The enzyme is one of the feed additive (ration adjustment) it is used by many companies (feedmill) as well as breeders. The use of enzymes is expected to increase the productivity of chickens by degrading certain components or compounds in the ration so that it can be used optimally by chickens.
What are enzymes?
Enzymes are protein compounds that function as catalysts to accelerate the breakdown of complex compounds into simpler ones. Enzymes are widely used in commercial applications as biocatalystors, working specifically and very efficiently (Tijaroh, 2009). Plants, animals and microbes can produce enzymes, but the most widely used today and more profitable is the use of enzymes from microbes (Thenawijaya, 1989). Enzyme function is influenced by several factors including substrate and enzyme concentration, temperature, acidity (pH) and environmental conditions (Zinn and Ware, 2002).
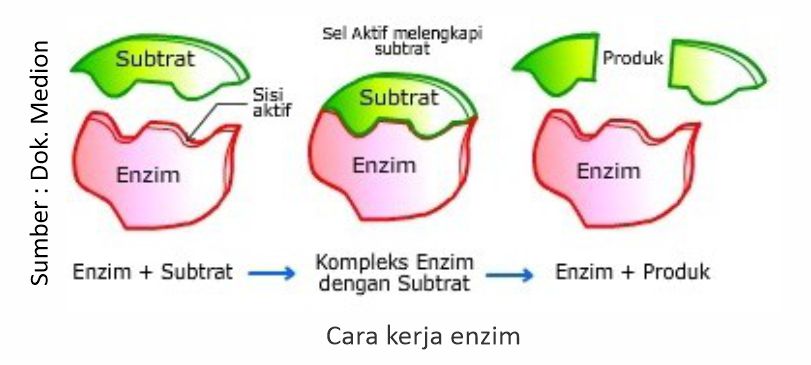
The Role Of Enzymes
Chickens use enzymes to digest food. Enzymes can be produced from the chicken's own body or produced by microbes found in the digestive tract. Monogastric livestock, such as chickens cannot digest 15-25% of the ration eaten because it contains indigestible antinutrients. Monogastric cattle also do not have specific enzymes to digest certain compounds so that the digestive process becomes imperfect.
The benefits of adding enzymes to the ration:
- Improve the digestibility of rations by breaking down antinutritional compounds or complex compounds so that the availability of nutrients is better
- Important for young chickens, where enzyme production is still limited
- Improve the environment, improve digestion and absorption of nutrients, reduce fecal production and low excretion of phosphorus and nitrogen
- Helps keep the digestive tract healthy by helping to digest nutrients that cannot be digested
Types Of Enzymes
More than 3,000 enzymes have been identified. The naming of the enzyme itself is usually taken from the substrate (compound to be broken down) with the addition of the suffix “–ase”. Some enzymes commonly used in poultry feed include :
1. Phytase Enzyme
Feed raw materials such as wheat, barley, corn and others, bind elemental phosphorus in the form of phytic acid. Whereas phosphorus itself is an essential element for chickens, because it is needed for the process of bone development, helps egg production, maintains immunity, and helps the growth process. Chickens themselves, only able to digest phosphorus in the form of phytic acid about 30-40%. As a result, undigested phosphorus will come out with feces (feces) and cause environmental pollution.
Phytase as an enzyme added to chicken feed, is able to release more phosphorus bound in phytic acid, protein and starch. This situation has a positive impact, namely increased digestibility and more optimal utilization.
In addition to playing a major role in the process of phosphorus absorption, phytase enzymes can also eliminate the antinutritional influence of phytic acid. The addition of this enzyme can also reduce the addition of inorganic phosphorus sources such as di calcium phosphate (DCP) and mono calcium phosphate (MCP) so that farmers can streamline feed costs.
Betterzym is a mixed feed powder preparation containing the latest generation phytase enzyme (6-phytate) that effectively improve the digestibility of nutrients, especially phosphorus (P). Betterzym will break the bonds of phytic acid so as to increase the availability and digestibility of such amino acids, carbohydrates and minerals, especially phosphorus.

