredients include Bran/ Bran, wheat pollardrice, wheat, sorghum and cassava Groats. To meet the high energy needs, especially for broiler feed, sometimes oil is also added crude palm oil (CPO) between 1-5%.
Protein source raw material
What is meant by protein source raw materials is feedstuffs containing crude protein (PK) ≥ 20%. Examples include soybean meal, meat bone meal, fishmeal, poultry meat meal, DDGS and corn gluten meal.
Mineral source raw materials
In this raw material mostly contained various minerals, such as calcium, phosphorus and NaCl. Examples include stone flour/grit, clam shell flour, bone flour, dicalcium phosphate (DCP), monocalcium phosphate (MCP) and salt.
Feed supplement
Feed supplement is a feed additive in the form of nutrients, especially micronutrients such as vitamins, minerals or amino acids.
Additions feed supplement in the feed serves to supplement or increase the availability of micronutrients that are often contained in the feed is less or not up to standard.

Feed additive
Slightly different from feed supplement, feed additive is an additional substance that is non-nutritive (not including nutrients), for example enzymes, toxin, mold inhibitor, etc. Roles feed additive in the feed depending on the type of substance content additive- his.
Feed additive with the enzyme content serves to improve the process of digestion and absorption of feed, while feed additive by content mold inhibitor it can inhibit the growth of fungi so as to maintain the nutritional quality of feed during storage.

Food quality Data in the field
Variations in the quality of raw materials are still often found in the field. The following in Graph 1 is an example of a description of the variation of raw materials in the field. The graph is the result of crude fiber test on Bran conducted in Medion Laboratories (MediLab) year 2022.
Trends in crude fiber content in Bran showed that out of a total of 61 samples, there were still 29 samples (47.5%) that were more than the maximum standard. Literately for crude fiber content in Bran maximum 18% quality III, 15% quality II and 12% quality I (SNI 3178:20123).
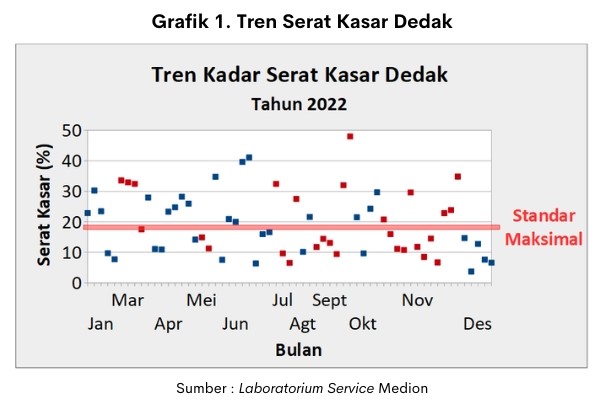
Excess fiber can lead to a decrease feed intake, decreased digestibility, bound minerals Ca, P and the occurrence of wet dropping. So its use needs to be limited. It is necessary to reformulate the feed to meet the nutritional needs of livestock. In addition, high fiber levels are usually correlated with high phytic acid.
Today there is also a lot of falsification of Bran with the addition of husks. This is also one of the causes of coarse fiber content in Bran increases, which will also affect the increase in phytic acid content.
Test Phloroglucinol can be one way to identify husk contamination in Bran. When dripped on Bran, within 5-10 minutes a change in color will be noticeable. The more contamination of the husk, the more red it becomes.

To break the bonds of phytic acid it is necessary to add phytase enzymes such as those contained in Betterzym (dosage 0.6 kg per ton of feed)/Prozyme (dose of 0.75 kg per ton of feed) so as to improve the digestibility of nutrient utilization, especially phosphorus (P).
In addition to Bran, graph 2 is an example of the variation in the quality of soybean meal (BKK) in the field. The graph is the result of a crude protein test on BKK conducted at the Medion Laboratory (MediLab) in 2022.
Trends in crude protein content in BKK showed that out of a total of 72 samples, there were still 22 samples (30.6%) that were less than the minimum standard. Literately for crude protein content in BKK at least 40% quality II, 46% quality I (SNI 01-4227-1996).
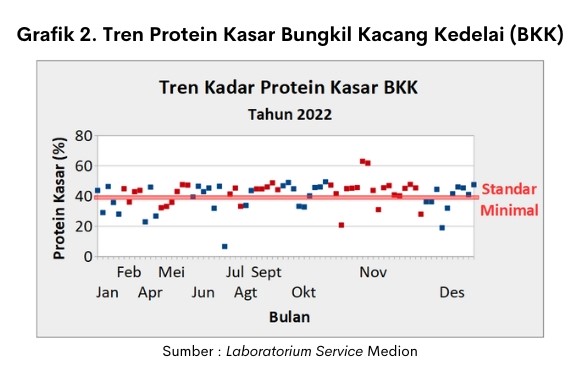
Low crude protein in BKK can increase the use of other protein source raw materials to be higher to meet the protein needs of livestock. Feed reformulation needs to be done to meet the nutritional needs of livestock as well as amino acid supplementation in feed mixtures such as Mix Plus LLM3A (dosage 15 kg per ton of feed)/ Mix Plus LLM3B (dosage 5 kg per ton of feed).
In addition, the high levels of crude protein in BKK also need to be considered because it can reduce the use of raw materials from other protein sources to meet the protein needs of livestock. It is necessary to reformulate the feed to meet the nutritional needs of livestock.
In addition, it is also necessary to beware of counterfeiting because of the recent trend of many protein source raw materials such as BKK which have low digestibility so that it will affect the performance of the resulting production.
Importance Of Quality Control Of Feed Ingredients
“Garbage in, garbage out” a suitable term to describe the importance of feed ingredient quality. The meaning of the term is that if the quality of the feed ingredients used is good to meet the standards, the resulting feed will also be of good quality. So that the performance of the chicken becomes optimal. Conversely, when the feed ingredients used are of poor quality, the quality of the feed produced will be poor.