2. Enzyme Xylanase
Xylane is usually found in corn which is antinutritive. The effect of these antinutrients include binding some nutrients such as energy, protein, and fat rations to be taken out with feces, so that the availability of these nutrients is reduced. (Williams 1997) states that xylanes can also increase the viscosity of the digestive tract, causing unfavorable effects on digestive efficiency.
Xylanases are a group of enzymes that have the ability to hydrolyze hemicelluloses such as xylanes or polymers of xylose and Xylo-oligosaccharides. Abrihandini (2009) states the enzyme xylanase will reduce the viscosity of gastric search in the small intestine, thereby facilitating the digestive tract and improve nutrient absorption. Nutrients that were originally bound by the hemicellulose cell wall will be released and can be utilized by the chicken's body. The enzyme xylanase also converts hemicellulose into simple sugars. The sugar can be utilized by the chicken's body, so the chicken will get enough energy from the ration with a small amount.
3. Enzyme Amylase
One of the main raw materials used in chicken rations is corn, where the raw material contains starch (energy source) which is very good. But in one of the studies mentioned that the starch in corn is only digested no more than 85%. The solution to deal with this is the addition of the enzyme amylase.
The enzyme amylase helps degrade starch in grains and by-products from grains. By increasing the digestibility of starch, amylase can provide more energy so that it becomes more efficient to increase meat and egg production.
The addition of amylase enzymes along with other enzymes in the critical period of chicks (the first 2 weeks of rearing), with symptoms of experiencing stress due to changes in their nutrition, environment and immune status, can help increase the production of endogenous enzymes. As a result, the digestive process becomes more optimal, thus maximizing the absorption of nutrients.
4. Enzim Protease
Protease is a protein-breaking enzyme stored in various ration ingredients. Moreover, the protein in the indigestible raw materials of the ration reaches 20-25% (Gauthier 2007). This is due to the presence of two kinds of protein antinutrients, namely trypsin inhibitors and lectins. Trypsin inhibitors are usually found in vegetable protein sources, such as soybean meal.
The content of these antinutrients can interfere with the digestive process and have an impact on the absorption of nutrients contained in soybeans. The digestive system in the chicks are not yet perfect to be the next problem, because it causes the chicks are not able to use large protein stores in soy (glycin and ß-conglycinin).
The addition of protease enzymes can help reduce the negative influence of antinutritional substances (trypsin inhibitors and lectins), resulting in better protein digestibility. Not only that, proteases can also break down large protein stores into smaller molecules so that they are easily absorbed.

Prozyme is a powder preparation containing a combination of enzymes xylanse, amylase, protease and phytase as well as minerals. The addition of enzymes plays a role in improving the digestibility of nutrients and reduce the negative effects of antinutritional compounds in feed. Although mineral Zinc and manganese acts as a cofactor of internal enzymes and a biocatalyst of metabolic reactions in the body so that the performance of the digestive system becomes better. Increased feed digestibility and metabolic activity will improve chicken performance, which is shown by better FCR, egg production, and egg shell quality.
Use Of Enzymes
Enzymes are available in powder and liquid form. Application its use is quite simple for the powder form is simply mixed with the ration directly. However, it must be considered that the mixing process must be homogeneous considering that this enzyme dose is very little used in rations. Enzyme liquid form application its use is to add water as much as 5% and then sprayed using a sprayer on the ration or ration material. When the ration will be made in the form pellet and crumble attention should be paid to temperature, enzymes are very susceptible to temperature changes or heat. If it passes the optimum temperature of the enzyme, denaturation will occur so that it cannot work optimally.
In terms of formulation, enzyme application can be divided into 2 techniques, namely botton specification and top up. Technique botton specification is an enzyme used to lower the nutritional content of the enzyme target. For example, the addition of fiatase enzymes will reduce phosphorus or phosphorus source raw materials in ration formulations or in other words phytase enzymes will replace phosphorus source raw materials. While the technique top up is the addition of enzymes do not need to make changes or adjustments to the formulation of the ration.
The use of enzymes in rations today and in the future will be a trend and the need to address the decreasing quantity and quality of raw materials rations. The addition of enzymes is expected to improve the performance of chickens. Thus information about the role of enzymes for poultry. Greetings.










